오늘은 미국 국립 생명공학 정보 센터 (National Center for Biotechnology Information)에 게제된 "니겔라 사티바(블랙 커민)의 항암 활동"에 대한 자료를 공유해 드리고자 합니다.
원본의 출처는 아래와 같습니다.

Nigella sativa has been used as traditional medicine for centuries. The crude oil and thymoquinone (TQ) extracted from its seeds and oil are effective against many diseases like cancer, cardiovascular complications, diabetes, asthma, kidney disease etc. ...
www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
Anticancer Activities of Nigella Sativa (Black Cumin)
니겔라 사티바(블랙 커민)의 항암 활동
Md Asaduzzaman Khan,1 Han-chun Chen,

1 Mousumi Tania,1 and Dian-zheng Zhang1,2
Author information Copyright and License information PMC Disclaimer
Copyright © Afr. J. Traditional Complementary and Alternative Medicines 2011
Abstract (개요)
Nigella sativa has been used as traditional medicine for centuries. The crude oil and thymoquinone (TQ) extracted from its seeds and oil are effective against many diseases like cancer, cardiovascular complications, diabetes, asthma, kidney disease etc. It is effective against cancer in blood system, lung, kidney, liver, prostate, breast, cervix, skin with much safety. The molecular mechanisms behind its anticancer role is still not clearly understood, however, some studies showed that TQ has antioxidant role and improves body's defense system, induces apoptosis and controls Akt pathway. Although the anti-cancer activity of N. sativa components was recognized thousands of years ago but proper scientific research with this important traditional medicine is a history of last 2∼3 decades. There are not so many research works done with this important traditional medicine and very few reports exist in the scientific database. In this article, we have summarized the actions of TQ and crude oil of N. sativa against different cancers with their molecular mechanisms.
니겔라 사티바는 수세기 동안 전통 의학으로 사용되어 왔습니다. 씨앗과 오일에서 추출한 원유와 티모퀴논 (TQ)은 암, 심혈관 합병증, 당뇨병, 천식, 신장 질환 등과 같은 많은 질병에 효과적입니다. 혈액계, 폐, 신장, 간, 전립선, 유방, 자궁 경부, 피부의 암에 효과적이며 매우 안전합니다. 항암 역할의 분자 기전은 아직 명확하게 밝혀지지 않았지만 일부 연구에 따르면 TQ는 항산화 역할을하고 신체의 방어 시스템을 개선하고 세포 사멸을 유도하며 Akt 경로를 제어하는 것으로 나타났습니다. N. sativa 성분의 항암 활성은 수천 년 전부터 알려졌지만, 이 중요한 전통 의학에 대한 적절한 과학적 연구는 최근 2∼3십 년의 역사입니다. 이 중요한 전통 의학으로 수행 된 연구 작업이 그리 많지 않으며 과학 데이터베이스에 존재하는 보고서가 거의 없습니다. 이 기사에서는 다양한 암에 대한 TQ와 N. sativa의 원유 작용을 분자 메커니즘으로 요약했습니다.
Keywords: Traditional medicine, Nigella sativa, Thymoquinone, Antioxidant, Anti-cancer mechanism
키워드: 전통 의학, 니겔라 사티바, 티모퀴논, 항산화제, 항암 메커니즘
Introduction (도입)
Cancer is one of the major threats of modern life, which is considered as the second cause of death after myocardial infarction (Grundy, 1991). Millions of people die every year in different types of cancer despite tremendous efforts to find methods of control and cure. In the last century, great advances were made in modern medical science to control disease. But many diseases like cancers are not yet curable fully. To find out new and authentic therapies, scientists are working with traditional or folk medicines in parallel of modern medicine. Nigella sativa has been used for medicinal purposes for centuries. It originated from Southeastern Asia and also used in ancient Egypt, Greece, Middle East and Africa. In Islam, it is regarded as one of the greatest forms of healing medicine available (Nigella-sativa-research.com, 2010; Wikipedia, 2010). It is a flowering plant, of which seed is used as a spice. The seed is called black cumin in English, while in old Latin it was called ‘Panacea’ meaning ‘cure all’; in Arabic it is termed as ‘Habbah Sawda’ or ‘Habbat el Baraka’ translated as ‘Seeds of blessing’. It is also known as ‘Kalo jeera’ (in Bangladesh), ‘Kalonji’ (in India) and ‘Hak Jung Chou’ in (China) (Aggarwal et al., 2008). Both seeds and oil extracted from this plant are used in medicinal purposes.
암은 심근경색에 이어 두 번째 사망 원인으로 꼽히는 현대 생활의 주요 위협 중 하나입니다(Grundy, 1991). 암을 통제하고 치료하는 방법을 찾기 위한 엄청난 노력에도 불구하고 매년 수백만 명의 사람들이 다양한 유형의 암으로 사망합니다. 지난 세기 동안 현대 의학은 질병을 통제하기 위해 큰 발전을 이루었습니다. 하지만 암과 같은 많은 질병은 아직 완전히 치료할 수 없습니다. 새롭고 확실한 치료법을 찾기 위해 과학자들은 현대 의학과 병행하여 전통 의학 또는 민간 요법을 연구하고 있습니다. 니겔라 사티바는 수세기 동안 의약 목적으로 사용되어 왔습니다. 동남아시아에서 유래했으며 고대 이집트, 그리스, 중동 및 아프리카에서도 사용되었습니다. 이슬람에서는 가장 위대한 형태의 치유 의학 중 하나로 간주됩니다(Nigella-sativa-research.com, 2010; Wikipedia, 2010). 그것은 씨앗이 향신료로 사용되는 꽃 식물입니다. 씨앗은 영어로 블랙 커민이라고 불리며, 고대 라틴어에서는 '만병통치약'이라는 뜻의 '파나시아'라고 불렸고, 아랍어에서는 '하바 소다' 또는 '하바트 엘 바라카'로 불리며 '축복의 씨앗'으로 번역됩니다. 방글라데시에서는 '칼로 제라', 인도에서는 '칼론지', 중국에서는 '학중초'로도 알려져 있습니다(Aggarwal et al., 2008). 이 식물에서 추출한 씨앗과 오일은 모두 약용으로 사용됩니다.
The active ingredients of N. sativa have beneficial effects against many diseases, including cancers. For example, it is effective in the diminishing the risk of atherosclerosis by decreasing the serum low density lipoprotein cholesterol level and increasing the serum high density lipoprotein cholesterol levels (Dahri et al., 2005; Nader et al., 2010); it exerts therapeutic and protective effect in diabetes by decreasing morphological changes and preserving pancreatic beta-cell integrity (Kanter et al., 2009) and by beneficially changing the hepatic enzyme activities (Pari and Sankaranarayanan, 2009); it is effective against hypertension (Khattab and Nagi, 2007; Dehkordi and Kamkhah, 2008); it has a potent antihistaminic effect on airways of asthmatic patients (Boskabady et al., 2010); its components are promising agents to complement schistosomiasis specific treatment (El Shenawy et al., 2008); its oil protects kidney tissue against oxygen free radicals, preventing renal dysfunction and morphological abnormalities (Bayrak et al., 2008; Uz et al., 2008; Ragheb et al., 2009). For thousands of year, the seeds, oils and extracts of N. sativa have been used as an anticancer agent by Unani, Ayurveda and the Chinese system of medicine that have originated from the Arab, Ind-Bangla and China, respectively. The modern scientific research with the investigation of anticancer activity of N. sativa is a comparatively recent affair (for the last 2∼3 decades). There are not so many research works done in this field and very few review articles exist in this area. We have searched the scientific databases like Pubmed, Web of Science and Google scholar and summarized the current scientific information about the anticancer activities of N. sativa with mechanisms of action.
N. sativa의 활성 성분은 암을 포함한 많은 질병에 유익한 효과가 있습니다. 예를 들어, 혈청 저밀도 지단백 콜레스테롤 수치를 감소시키고 혈청 고밀도 지단백 콜레스테롤 수치를 증가시켜 죽상경화증의 위험을 감소시키는 데 효과적입니다(Dahri et al., 2005; Nader et al., 2010). 이는 형태학적 변화를 감소시키고 췌장 베타세포 완전성을 보존하고(Kanter et al., 2009) 간 효소 활성을 유익하게 변화시킴으로써(Pari and Sankaranarayanan, 2009) 당뇨병에서 치료 및 보호 효과를 발휘합니다. 이는 고혈압에 효과적입니다(Khattab 및 Nagi, 2007; Dehkordi 및 Kamkhah, 2008). 천식 환자의 기도에 강력한 항히스타민 효과가 있습니다(Boskabady et al., 2010). 그 구성요소는 주혈흡충증 특정 치료를 보완하는 유망한 제제입니다(El Shenawy et al., 2008). 그 오일은 산소 자유 라디칼로부터 신장 조직을 보호하여 신장 기능 장애 및 형태학적 이상을 예방합니다(Bayrak et al., 2008; Uz et al., 2008; Ragheb et al., 2009). 수천년 동안 N. sativa의 씨앗, 오일 및 추출물은 Unani, Ayurveda 및 아랍, Ind-Bangla 및 중국에서 유래한 중국 의학 시스템에서 항암제로 사용되었습니다. N. sativa의 항암 활성을 조사하는 현대 과학 연구는 비교적 최근(지난 2~30년 동안)에 이루어졌습니다. 이 분야에서 수행된 연구 작업은 그리 많지 않으며 이 분야에 대한 리뷰 기사도 거의 없습니다. 우리는 Pubmed, Web of Science 및 Google 학자와 같은 과학 데이터베이스를 검색하고 N. sativa의 항암 활성에 대한 최신 과학 정보를 작용 메커니즘으로 요약했습니다.
Role of N. sativa as an anticancer agent
항암제로서 N. sativa의 역할
Many active ingredients have been found in the seeds of N. sativa. The seeds contain both fixed and essential oils, proteins, alkaloids and saponin (Ali and Blunden, 2003). Ghosheh et al. (1999) described the quantification of four pharmacologically important components: thymoquinone (TQ), dithymoquinone (DTQ), thymohydroquinone (THQ), and thymol (THY), in the oil of N. sativa seed by HPLC. Much of the biological activities of the seeds have been shown to be due to thymoquinone, the major component of the essential oil, which is also present in the fixed oil (Ali and Blunden, 2003). TQ is considered as potent anti-oxidant (Badary et al., 2003), anti-carcinogenic and anti-mutagenic agent (Bourgou et al., 2008; Khader et al., 2010) (structure of thymoquinone is shown in Figure 1a). Moreover, TQ is a relatively safe compound, particularly when given orally to experimental animals (Al-Ali et al., 2008). Alpha (α)-hederin, a pentacyclic triterpene saponin (structure: Figure 1b) isolated from the seeds of N. sativa, was also reported to have potent in vivo antitumor activity (Swamy and Huat, 2003).
N. sativa의 씨앗에서 많은 활성 성분이 발견되었습니다. 씨앗에는 고정 및 에센셜 오일, 단백질, 알칼로이드 및 사포닌이 모두 포함되어 있습니다 (Ali and Blunden, 2003). Ghosheh et al. (1999)는 약리학적으로 중요한 네 가지 성분인 티모퀴논(TQ), 디티모퀴논(DTQ), 티모하이드로퀴논(THQ), 티몰(THY)의 정량화를 HPLC를 통해 설명했습니다: N. sativa 종자의 오일에서. 씨앗의 생물학적 활성의 대부분은 고정 오일에도 존재하는 에센셜 오일의 주성분 인 티모 퀴논에 기인하는 것으로 나타났습니다 (Ali and Blunden, 2003). 티모퀴논은 강력한 항산화제(Badary et al., 2003), 항암 및 항돌연변이 유발 물질(Bourgou et al., 2008; Khader et al., 2010)로 간주됩니다(티모퀴논의 구조는 그림 1a에 나와 있습니다). 또한, TQ는 특히 실험 동물에게 경구 투여할 때 비교적 안전한 화합물입니다(Al-Ali et al., 2008). N. sativa의 씨앗에서 분리된 펜타사이클릭 트리테르펜 사포닌(구조: 그림 1b)인 알파(α)-헤데린도 강력한 생체 내 항종양 활성을 가진 것으로 보고되었습니다(Swamy and Huat, 2003).
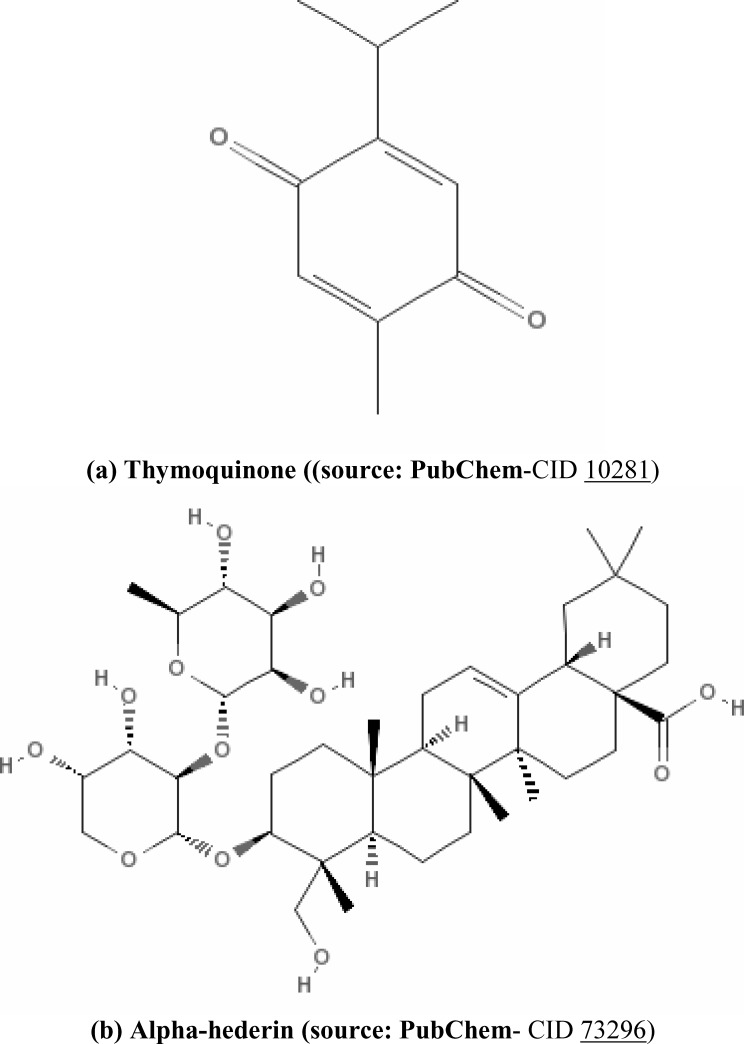
Figure 1
Chemical structure of anti-tumor agents isolated from N. sativa
그림 1
N. sativa에서 분리한 항암제의 화학 구조
N. sativa seeds or oils or its active ingredients like TQ are effective against different cancers:
N. sativa 씨앗이나 오일 또는 TQ와 같은 활성 성분은 다양한 암에 효과적
Blood Cancer
혈액 암
El-Mahdy et al. (2005) reported that TQ exhibits anti-proliferative effect in human myeloblastic leukemia HL-60 cells. Derivatives of TQ bearing terpene-terminated 6-alkyl residues were tested in HL-60 cells and 518A2 melanoma by Effenberger et al. (2010). They found the derivatives induce apoptosis associated with DNA laddering, a decrease in mitochondrial membrane potential and a slight increase in reactive oxygen species. Swamy and Huat (2003) observed that α-hederin also induced death of murine leukemia P388 cells by a dose- and time-dependent increase in apoptosis.
El-Mahdy 등(2005)은 TQ가 인간 골수성 백혈병 HL-60 세포에서 항증식 효과를 나타낸다고 보고했습니다. 테르펜-말단 6-알킬 잔기를 갖는 TQ 유도체는 Effenberger 등(2010)에 의해 HL-60 세포와 518A2 흑색종에서 테스트되었습니다. 그들은 유도체가 DNA 래더링, 미토콘드리아 막 전위 감소 및 활성 산소 종의 약간의 증가와 관련된 세포 사멸을 유도한다는 것을 발견했습니다. Swamy와 Huat(2003)는 α-헤데린이 용량 및 시간 의존적으로 세포 사멸을 증가시켜 쥐 백혈병 P388 세포의 사멸을 유도하는 것을 관찰했습니다.
Breast Cancer
유방암
Aqueous and alcohol extracts of N. sativa were found to be effective in vitro in inactivating MCF-7 breast cancer cells (Farah and Begum, 2003). N. sativa, in combination with melatonin and retinoic acid reduced the carcinogenic effects of DMBA (7, 12-di-methylbenz(a)anthracene) in mammary carcinoma of rats (El-Aziz et al., 2005). Terpene-terminated 6-alkyl residues of TQ were tested in MCF-7/Topo breast carcinoma by Effenberger et al. (2010). They found the derivatives inducing cell death by apoptosis.
N. sativa의 수성 및 알코올 추출물은 시험관 내에서 MCF-7 유방암 세포를 비활성화하는 데 효과적인 것으로 밝혀졌습니다 (Farah and Begum, 2003). 멜라토닌 및 레티노산과 함께 N. sativa는 쥐의 유방암에서 DMBA (7, 12- 디- 메틸 벤즈 (a) 안트라센)의 발암 효과를 감소시켰습니다 (El-Aziz et al., 2005). TQ의 테르펜 말단 6-알킬 잔기는 Effenberger 등(2010)에 의해 MCF-7/Topo 유방암에서 테스트되었습니다. 그들은 이 유도체가 세포 사멸을 유도하는 것을 발견했습니다.
Colon Cancer
대장암
Gali-Muhtasib et al. (2004) suggested that TQ is anti-neoplastic and pro-apoptotic against colon cancer cell line HCT116. Salim and Fukushima (2003) demonstrated that the volatile oil of N. sativa has the ability to inhibit colon carcinogenesis of rats in the post-initiation stage, with no evident adverse side effects. Norwood et al. (2006) suggested TQ as chemotherapeutic agent on SW-626 colon cancer cells, in potency, which is similar to 5-flurouracil in action. However, on HT-29 (colon adenocarcinoma) cell, no effect of TQ was found (Rooney and Ryan, 2005).
Gali-Muhtasib et al.(2004)는 TQ가 대장암 세포주 HCT116에 대해 항 종양 및 세포 사멸 촉진제임을 제안했습니다. 살림과 후쿠시마(2003)는 N. 사티바의 휘발성 오일이 발병 후 단계에서 쥐의 대장 발암을 억제하는 능력이 있으며, 명백한 부작용이 없음을 입증했습니다. Norwood 등(2006)은 SW-626 대장암 세포에 대한 화학 요법제로서 5-플루오로우라실과 유사한 효능을 가진 TQ를 제안했습니다. 그러나 HT-29 (대장 선암종) 세포에서는 TQ의 효과가 발견되지 않았습니다 (Rooney and Ryan, 2005).
Pancreatic Cancer
췌장암
Chehl et al. (2009) showed that TQ, the major constituent of N. sativa oil extract, induced apoptosis and inhibited proliferation in PDA (pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma) cells. They also suggested TQ as a novel inhibitor of pro-inflammatory pathways, which provides a promising strategy that combines anti-inflammatory and proapoptotic modes of action. TQ also can abrogate gemcitabine- or oxaliplatin-induced activation of NF-kappa B, resulting in the chemosensitization of pancreatic tumors to conventional therapeutics (Banerjee et al., 2009). The high molecular weight glycoprotein mucin 4 (MUC4) is aberrantly expressed in pancreatic cancer and contributes to the regulation of differentiation, proliferation, metastasis, and the chemoresistance of pancreatic cancer cells. Torres et al. (2010) evaluated the down-regulatory effect of TQ on MUC4 in pancreatic cancer cells. But in a study, Rooney and Ryan (2005) did not find any preventive role of TQ on MIA PaCa-2 (pancreas carcinoma) cells.
Chehl 등(2009)은 N. sativa 오일 추출물의 주성분인 TQ가 PDA(췌관 선암종) 세포에서 세포 사멸을 유도하고 증식을 억제한다는 사실을 보여주었습니다. 또한, 연구진은 항염증 작용과 세포 사멸 작용을 결합하는 유망한 전략을 제공하는 새로운 전 염증 경로 억제제로서 TQ를 제안했습니다. 또한 TQ는 젬시타빈 또는 옥살리플라틴에 의해 유도된 NF-카파 B의 활성화를 무효화하여 기존 치료제에 대한 췌장 종양의 화학감작을 초래할 수 있습니다(Banerjee 외., 2009). 고분자량 당단백질 뮤신 4 (MUC4)는 췌장암에서 비정상적으로 발현되며 췌장암 세포의 분화, 증식, 전이 및 화학 저항성 조절에 기여합니다. Torres 등(2010)은 췌장암 세포에서 MUC4에 대한 TQ의 하향 조절 효과를 평가했습니다. 그러나 Rooney와 Ryan(2005)의 연구에서는 MIA PaCa-2(췌장암) 세포에 대한 TQ의 예방적 역할을 발견하지 못했습니다.
Hepatic Cancer
간암
The cytotoxic activity of N. sativa seed was tested on the human hepatoma HepG2 cell line by Thabrew et al. (2005), and 88% inhibitory effect on HepG2 was found after 24-hr incubation with different concentrations (0–50 mg/ml) of the N. sativa extract. Nagi and Almakki (2009) reported that oral administration of TQ is effective in increasing the activities of quinone reductase and glutathione transferase and makes TQ a promising prophylactic agent against chemical carcinogenesis and toxicity in hepatic cancer
N. sativa 종자의 세포 독성 활성은 Thabrew 등 (2005)에 의해 인간 간종 HepG2 세포주에 대해 시험되었으며, 다양한 농도 (0-50 mg / ml)의 N. sativa 추출물로 24 시간 배양 후 HepG2에 대한 88 %의 억제 효과가 발견되었습니다. Nagi와 Almakki (2009)는 TQ의 경구 투여가 퀴논 환원 효소 및 글루타티온 전이 효소의 활성을 증가시키는 데 효과적이며 간암의 화학 발암 및 독성에 대한 유망한 예방 제제라고보고했습니다.
Lung Cancer
폐암
Swamy and Huat (2003) mentioned the antitumor activity of α-hederin from N. sativa against LL/2 (Lewis Lung carcinoma) in BDF1 mice. Also, Mabrouk et al. (2002) showed that supplementation of diet with honey and N. sativa has a protective effect against MNU (methylnitrosourea)-induced oxidative stress, inflammatory response and carcinogenesis in lung, skin and colon. However, Rooney and Ryan (2005) reported that α-hederin and TQ, the two principal bioactive constituents of N. sativa enhance neither cytotoxicity nor apoptosis in A549 (lung carcinoma), HEp-2 (larynx epidermoid carcinoma) cells.
Swamy와 Huat (2003)는 BDF1 마우스에서 LL/2 (루이스 폐암종)에 대한 N. sativa의 α- 헤데린의 항 종양 활성을 언급했습니다. 또한 Mabrouk 등 (2002)은 꿀과 N. sativa로 식단을 보충하면 폐, 피부 및 결장에서 MNU (메틸 니트로 소우레아)에 의한 산화 스트레스, 염증 반응 및 발암에 대한 보호 효과가 있음을 보여주었습니다. 그러나 Rooney와 Ryan(2005)은 N. sativa의 두 가지 주요 생리 활성 성분인 α-헤데린과 TQ가 A549(폐암), HEp-2(후두 표피암) 세포에서 세포 독성이나 세포 자멸사를 강화하지 않는다고 보고했습니다.
Skin cancer
피부암
Topical application of N. sativa extract inhibited two-stage initiation/promotion [dimethylbenz[a]anthracene (DMBA)/croton oil] skin carcinogenesis in mice. Again, intraperitoneal administration of N. sativa (100 mg/kg body wt) 30 days after subcutaneous administration of MCA (20-methylcholanthrene) restricted soft tissue sarcomas to 33.3% compared with 100% in MCA-treated controls (Salomi et al., 1991).
N. sativa 추출물의 국소 도포는 생쥐의 2단계 개시/촉진 [디메틸벤즈[a]안트라센(DMBA)/크로톤 오일] 피부 발암을 억제했습니다. 다시 말하지만, MCA(20-메틸콜란트렌) 피하 투여 30일 후 N. sativa(100 mg/kg 체중)를 복강 내 투여하면 연조직 육종이 33.3%로 제한되어 MCA로 처리한 대조군의 100%와 비교되었습니다(Salomi et al., 1991).
Fibrosarcoma
섬유육종
TQ from N. sativa was administrated (0.01% in drinking water) one week before and after MCA treatment significantly inhibited the tumor incidence (fibrosarcoma) and tumor burden by 43% and 34%, respectively, compared with the results in the group receiving MCA alone. Moreover, TQ delayed the onset of MCA-induced fibrosarcoma tumors. Also in vitro studies showed that TQ inhibited the survival of fibrosarcoma cells with IC50 of 15 mM (Badary and Gamal, 2001). Oil of N. sativa also decreased the fibrinolytic potential of the human fibrosarcoma cell line (HT1080) in vitro (Awad, 2005).
MCA 치료 1주일 전과 후에 N. sativa의 TQ를 투여(식수에 0.01%)한 결과, MCA만 투여한 그룹에 비해 종양 발생률(섬유육종)과 종양 부담이 각각 43%, 34% 유의미하게 억제된 것으로 나타났습니다. 또한 TQ는 MCA로 유발된 섬유육종 종양의 발병을 지연시켰습니다. 또한 시험관 내 연구에 따르면 TQ는 IC50이 15mM인 섬유육종 세포의 생존을 억제하는 것으로 나타났습니다(Badary and Gamal, 2001). N. sativa 오일은 또한 시험관 내에서 인간 섬유육종 세포주(HT1080)의 섬유소 용해 잠재력을 감소시켰습니다(Awad, 2005).
Renal Cancer
신장암
Khan and Sultana (2005) reported the chemo-preventive effect of N. sativa against ferric nitrilotriacetate (Fe-NTA)-induced renal oxidative stress, hyper-proliferative response and renal carcinogenesis. Treatment of rats orally with N. sativa (50 100 mg/kg body wt) resulted in significant decrease in H2O2 generation, DNA synthesis and incidence of tumors.
칸과 술타나(2005)는 철 니트릴로트리아세테이트(Fe-NTA)에 의한 신장 산화 스트레스, 과증식 반응 및 신장 발암에 대한 N. 사티바의 화학적 예방 효과를 보고했습니다. 쥐를 경구 투여한 결과, N. sativa(50 100mg/kg 체중)를 경구 투여한 쥐는 H2O2 생성, DNA 합성 및 종양 발생이 현저히 감소했습니다.
Prostate Cancer
전립선 암
TQ, from N. sativa, inhibited DNA synthesis, proliferation, and viability of cancerous (LNCaP, C4-B, DU145, and PC-3) but not non-cancerous (BPH-1) prostate epithelial cells by down-regulating AR (androgen receptor) and E2F-1 (a transcription factor) (Kaseb et al., 2007). In this study, they suggested TQ as effective in treating hormone-sensitive as well as hormone-refractory prostate cancer. Yi et al. (2008) found that TQ blocked angiogenesis in vitro and in vivo, prevented tumor angiogenesis in a xenograft human prostate cancer (PC3) model in mouse, and inhibited human prostate tumor growth at low dosage with almost no chemotoxic side effects. Furthermore, they observed that endothelial cells were more sensitive to TQ-induced cell apoptosis, cell proliferation, and migration inhibition compared with PC3 cancer cells. TQ also inhibited vascular endothelial growth factor-induced extracellular signal-regulated kinase activation but showed no inhibitory effects on vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 activation.
N. sativa에서 추출한 TQ는 AR(안드로겐 수용체)과 E2F-1(전사인자)을 하향 조절하여 암성(LNCaP, C4-B, DU145 및 PC-3) 전립선 상피 세포의 DNA 합성, 증식 및 생존을 억제했지만 비암성(BPH-1)은 억제하지 않았습니다(Kaseb et al., 2007). 이 연구에서 그들은 호르몬 민감성 및 호르몬 불응성 전립선암을 치료하는 데 TQ가 효과적이라고 제안했습니다. Yi 등(2008)은 TQ가 시험관 및 생체 내에서 혈관 신생을 차단하고 생쥐의 이종 이식 인간 전립선암(PC3) 모델에서 종양 혈관 신생을 예방하며 화학 독성 부작용이 거의 없는 저용량으로 인간 전립선 종양 성장을 억제한다는 사실을 발견했습니다. 또한 내피 세포가 PC3 암세포에 비해 TQ에 의한 세포 사멸, 세포 증식 및 이동 억제에 더 민감하게 반응하는 것을 관찰했습니다. 또한 TQ는 혈관 내피 성장 인자에 의한 세포 외 신호 조절 키나아제 활성화를 억제했지만 혈관 내피 성장 인자 수용체 2 활성화에는 억제 효과가 나타나지 않았습니다.
Cervical Cancer
자궁경부암
Shafi et al. (2009) reported that methanol, n-Hexane and chloroform extracts of N. sativa effectively killed HeLa (human epithelial cervical cancer) cells by inducing apoptosis. Effenberger et al. (2010) tested terpene-terminated 6-alkyl residues of TQ on multidrug-resistant KB-V1/Vb1 cervical carcinoma and found the derivatives inducing cell death by apoptosis.
Shafi et al.(2009)은 N. sativa의 메탄올, n-헥산 및 클로로포름 추출물이 세포 사멸을 유도하여 HeLa(인간 상피성 자궁경부암) 세포를 효과적으로 사멸시킨다고 보고했습니다. Effenberger et al.(2010)은 다제내성 KB-V1/Vb1 자궁경부암에 대해 테르펜 말단 6-알킬 잔기의 TQ를 테스트한 결과, 이 유도체가 세포 사멸을 유도하여 세포 사멸을 유도하는 것을 발견했습니다.
Molecular mechanisms of N. sativa action against cancer
암에 대한 N. sativa 작용의 분자 메커니즘
Cancers are the abnormal cell growth caused by genetic alteration. So, any agent which has anti-cancer activity, either protect genetic material from alteration or kill the genetically altered cancer cells. The active ingredients (mainly TQ) from N. sativa act on cancer cell to help to kill them by several molecular pathways (Figure 2).
암은 유전자 변형으로 인한 비정상적인 세포 성장입니다. 따라서 항암 작용을 하는 모든 약제는 유전 물질이 변형되지 않도록 보호하거나 유전적으로 변형된 암세포를 죽입니다. N. sativa의 활성 성분(주로 TQ)은 암세포에 작용하여 여러 분자 경로를 통해 암세포를 죽이는 데 도움을 줍니다(그림 2).
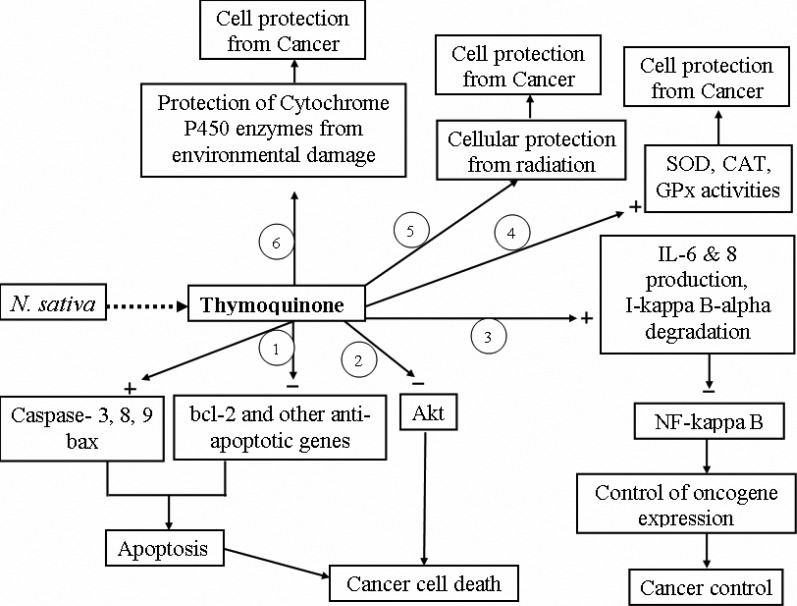
Figure 2
Possible mechanisms of thymoquinone (TQ) action. (1) TQ induces apoptotic cell death in cancerous tissues by up-regulating expression of apoptotic genes (caspases and bax) and down-regulating expression of anti-apoptotic genes (e.g., bcl 2); (2) TQ suppresses Akt activation by dephosphorylation and thus blocks cancer cell survival; (3) TQ deactivates NF-kappa B pathway by inducing cytokine production, and thus control oncogenic expression; (4) TQ increases the activities of antioxidant enzymes and protects cell against cancer; (5) TQ protects normal cells' injury caused by ionizing radiation in the treatment of cancer; (6) TQ prevents CYP450 enzymes from damage. ‘+’ indicates increasing effect and ‘−’ indicates decreasing effect.
그림 2
티모퀴논(TQ) 작용의 가능한 메커니즘. (1) TQ는 세포사멸 유전자(카스파제 및 박스)의 발현을 상향 조절하고 항세포사멸 유전자(예, bcl 2), (2) 탈인산화에 의한 Akt 활성화를 억제하여 암세포 생존을 차단하고, (3) 사이토카인 생성을 유도하여 NF-카파 B 경로를 비활성화하여 발암성 발현을 조절하며, (4) 항산화 효소의 활성을 증가시켜 암으로부터 세포를 보호하고, (5) 암 치료 시 전리 방사선에 의한 정상 세포의 손상을 보호하며, (6) CYP450 효소가 손상되는 것을 방지합니다. '+'는 효과 증가를, '-'는 효과 감소를 나타냅니다.
El-Mahdy et al. (2005) suggested the apoptotic mechanisms behind the anti-proliferative effect of TQ (from N. sativa) on myeloblastic leukemia HL-60 cells. They reported that TQ induces apoptosis, disrupts mitochondrial membrane potential and triggers the activation of caspases 8, 9 and 3 in HL-60 cells. The apoptosis induced by TQ was inhibited by a general caspase inhibitor, z-VAD-FMK; a caspase-3-specific inhibitor, z-DEVD-FMK; as well as a caspase-8-specific inhibitor, z-IETD-FMK. Moreover, the caspase-8 inhibitor blocked the TQ-induced activation of caspase-3, PARP cleavage and the release of cytochrome c from mitochondria into the cytoplasm. In addition, TQ treatment of HL-60 cells caused a marked increase in Bax/Bcl2 ratios due to upregulation of Bax and downregulation of Bcl2 proteins. Their results indicated that TQ-induced apoptosis is associated with the activation of caspases 8, 9 and 3, with caspase-8 acting as an upstream activator and activated caspase-8 initiates the release of cytochrome c during TQ-induced apoptosis. TQ action was also found as pro-apoptotic against colon cancer cell line HCT116 (Gali-Muhtasib et al., 2004). It was showed that the apoptotic effects of TQ are modulated by Bcl-2 protein and are linked to and dependent on p53. TQ also down-regulates the expression of NF-kappa B-regulated antiapoptotic (IAP1, IAP2, XIAP Bcl-2, Bcl-xL, and survivin) gene products (Sethi et al., 2008). Torres et al. (2010) found TQ inducing apoptosis by the activation of c-Jun NH(2)-terminal kinase and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways in pancreatic cancer cell.
El-Mahdy et al.(2005)는 골수모세포성 백혈병 HL-60 세포에 대한 TQ(N. sativa)의 항증식 효과에 대한 세포 사멸 메커니즘을 제시했습니다. 그들은 TQ가 세포 사멸을 유도하고 미토콘드리아 막 전위를 방해하며 HL-60 세포에서 카스파제 8, 9 및 3의 활성화를 촉발한다고 보고했습니다. TQ에 의해 유도된 세포 사멸은 일반적인 카스파제 억제제인 z-VAD-FMK, 카스파제-3 특이적 억제제인 z-DEVD-FMK, 카스파제-8 특이적 억제제인 z-IETD-FMK에 의해 억제되었습니다. 또한, 카스파제-8 억제제는 TQ에 의한 카스파제-3의 활성화, PARP 절단 및 미토콘드리아에서 세포질로 방출되는 사이토크롬 C를 차단했습니다. 또한, HL-60 세포에 TQ를 처리하면 Bax의 상향 조절과 Bcl2 단백질의 하향 조절로 인해 Bax/Bcl2 비율이 현저하게 증가했습니다. 연구 결과에 따르면 TQ에 의한 세포 사멸은 카스파제 8, 9 및 3의 활성화와 관련이 있으며, 카스파제 8은 상류 활성화제 역할을 하고 활성화된 카스파제 8은 TQ에 의한 세포 사멸 중에 사이토크롬 C의 방출을 개시합니다. TQ 작용은 대장암 세포주 HCT116에 대해서도 세포 사멸을 촉진하는 것으로 밝혀졌습니다(Gali-Muhtasib 외., 2004). TQ의 세포 사멸 효과는 Bcl-2 단백질에 의해 조절되며 p53과 관련이 있고 의존적이라는 것이 밝혀졌습니다. 또한 TQ는 NF-카파 B-조절 항세포사멸(IAP1, IAP2, XIAP Bcl-2, Bcl-xL 및 서바이빈) 유전자 산물의 발현을 하향 조절합니다(Sethi et al., 2008). Torres 등(2010)은 췌장암 세포에서 c-Jun NH(2)-말단 키나아제 및 p38 미토겐 활성화 단백질 키나아제 경로의 활성화에 의해 세포 사멸을 유도하는 TQ를 발견했습니다.
TQ has also been reported to be active in controlling Akt pathway. Yi et al. (2008) found that TQ effectively inhibited human umbilical vein endothelial cell migration, invasion, and tube formation by suppressing the activation of AKT and extracellular signal-regulated kinase. Xuan et al. (2010) found that LPS (lipopolysaccharides: a bacterial component)-induced phosphorylation of prosurvival kinases Akt and ERK1/2 was abrogated by TQ in dendritic cells.
TQ는 또한 Akt 경로를 제어하는데 활성적이라고 보고되었습니다. Yi 등(2008)은 TQ가 AKT 및 세포 외 신호 조절 키나아제의 활성화를 억제하여 인간 제대 정맥 내피 세포의 이동, 침입 및 관 형성을 효과적으로 억제한다는 사실을 발견했습니다. Xuan 등(2010)은 수지상 세포에서 LPS(지질 다당류: 박테리아 성분)에 의해 유도된 생존 키나아제 Akt 및 ERK1/2의 인산화가 수지상 세포에서 TQ에 의해 제거된다는 사실을 발견했습니다.
NF-kappa B plays a key role in regulating the immune response, and incorrect regulation of NF-kappa B has been found to be linked to cancer (Albensi and Mattson, 2000). Sethi et al. (2008) found that TQ suppressed tumor necrosis factor-induced NF-kappa B activation in a dose- and time-dependent manner and inhibited NF-kappa B activation induced by various carcinogens and inflammatory stimuli. The suppression of NF-kappa B activation is correlated with sequential inhibition of the activation of I kappa B alpha kinase, I kappa B alpha phosphorylation, I-kappa-B-alpha degradation, p65 phosphorylation, p65 nuclear translocation, and the NF-kappa B-dependent reporter gene expression. Also Oberg et al. (2009) reported that a herbal melanin (HM) from N. sativa modulates cytokine production and suggested it as a ligand for TLR4 (toll-like receptor 4). They investigated the possibility that the HM-induced cytokine production is via an NF-kappa B signaling pathway and found that HM induced the degradation of I kappa B-alpha, a key step in the activation of NF-kappa B. Moreover, addition of I kappa B kinase (IKK) specific inhibitors effectively inhibited the observed HM-induced production of IL-8 and IL-6 by TLR4-transfected HEK293 (embryonic kidney 293) cells and THP-1 (Human acute monocytic leukemia) cells (Oberg et al., 2009).
NF-카파 B는 면역 반응을 조절하는 데 핵심적인 역할을 하며, NF-카파 B의 잘못된 조절은 암과 관련이 있는 것으로 밝혀졌습니다(Albensi and Mattson, 2000). Sethi 등(2008)은 TQ가 용량 및 시간 의존적으로 종양괴사인자에 의해 유도된 NF-카파 B 활성화를 억제하고, 다양한 발암물질 및 염증 자극에 의해 유도된 NF-카파 B 활성화를 억제한다는 사실을 발견했습니다. NF-카파 B 활성화의 억제는 I-kappa B 알파 키나아제의 활성화, I-kappa B 알파 인산화, I-kappa-B 알파 분해, p65 인산화, p65 핵 전위 및 NF-카파 B 의존성 리포터 유전자 발현의 순차적인 억제와 상관관계가 있습니다. 또한 Oberg 등(2009)은 N. sativa의 허브 멜라닌(HM)이 사이토카인 생성을 조절한다고 보고하고 이를 TLR4(톨유사수용체 4)의 리간드로 제안했습니다. 연구팀은 HM에 의한 사이토카인 생산이 NF-카파 B 신호 경로를 통해 이루어질 가능성을 조사했고, HM이 NF-카파 B 활성화의 핵심 단계인 I 카파 B-알파의 분해를 유도한다는 사실을 발견했습니다. 또한, I kappa B 키나아제(IKK) 특이적 억제제를 추가하면 TLR4가 이식된 HEK293(배아 신장 293) 세포와 THP-1(인간 급성 단핵구 백혈병) 세포에서 관찰된 HM에 의한 IL-8 및 IL-6의 생성을 효과적으로 억제할 수 있었습니다(Oberg et al, 2009).
Many studies showed that N. sativa oil or TQ has antioxidant activity and increases the activities of antioxidant enzymes such as superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase (CAT) glutathione peroxidase (GPx) etc (Ebru et al., 2008; Barron et al., 2008; Ismail et al., 2010). And antioxidant enzymes are clearly related to cancer- mostly their increased activities are beneficial against different types of cancer (Khan et al., 2010). Administration of N. sativa oil or TQ can lower the toxicity of other anticancer drugs (for example, cyclophosphamide) by an up-regulation of antioxidant mechanisms, indicating a potential clinical application for these agents to minimize the toxic effects of treatment with anticancer drugs (Alenzi et al., 2010).
많은 연구에 따르면 N. sativa 오일 또는 TQ는 항산화 활성을 가지고 있으며 슈퍼옥사이드 디스뮤타제(SOD), 카탈라아제(CAT) 글루타치온 퍼옥시다제(GPx) 등과 같은 항산화 효소의 활성을 증가시킵니다(Ebru et al., 2008; Barron et al., 2008; Ismail et al., 2010). 그리고 항산화 효소는 암과 분명히 관련이 있으며, 대부분 증가 된 활동은 다양한 유형의 암에 대해 유익합니다 (Khan et al., 2010). N. sativa 오일 또는 TQ의 투여는 항산화 메커니즘의 상향 조절을 통해 다른 항암제(예: 사이클로포스파마이드)의 독성을 낮출 수 있으며, 이는 항암제 치료의 독성 효과를 최소화하기 위한 이러한 약제의 잠재적 임상 적용 가능성을 나타냅니다(Alenzi et al., 2010).
In addition to these cancer inhibiting properties, components of N. sativa have cancer protective roles. Ibrahim et al. (2008) reported that N. sativa oil administration has a protective effect against the CCl4-mediated suppression of CYP (drug-metabolizing cytochrome P450 enzymes). And genetic abnormalities and polymorphisms of CYP enzymes are associated with cancer (Sim and Ingelman-Sundberg, 2006; Chen et al., 2008). Radiotherapy is one of the most common strategies for treating human cancers but this treatment is somehow risky for normal tissue. Cemek et al. (2006) showed that N. sativa and glutathione treatment significantly antagonize the effects of radiation. Therefore, N. sativa may be a beneficial agent in protection against ionizing radiation-related tissue injury. Assayed (2010) investigated the radio-protective potential of N. sativa crude oil against hemopoietic adverse effects of gamma irradiation. He found that irradiation resulted in significant reduction in hemolysin antibodies titers and delayed type hypersensitivity reaction of irradiated rats, in addition to significant leukopenia and significant decrease in plasma total protein and globulin concentration and depletion of lymphoid follicles of spleen and thymus gland. Furthermore, there was a significant increase in malondialdehyde concentration with a significant decrease in plasma GPx, CAT and erythrocyte SOD activities. But oral administration of N. sativa oil before irradiation considerably normalized all the above-mentioned criteria; and produced significant regeneration in spleen and thymus lymphoid follicles. Thus N. sativa oil is recognized as a promising natural radioprotective agent against immunosuppressive and oxidative effects of ionizing radiation.
이러한 암 억제 특성 외에도 N. sativa의 성분은 암을 보호하는 역할을 합니다. 이브라힘 등(2008)은 N. sativa 오일 투여가 CYP(약물 대사 시토크롬 P450 효소)의 CCl4 매개 억제에 대한 보호 효과를 가지고 있다고 보고했습니다. 그리고 CYP 효소의 유전적 이상과 다형성은 암과 관련이 있습니다 (Sim and Ingelman-Sundberg, 2006; Chen et al., 2008). 방사선 치료는 인간 암을 치료하는 가장 일반적인 전략 중 하나이지만 이 치료는 정상 조직에는 다소 위험합니다. Cemek 등(2006)은 N. sativa와 글루타치온 치료가 방사선의 효과를 상당히 길항한다는 것을 보여주었습니다. 따라서 전리방사선 관련 조직 손상에 대한 보호에 N. sativa가 유익한 약제가 될 수 있습니다. Assayed (2010)는 감마선 조사의 조혈 부작용에 대한 N. sativa 원유의 방사선 보호 잠재력을 조사했습니다. 그는 방사선 조사로 인해 헤몰리신 항체 역가가 현저히 감소하고 조사 된 쥐의 유형 과민 반응이 지연되었으며, 상당한 백혈구 감소증과 혈장 총 단백질 및 글로불린 농도의 현저한 감소 및 비장 및 흉선의 림프 모낭 고갈이 발생했음을 발견했습니다. 또한 혈장 GPx, CAT 및 적혈구 SOD 활성의 현저한 감소와 함께 말론디알데히드 농도가 유의하게 증가했습니다. 그러나 방사선 조사 전에 N. sativa 오일을 경구 투여하면 위에서 언급한 모든 기준이 상당히 정상화되었으며 비장 및 흉선 림프 모낭에서 상당한 재생이 발생했습니다. 따라서 N. sativa 오일은 이온화 방사선의 면역 억제 및 산화 효과에 대한 유망한 천연 방사선 보호제로 인식되고 있습니다.
Concluding remarks (결론)
The anti-cancer activities of N. sativa components were recognized thousands of years ago but proper scientific research with this important traditional medicine is a very recent story. More research works should be emphasized behind this because it is a safe and promising anticancer agent. Specially, researchers should investigate the active ingredients more broadly, because, there is very few authentic reports about the chemical composition of seeds or oil of N. sativa exist. Also, the exact molecular mechanisms of thymoquinone and other components on different cancers should be investigated with more emphasis because current understandings are mostly unclear. For example, it is reported that N. sativa oil can protect cells from radiation, but the molecular mechanisms behind this is not properly understood. Currently, in some parts of the world, there is a renaissance of interest in traditional remedies. Many investigators now believe that traditional medicine is a promising source of new therapeutics against cancer. Extensive research with N. sativa may contribute to the discovery of new anticancer strategies.
N. sativa 성분의 항암 작용은 수천 년 전에 인식되었지만 이 중요한 전통 의학에 대한 적절한 과학적 연구는 매우 최근의 이야기입니다. 안전하고 유망한 항암제이기 때문에 더 많은 연구 작업이 강조되어야합니다. 특히, 연구자들은 N. sativa의 씨앗이나 오일의 화학 성분에 대한 확실한 보고가 거의 없기 때문에 활성 성분을 더 광범위하게 조사해야합니다. 또한 티모퀴논 및 기타 성분이 다양한 암에 미치는 정확한 분자 메커니즘은 현재 이해가 대부분 불분명하기 때문에 더욱 중점적으로 연구되어야 합니다. 예를 들어, N. sativa 오일은 방사선으로부터 세포를 보호 할 수 있다고 보고되었지만 그 뒤에 있는 분자 메커니즘은 제대로 이해되지 않았습니다. 현재 세계 일부 지역에서는 전통 요법에 대한 관심이 르네상스를 맞이하고 있습니다. 현재 많은 연구자들은 전통 의학이 암에 대한 새로운 치료법의 유망한 원천이라고 믿고 있습니다. N. sativa에 대한 광범위한 연구는 새로운 항암 전략의 발견에 기여할 수 있습니다.
REFERENCES (참조) - 생략
'게시판' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 기관지 천식에서 니겔라 사티바의 의학적 이점: 문헌 검토 (0) | 2024.06.07 |
|---|---|
| 류마티스 관절염 치료에서 니겔라 사티바(블랙커민씨드)의 생리 활성 화합물의 역할 - 최신 보고서 (0) | 2024.06.06 |
| 광범위한 질병에 대한 유망한 자연 치료법 (0) | 2024.06.06 |
| Nigella sativa (Black Seed, 블랙씨드)가 관절염 및 통풍 질환에 미치는 영향 (0) | 2024.06.06 |
| 블랙씨드가 하시모토 갑상선염 환자의 갑상선 기능, 혈청 혈관내피성장인자(VEGF) – 1, Nesfatin-1 및 인체측정학적 특징에 미치는 영향 : 무작위 대조 (0) | 2024.06.06 |