그동안 귀차니즘에 빠져 정리해서 올리려던 글을 겨우 겨우 정리하여 올려봅니다.
현재 국내 모 밴드와 당사에서 판매하는 '악수비탈사의 블랙씨드 오일 100캡슐(1캡슐 1,000mg) 제품'의 공동구매를 진행하면서 밴드의 한 회원님으로부터 몇 가지 질문사항이 있어 그에 대한 자료를 조사하던 중 알게 된 내용을 공유해 드리고자 합니다.
역시 오늘 소개해 드리는 자료도 미국생명공학 정보센터에서 발췌한 자료이며 내용은 아래와 같습니다.
Hashimoto’s thyroiditis is an autoimmune disorder and the most common cause of hypothyroidism. The use of Nigella sativa, a potent herbal medicine, continues to increase worldwide as an alternative treatment of several chronic diseases including ...
www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
블랙씨드가 하시모토 갑상선염 환자의 갑상선 기능, 혈청 혈관내피성장인자(VEGF) -1, Nesfatin - 1 및 인체측정학적 특징에 미치는 영향 : 무작위 대조
Background
Hashimoto’s thyroiditis is an autoimmune disorder and the most common cause of hypothyroidism. The use of Nigella sativa, a potent herbal medicine, continues to increase worldwide as an alternative treatment of several chronic diseases including hyperlipidemia, hypertension and type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). The aim of the current study was to evaluate the effects of Nigella sativa on thyroid function, serum Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF) – 1, Nesfatin-1 and anthropometric features in patients with Hashimoto’s thyroiditis.
배경
하시모토 갑상선염은 자가면역 질환이며 갑상선 기능 저하증의 가장 흔한 원인이다. 강력한 약초인 니겔라 사티바의 사용은 고지혈증, 고혈압, 제2형 당뇨병(T2DM)을 포함한 여러 만성 질환의 대체 치료법으로서 전세계적으로 계속 증가하고 있다. 본 연구의 목적은 Nigella sativa(블랙씨드)가 하시모토 갑상선염 환자의 갑상선 기능, 혈청 혈관내피성장인자(VEGF) – 1, Nesfatin-1 및 인체측정학 특성에 미치는 영향을 평가하는 것이었다.
Methods
Forty patients with Hashimoto’s thyroiditis, aged between 22 and 50 years old, participated in the trial and were randomly allocated into two groups of intervention and control receiving powdered Nigella sativa or placebo daily for 8 weeks. Changes in anthropometric variables, dietary intakes, thyroid status, serum VEGF and Nesfatin-1 concentrations after 8 weeks were measured.
방법들
22세에서 50세 사이의 하시모토 갑상선염 환자 40명이 실험에 참여했고 8주 동안 매일 니겔라 사티바 가루나 플라시보를 받는 중재와 통제 두 그룹으로 무작위로 배정됐다. 인체측정학 변수, 식이 섭취량, 갑상선 상태, 혈청 VEGF 및 Nesfatin-1 농도의 변화가 8주 후에 측정되었다.
Results
Treatment with Nigella sativa significantly reduced body weight and body mass index (BMI). Serum concentrations of thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) and anti-thyroid peroxidase (anti-TPO) antibodies decreased while serum T3 concentrations increased in Nigella sativa-treated group after 8 weeks. There was a significant reduction in serum VEGF concentrations in intervention group. None of these changes had been observed in placebo treated group. In stepwise multiple regression model, changes in waist to hip ratio (WHR) and thyroid hormones were significant predictors of changes in serum VEGF and Nesgfatin-1 values in Nigella sativa treated group (P < 0.05).
결과.
Nigella sativa를 사용한 치료는 체중과 체질량지수(BMI)를 크게 감소시켰다. 니겔라 사티바 치료군에서 8주 후 혈청 T3 농도가 증가한 반면 갑상선 자극 호르몬(TSH)과 항갑상선 과산화효소(anti-tyroid peroxidase) 항체의 혈청 농도는 감소했다. 개입군에서 혈청 VEGF 농도가 유의하게 감소하였다. 이러한 변화는 플라시보 치료 그룹에서 관찰되지 않았다. 단계적 다중회귀 모델에서 허리 대 엉덩이 비율(WHR)과 갑상선 호르몬의 변화는 Nigella sativa 치료군에서 혈청 VEGF와 Nesgfatin-1 값의 변화를 유의미한 예측 변수였다(P < 0.05).
Conclusions
Our data showed a potent beneficial effect of powdered Nigella sativa in improving thyroid status and anthropometric variables in patients with Hashimoto’s thyroiditis. Moreover, Nigella sativa significantly reduced serum VEGF concentrations in these patients. Considering observed health- promoting effect of this medicinal plant in ameliorating the disease severity, it can be regarded as a useful therapeutic approach in management of Hashimoto’s thyroiditis.
결론
우리의 데이터는 하시모토 갑상선염 환자의 갑상선 상태와 인체측정학 변수를 개선하는 데 니겔라 사티바의 잠재적인 유익한 효과를 보여주었다. 게다가, Nigella sativa는 이러한 환자들에서 혈청 VEGF 농도를 유의미하게 감소시켰다. 이 약용식물이 질병의 중증도를 개선하는 데 있어 관찰된 건강증진 효과를 고려하면 하시모토 갑상선염 관리에 유용한 치료방법으로 볼 수 있다.
Trial registration
Iranian registry of clinical trials (registration number IRCT2015021719082N4- Registered March-15-2015).
평가판 등록
이란 임상시험 등록부(등록번호 IRCT2015021719082N4-등록번호: 2015년 3월 15일-2015.
Background
Hashimoto’s thyroiditis (HT) is an organ-specific T-cell mediated disease that affects the thyroid glands and is one of the most common human autoimmune disorders [1]. The disease affects 2% of general population and is ten times more prevalent in women than in men [2, 3]. A significant proportion of patients have asymptomatic chronic autoimmune thyroiditis and 8% of woman (10% of woman over 55 years of age) and 3% of men have subclinical hypothyroidism [4].
Hashimoto’s thyroiditis is characterized by the presence of thyroid auto-antibodies such as anti-thyroid peroxidase (TPO-Ab) and anti-thyroglobulin (TG-Ab) antibodies in the serum while these antibodies have potential ability to deteriorate thyroid cells [5, 6]. The disease is characterized by gradual thyroid failure and occasional goiter development and the untreated forms of Hashimoto’s thyroiditis can ever lead to papillary thyroid cancer and thyroid carcinoma [7, 8].
From pathological point of view, thyroid enlargement and hyper-function in Hashimoto’s thyroiditis is accompanied by a markedly increased blood flow and increased vascularization [9]. A number of growth and vasoactive factors are produced in thyroid and are considered to be potentially responsible for changes in thyroid microvasculature and blood flow; vascular endothelial growth factors (VEGF) is a hemodynamic glycoprotein with potent angiogenic and vascular permeability enhancing activities [10]. It has been proposed that VEGF and its receptors are present in epithelial cells of the thyroid and contribute in regulation of development and function of thyroid epithelial cells [10]. In fact VEGF is unique among angiogenic factors because it is both vascular endothelial cell-specific mitogen and is secreted by thyroid cancer cells and high thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) concentrations in Hashimoto’s thyroiditis promotes VEGF secretion from thyroid cancer cell lines [11].
Nesfatin-1, a peptide secreting from peripheral tissues, central and peripheral nervous system, is involved in the regulation of energy homeostasis related with food consumption mostly by passing through the blood–brain barrier [12]. Moreover, several recent studies have proposed the possible role of Nesfatin-1 in in thyroid dysfunction [13, 14]. Liu et al. [15] reported that plasma Nesfain-1 levels are independently correlated with serum TSH concentrations in patients with T2DM. The Nesfatin-1 immuno-positive neurons have been reported to be co-localized with thyrotropin releasing hormone (TRH) neurons in the paraventricular nucleous (PVN) and the central Nesfatin-1 affects the membrane potential of TRH neurons suggesting the possible role of Nesfatin-1 in regulation of thyroid hormone function [16, 17].
Levothyroxine sodium is the treatment of choice for Hashimoto’s thyroiditis; however its chronic use is related with cardiac dysfunction, left ventricular hypertrophy [18, 19] and rapid bone loss [20]. Nigella sativa is one of the medicinal plants and belongs to the Ranunculaceae family [21]. The seeds of the Nigella sativa are the main source of its active ingredients with considerable health promoting effects including antioxidant, anti-inflammatory and immune-modulatory properties and no side effects [21, 22]. Numerous researches have extensively studied therapeutic actions of Nigella sativa in improving chronic disease status including diabetes, hyperlipidemia, hypertension and gastritis especially in animal models; while human studies in this filed are scarce and limiting [23, 24]. Moreover the health effects of Nigella sativa in Hashimoto’s thyroiditis has been studied in only one animal model indicating its protective role in reversing hypothyroid status and ameliorating oxidative stress and thyroid cell damage in propylthiouracil (PTU)-induced hypothyroidism in rats [25]. In the current randomized clinical trial we aimed to evaluate the potential therapeutic effects of Nigella sativa powder on thyroid function and serum VEGF and Nesfatin-1 concentrations in patients with Hashimoto thyroiditis.
배경
하시모토 갑상선염(HT)은 갑상선에 영향을 미치는 장기 특이적 T세포 매개 질환으로 가장 흔한 인간 자가면역 질환 중 하나이다[1]. 이 질병은 일반 인구의 2%에 영향을 미치고 남성보다 여성에게 10배 더 널리 퍼져 있다[2, 3]. 환자의 상당수는 무증상 만성 자가면역 갑상선염을 가지고 있으며, 여성의 8%(55세 이상 여성의 10%)와 남성의 3%는 아임상성 갑상선 기능 저하증을 가지고 있다[4].
하시모토 갑상선염은 혈청 내에 항갑상선 과산화효소(TPO-Ab) 및 항갑상선글로불린(TG-Ab) 항체와 같은 갑상선 자가 항체가 존재하는 반면, 이들 항체는 갑상선 세포를 악화시킬 수 있는 잠재적 능력을 가지고 있는 것이 특징이다[5,6]. 이 질환은 점진적인 갑상선 기능 부전과 가끔 갑상선 발육이 특징이며 하시모토 갑상선염의 치료되지 않은 형태는 유두 갑상선암과 갑상선암을 유발할 수 있다[7, 8].
병리학적 관점에서 보면 하시모토 갑상선염의 갑상선 비대 및 과기능은 혈류량의 현저한 증가와 혈관화의 증가를 동반한다[9]. 많은 성장 및 혈관 활성 인자는 갑상선에서 생성되며 갑상선 미세 혈관 구조와 혈액 흐름의 변화에 잠재적으로 책임이 있는 것으로 간주된다. 혈관 내피 성장 인자(VEGF)는 강력한 혈관신생 및 혈관 투과성 강화 활성을 가진 혈류역학적 당단백질이다 [10]. VEGF와 그 수용체는 갑상선의 상피세포에 존재하며 갑상선 상피세포의 발달 및 기능 조절에 기여한다고 제안되었다[10]. 사실 VEGF는 혈관내피세포 특이적 마이트젠이며 갑상선암세포에 의해 분비되고 하시모토 갑상선염의 높은 갑상선자극호르몬(TSH) 농도는 갑상선암세포주로부터의 VEGF 분비를 촉진하기 때문에 혈관신생인자 중에서 특이하다[11].
말초 조직, 중추 및 말초 신경계에서 분비되는 펩타이드인 Nesfatin-1은 주로 혈액-뇌 장벽을 통과함으로써 음식 소비와 관련된 에너지 항상성 조절에 관여한다[12]. 또한, 최근 몇 가지 연구는 갑상선 기능 장애에서 네스파틴-1의 가능한 역할을 제안했다[13, 14]. 류 외. [15]는 혈장 Nesfain-1 수준이 T2DM 환자에서 혈청 TSH 농도와 독립적으로 상관관계가 있다고 보고했다. Nesfatin-1 면역 양성 뉴런은 부실핵(PVN)에서 티로트로핀 방출 호르몬(TRH) 뉴런과 함께 국재하는 것으로 보고되었으며, 중심 Nesfatin-1은 TRH 뉴런의 막 전위에 영향을 미쳐 갑상선 호르몬 기능 조절에서 Nesfatin-1의 가능한 역할을 시사한다[16, 17].
레보시록신나트륨은 하시모토 갑상선염의 치료제이지만 만성적인 사용은 심장 기능 장애, 좌심실 비대[18, 19] 및 급격한 뼈 손실[20]과 관련이 있다. Nigella sativa는 약용 식물 중 하나이며 Ranunculaceae과에 속한다[21]. Nigella sativa의 씨앗은 항산화제, 항염증 및 면역조절 특성을 포함한 상당한 건강 증진 효과가 있고 부작용이 없는 활성 성분의 주요 공급원이다[21, 22]. 많은 연구가 당뇨병, 고지혈증, 고혈압, 위염을 포함한 만성 질환 상태를 개선하기 위한 니겔라 사티바의 치료 작용을 광범위하게 연구한 반면, 이 문서에서의 인간 연구는 드물고 제한적이다[23, 24]. 더욱이 하시모토 갑상선염에서 니겔라 사티바의 건강 영향은 쥐의 프로필티오우라실(PTU) 유도 갑상선 기능 저하증에서 갑상선 기능 저하 상태를 역전시키고 산화 스트레스와 갑상선 세포 손상을 개선하는 데 있어 보호 역할을 나타내는 한 동물 모델에서만 연구되었다[25]. 현재 무작위 임상 시험에서 우리는 하시모토 갑상선염 환자의 갑상선 기능 및 혈청 VEGF 및 Nesfatin-1 농도에 대한 Nigella sativa 분말의 잠재적 치료 효과를 평가하는 것을 목표로 했다.
Methods
Patients
In the current double-blinded placebo-controlled trial, 40 patients with Hashimoto’s thyroiditis were enrolled (Fig. 1). Subjects were recruited from outpatient endocrinology and metabolism clinics of Isfahan University of Medical Sciences. Inclusion criteria were as follows: age between 20 and 50 years and having Hashimoto’s thyroiditis according to physician diagnosis. Exclusion criteria were as follows: taking any nutritional supplements for at least 3 months prior participation or during the trial, any history of autoimmune disease, cardiovascular events, other thyroid abnormalities including Grave’s disease, being pregnant or lactating, any history of thyroid surgeries and being on any dietary regimens during and 3 months before recruitment in the trial. Participants were treated with levothyroxine while the drug dosage was stable from 6 weeks prior participation in the study to the end of the trial. The average full replacement dose of levothyroxine sodium was approximately 1.7 mcg/kg/day (e.g., 100–125 mcg/day for a 70 kg adult).
방법들
환자
현재 이중맹검 플라시보 대조 실험에서는 하시모토 갑상선염 환자 40명이 등록되었다(그림 1). 대상자들은 이스파한 의과대학의 외래 내분비학과와 신진대사 클리닉에서 모집되었다. 포함 기준은 20세에서 50세 사이의 나이와 의사 진단에 따른 하시모토 갑상선염이었다. 제외 기준은 다음과 같았다: 참여 전 최소 3개월 동안 또는 시험 기간 동안 모든 영양 보충제를 복용하거나, 자가 면역 질환, 심혈관계 사건, 그레이브 병을 포함한 기타 갑상선 이상 기록, 임신 또는 수유, 갑상선 수술 기록 및 식이요법 중 모든 식이요법을 받았다. 그리고 재판에서 채용되기 3개월 전에. 실험 참여 6주 전부터 실험 종료까지 약물 복용량이 안정적인 상태에서 실험 참가자들에게 레보티록신을 투여했다. 레보티록신 나트륨의 평균 전체 치환량은 약 1.7 mcg/kg/일(예: 70 kg 성인의 경우 100–125 mcg/일)이었다.
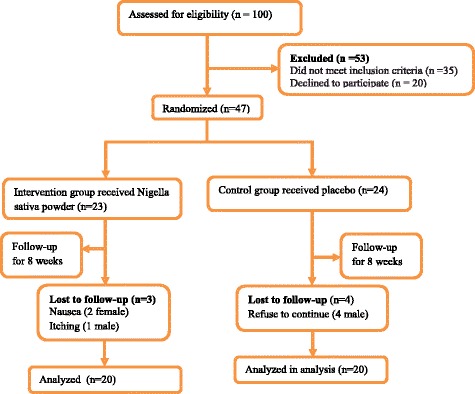
사진 설명을 입력하세요.
Fig. 1 그림 1
CONSORT Flow diagram of subject recruitment CONSORT 대상자 모집 흐름도
Study design
From 100 recruited subjects, 53 participants were excluded because of not meeting the inclusion criteria or decline to participate. Among remaining 47 patients, random permuted block procedure was performed and participants were randomly allocated into Nigella sativa-treated (n = 23) or placebo-treated (n = 24) groups. During the trial, three patients in Nigella sativa-treated group were excluded from the study because of itching and nausea; while four patients in control group refused to continue the trial. Therefore, totally 20 patients in each group completed the study. Patients in the intervention group received a daily dose of 2 g Nigella sativa powder per day and placebo group received 2 g starches per day for 8 weeks. The dose of the Nigella sativa and time period of the study had been selected according to review of the previous studies indicating the effectiveness of 2 g of Nigella sativa or even lesser doses and 8 weeks study duration in treatment of numerous metabolic disorders including immune disturbances and lipid abnormalities [26, 27].
Black seed powders were obtained from corns grown in Isfahan bought by a local market (Sad-Giah market, Isfahan, Iran) and were prepared by the Goldaroo pharmaceutical company (Goldaro Pharmaceutical Co. Isfahan, Iran). The black seeds were milled in a grinder and a purified powder was prepared. The seeds were identified and authenticated by Dr. Mahdieh Abbasalizad Farhangi, supervisor of the project from Department of Nutrition, Tabriz University of Medical Sciences, Tabriz, Iran. Thereafter, Nigella sativa seeds were processed into pharmaceutical grade capsules containing Nigella sativa powder and bottled according to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP). Each capsule was prepared containing 1 g powder of Nigella Sativa, and each bottle contained 112 capsules, for 8 weeks period of the study. While for the placebo, we used starch bought from the same market and the entire processes of its capsulation was similar to Nigella sativa seeds preparation. Participants in intervention and placebo groups received two capsules daily, taking it immediately before lunch and dinner respectively.
Randomization procedure was performed by a third investigator who had no clinical involvement in the trial to ensure complete blinding in the randomization process. Randomization was done according to computer- generated numbers and was kept in consecutively numbered envelopes opened at the moment of participant enrollment into the study. A follow-up procedure was done with weekly telephone contacts to ensure that subjects consumed the supplements regularly.
연구설계
모집 대상 100명 중 53명이 포함 기준을 충족하지 못하거나 참여를 거부해 제외됐다. 나머지 47명의 환자 중 무작위 순열 블록 시술을 시행하고 참가자를 무작위로 니겔라 사티바 치료(n = 23) 또는 플라시보 치료(n = 24) 그룹에 할당했다. 실험 동안, 니겔라 사티바 치료 그룹의 3명의 환자는 가려움과 메스꺼움 때문에 연구에서 제외되었고, 대조군 그룹의 4명의 환자는 실험을 계속하기를 거부했다. 따라서 각 그룹에서 총 20명의 환자가 연구를 완료했습니다. 중재 그룹의 환자들은 하루에 2 g의 니겔라 사티바 가루를, 플라시보 그룹은 8주 동안 하루에 2 g의 녹말을 받았다. Nigella sativa의 용량 및 연구 기간은 면역 장애와 지질 이상을 포함한 수많은 대사 장애의 치료에서 Nigella sativa의 2 g 또는 더 적은 용량 및 8주 연구 기간을 나타내는 이전 연구 검토에 따라 선택되었다[26, 27].
검은 종자 분말은 현지 시장(이란 이스파한주 이스파한시장)이 사들인 이스파한에서 재배한 옥수수로 얻어 골다루 제약사(골다로제약)가 준비했다. 이스파한, 이란). 검은 씨앗을 분쇄기에 빻아 정제된 분말을 준비하였다. 이 씨앗은 이란 타브리즈 의과대학 영양학과 책임자인 Mahdieh Abbsalizad Farhangi 박사에 의해 확인되고 인증되었습니다. 그 후, Nigella sativa 씨앗은 Nigella sativa 분말이 포함된 약학급 캡슐로 가공되어 GMP(Good Manufacturing Practices)에 따라 병에 담았습니다. 각 캡슐에는 1g의 니겔라 사티바가 들어 있었고, 각 병에는 연구 기간 동안 112개의 캡슐이 들어 있었다. 위약의 경우, 우리는 같은 시장에서 구입한 녹말을 사용했고 그 캡슐화의 전체 과정은 Nigella sativa 씨앗 준비와 유사했다. 중재와 플라시보 그룹의 참가자들은 점심과 저녁 식사 직전에 각각 두 개의 캡슐을 복용했다.
무작위화 절차는 무작위화 과정에서 완전한 맹목을 보장하기 위해 임상적 개입이 없는 세 번째 조사자에 의해 수행되었다. 무작위화는 컴퓨터가 생성한 숫자에 따라 수행되었으며 참가자가 연구에 등록하는 순간 열린 연속 번호 봉투에 보관되었다. 실험 대상자들이 정기적으로 보충제를 섭취하도록 하기 위해 매주 전화 연락 담당자와 함께 후속 절차를 수행했다.
Anthropometric and nutritional assessments
Body weight and height were measured with a calibrated digital scale and stadimeter respectively. BMI was calculated as weight (kg) divided by height (cm) squared. Waist circumference (WC) was measured in horizontal plane, midway between the lowest rib and the iliac crest with a measuring tape in centimeter. Waist to hip ratio (WHR) was calculated by WC divided by hip circumference (HC). The dietary assessments were performed using a 3-day food record, covering two weekdays and one weekend day, to estimate total energy, carbohydrate, protein, fat and antioxidant vitamins consumption. Because of the antioxidant nature of Nigella sativa the intake of vitamin E and C were specifically evaluated to ensure that no change in their consumption has been occurred throughout the trial and to rule out their possible confounding effect on study parameters. Nutrient analysis of the 3-day food record was performed using the Nutritionist IV software (N-squared Computing, Salem, OR, USA).
인체측정학 및 영양학적 평가
체중과 키는 각각 보정된 디지털 저울과 스타디미터를 사용하여 측정되었다. BMI는 체중(kg)을 키(cm) 제곱으로 나눈 값으로 계산했다. 허리둘레(WC)는 가장 낮은 갈비뼈와 장골문 사이의 중간인 수평면에서 센티미터 단위로 측정되었다. 허리 대 엉덩이 비율(WHR)은 WC를 엉덩이 둘레(HC)로 나눈 값이다. 식이 평가는 총 에너지, 탄수화물, 단백질, 지방 및 항산화 비타민 섭취량을 추정하기 위해 평일 2일과 주말 1일을 포함하는 3일간의 음식 기록을 사용하여 수행되었다. Nigella sativa의 항산화 특성으로 인해 비타민 E와 C의 섭취는 시험 내내 섭취에 변화가 발생하지 않았는지 확인하고 연구 매개변수에 대한 가능한 교란 효과를 배제하기 위해 구체적으로 평가되었다. 3일 음식 기록의 영양소 분석은 Nutritionist IV 소프트웨어(N-square Computing, Salem, OR, USA)를 사용하여 수행되었다.
Biochemical assays
Fasting blood samples were obtained from all of the participants at the beginning and end of the trial. The serum and plasma samples were separated by centrifugation at 2500 rpm for 10 min (Beckman Avanti J-25; Beckman Coulter, Brea, CA, USA) at room temperature. The serum samples were stored at −70 °C immediately after centrifugation until their assays. Serum thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), total triiodothyronine (T3) and total thyroxine (T4) were analyzed by enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA Kit, Pishtaz Tebe Co., Tehran, Iran) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Anti-thyroid peroxidase antibody was measured by the commercially solid-phase ELISA kit (Aeskulisa, Wendelsheim, Germany). Serum concentration of VEGF and Nesfatin-1 were measured by commercial ELISA kits (Hangzhou East biopharm Co, USA). The sensitivity of these assays was 10.42 ng/l and 0.15 ng/ml respectively.
생화학 분석
공복혈액 샘플은 임상시험 시작과 종료 시 참가자 전원에게서 얻었다. 혈청 및 혈장 검체는 상온에서 10분 동안 2500 rpm으로 원심분리(Beckman Avanti J-25, Beckman Coulter, Brea, CA, USA)하였다. 혈청 샘플은 검사될 때까지 원심분리 후 즉시 -70°C에 저장되었다. 혈청 갑상선자극호르몬(TSH), 총트리아이오도티로닌(T3) 및 총티록신(T4)을 효소연계면역흡착검사(ELISA Kit, Pishtaz Tebe Co., 이란 테헤란, 이란)에 따라 분석하였다. 항갑상선 과산화효소 항체는 상업용 고체상 ELISA 키트(독일 웬델스하임 아에스쿨리사)를 통해 측정되었다. VEGF와 Nesfatin-1의 혈청 농도는 상용 ELISA 키트(미국 항저우 이스트 바이오팜 Co.)를 통해 측정되었다. 이들 검사의 민감도는 각각 10.42 ng/l와 0.15 ng/ml이었다.
Statistical assays
Statistical analysis was performed by SPSS™ statistical software (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA). Quantitative data were presented as mean ± standard deviation (SD), and qualitative data were demonstrated as frequency and percent. One-sample Kolmogorov-Smirnov test was used to assess the normality of data. Between groups comparisons of continuous variables were performed by independent sample t-test. Paired t-test was used for before and after intervention comparisons. Analysis of covariance (ANCOVA) was used to identify any differences between two treatment groups after intervention adjusting for the confounding effects of baseline concentrations of parameter, age and gender. Stepwise multivariate linear regression model was used to evaluate the predictors of changes in VEGF and Nesfatin-1 concentrations. P-values less than 0.05 were considered to be significant. Sample size calculation was performed based on 80% power and an α-error of 5% to detect treatment effect of Nigella sativa on serum TSH. Totally, 14 individuals were calculated. Allowing for 30% drop-out over 8 weeks of intervention, the total sample size required for the study was 40 individuals.
통계분석
통계 분석은 SPSS™ 통계 소프트웨어(SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA)에 의해 수행되었다. 정량적 데이터는 평균 ± 표준 편차(SD)로 제시되었고, 정성적 데이터는 빈도 및 백분율로 입증되었다. 데이터의 정규성을 평가하기 위해 일표본 Kolmogorov-Smirnov 검정이 사용되었다. 그룹 간 연속형 변수 비교는 독립적인 표본 t-검정을 통해 수행되었습니다. 쌍체 t-검정은 개입 전후의 비교에 사용되었다. 공분산 분석(ANCOVA)은 매개 변수, 연령 및 성별의 기준선 농도의 교란 효과에 대한 개입 조정 후 두 치료 그룹 간의 차이를 식별하는 데 사용되었다. 단계적 다변량 선형 회귀 모델을 사용하여 VEGF와 Nesfatin-1 농도 변화의 예측 변수를 평가하였다. 0.05보다 작은 P-값은 유의한 것으로 간주되었다. 검체 크기 계산은 혈청 TSH에 대한 Nigella sativa의 치료 효과를 검출하기 위해 80% 출력과 5%의 α-오차를 기반으로 수행되었다. 총 14명이 계산되었습니다. 8주간의 개입에서 30%의 중퇴를 허용한 결과, 연구에 필요한 총 표본 크기는 40명이었다.
Results
The flowchart of the study is given in Fig. 1. A total of 40 patients completed the study. Three patients in Nigella sativa-treated group were excluded from the study because of itching and nausea; while four patients in control group refused to continue the trial. No other side effects were observed in the current study.
At baseline, there was no significant difference in general characteristics among groups. Nigella sativa supplementation significantly reduced anthropometric variables including weight, BMI, WC and HC in patients with Hashimoto’s thyroiditis (P < 0.05); while no significant change in placebo-treated group has been occurred (Table 1). Dietary energy and nutrient intakes before and after intervention are presented in Table 2. Energy and nutrient intakes were similar between groups before intervention and no significant change was observed after intervention. Serum TSH and anti-TPO concentrations reduced while serum T3 increased in Nigella sativa treated group (P < 0.05). Moreover, serum VEGF reduced significantly after 8 weeks of Nigella sativa supplementation (P = 0.02, Table 3). In stepwise multiple linear regression analysis when change in serum VEGF concentrations was entered as dependent variable and change in anthropometric variables and thyroid hormones as independent variables (Table 4) one model was obtained indicating change in WHR as predictor of change in VEGF concentrations. In similar procedure when change in serum Nesfatin-1 was entered as dependent variable, change in WHR, TSH and T3 were its predictors (P < 0.05).
결과.
연구의 흐름도는 위의 그림 1과 같다. 총 40명의 환자가 연구를 완료하였다. Nigella sativa 치료 그룹의 3명의 환자는 가려움과 메스꺼움 때문에 연구에서 제외되었고, 대조 그룹의 4명의 환자는 실험을 계속하기를 거부했다. 현재 연구에서 다른 부작용은 관찰되지 않았다.
기준선에서는 집단 간 일반 특성에서 유의미한 차이가 없었다. 니겔라 사티바 보충제는 하시모토 갑상선염 환자에서 체중, BMI, WC, HC를 포함한 인체측정학 변수를 유의하게 감소시켰다(P < 0.05). 반면 위약 처리된 그룹에는 유의한 변화가 발생하지 않았다(표 1). 중재 전후의 식이 에너지와 영양소 섭취는 표 2에 제시되어 있다. 에너지와 영양소 섭취는 개입 전 그룹 간에 유사했으며 개입 후 유의미한 변화는 관찰되지 않았다. 혈청 TSH 및 항TPO 농도는 감소하였으며, Nigella sativa 처리군에서는 혈청 T3가 증가하였다(P < 0.05). 또한 Nigella sativa 보충 8주 후 혈청 VEGF가 유의하게 감소하였다(P = 0.02, Table 3). 혈청 VEGF 농도의 변화를 종속변수로 입력하고 인체측정학 변수와 갑상선 호르몬의 변화를 독립변수로 입력한 단계적 다중 선형 회귀 분석(표 4)에서 VEGF 농도 변화의 예측자로서 WHR의 변화를 나타내는 하나의 모델을 얻었다. 혈청 Nesfatin-1의 변화가 종속변수로 입력되었을 때 유사한 절차에서 WHR, TSH 및 T3의 변화가 예측 변수였다(P < 0.05).
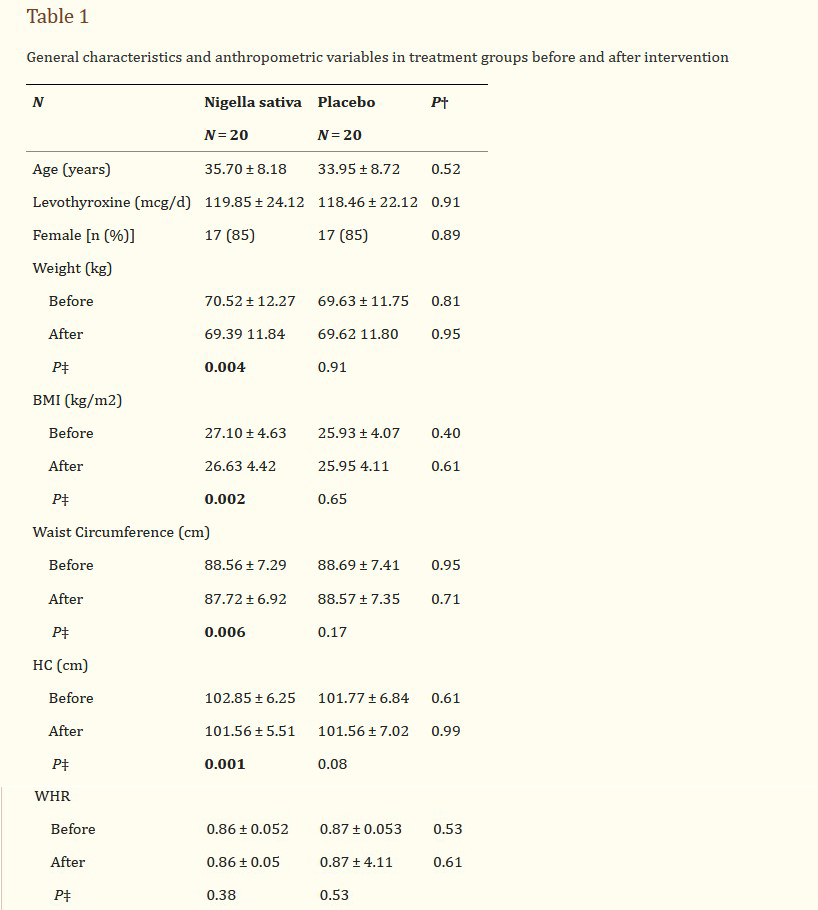
사진 설명을 입력하세요.
Table 1
General characteristics and anthropometric variables in treatment groups before and after intervention
표 1.
개입 전후의 치료 그룹의 일반 특성 및 인체측정학 변수
BMI body mass index, WC waist circumference, HC hip circumference, WHR waist to hip ratio, †P values for ANOCOVA after adjustment for age, gender, duration of the disease and variable’s baseline value; ‡P values for paired t-test. Data are presented as mean ± SD or number (percent), the bolded P values are statistically significant
BMI 체질량지수, WC 허리둘레, HC 엉덩이둘레, WHR 허리 대 엉덩이 비율, 연령, 성별, 질병 기간 및 변수 기준값 조정 후 ANOCOVA에 대한 P값, 쌍체 t-검사의 P값. 데이터는 평균 ±로 표시됩니다. SD 또는 숫자(백분율), 굵게 표시된 P 값은 통계적으로 유의하다.
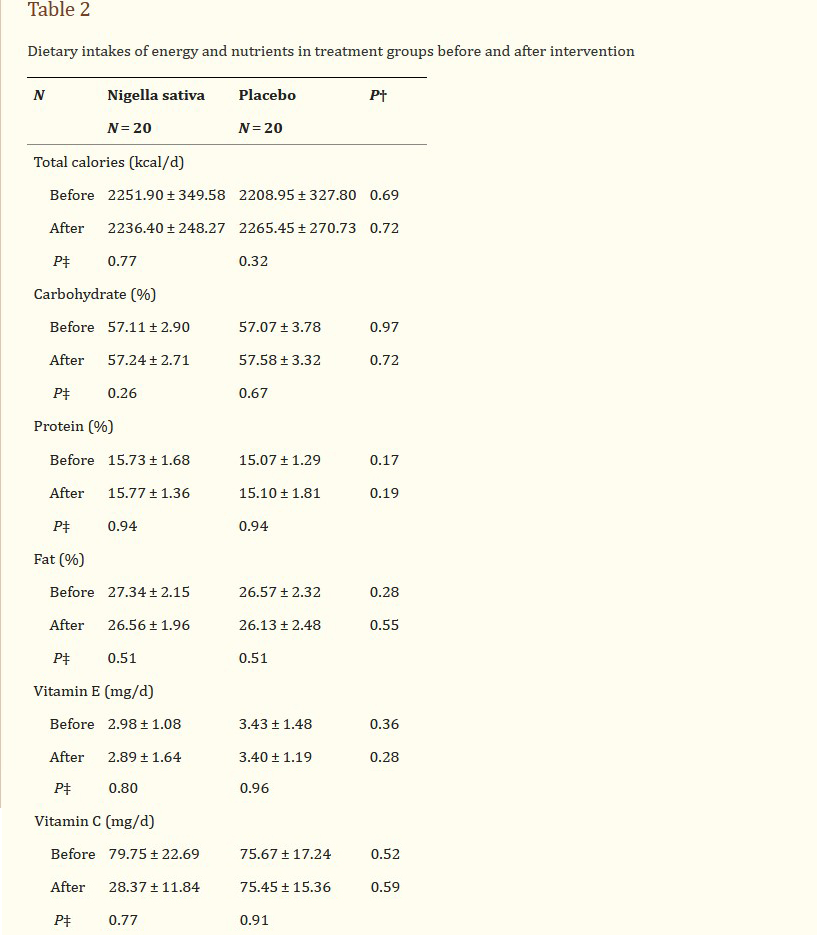
사진 설명을 입력하세요.
Table 2
Dietary intakes of energy and nutrients in treatment groups before and after intervention
Data are presented as mean ± SD, †P values for ANOCOVA after adjustment for age, gender, duration of the disease and variable’s baseline value; ‡P values for paired t-test
표 2
치료 전후의 치료 그룹 내 에너지 및 영양소 섭취
데이터는 연령, 성별, 질병 기간 및 변수의 기준값 조정 후 ANOCOVA에 대한 평균 ± SD, γP 값으로 제시된다. γP 값은 쌍체 t-검정에 대한 것이다
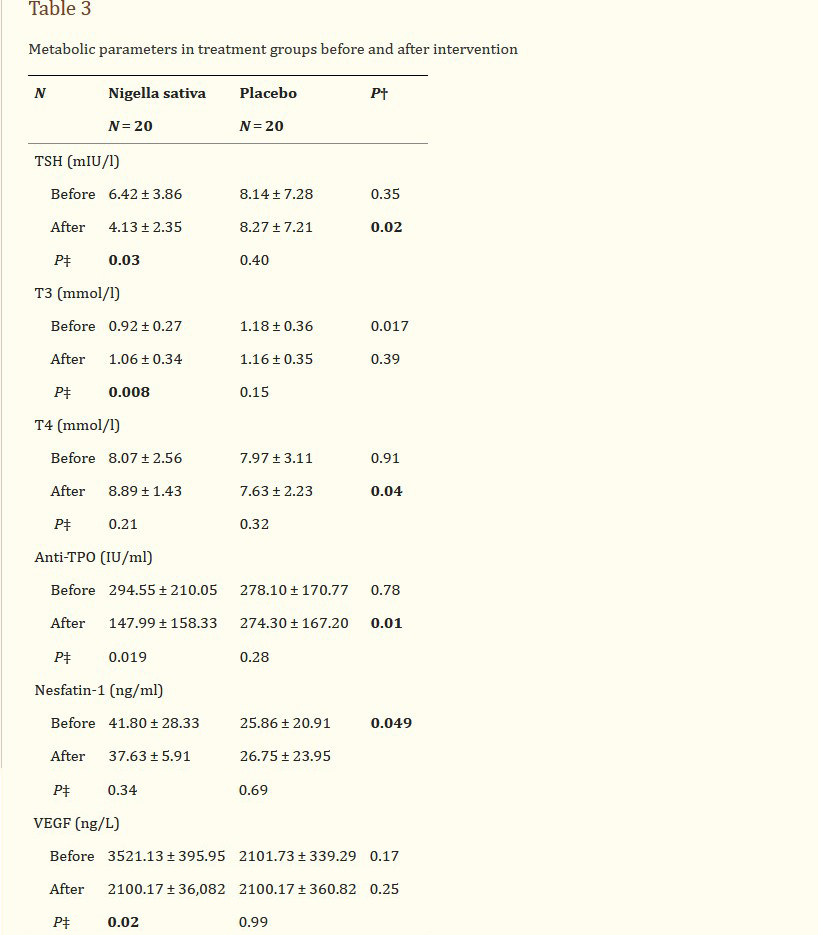
사진 설명을 입력하세요.
Table 3
Metabolic parameters in treatment groups before and after intervention
Data are presented as mean ± SD. † P values for ANOCOVA after adjustment for age, gender and baseline concentration of parameter; ‡P values for paired t-test. TSH, thyroid-stimulating hormone; T3 triiodothyronine, T4 thyroxine, VEGF vascular endothelial growth factor, the bolded P values are statistically significant
표 3
중재 전후의 치료 그룹 내 대사 매개 변수
데이터는 평균 ±로 표시된다. SD. p 파라미터의 연령, 성별 및 기준 농도에 대한 조정 후 ANOCOVA에 대한 P 값; 쌍체 t-검정의 경우 P 값. TSH, 갑상선 자극 호르몬; T3 트리요오드티로닌, T4 티록신, VEGF 혈관 내피 성장인자, 굵은 P 값은 통계적으로 유의하다.
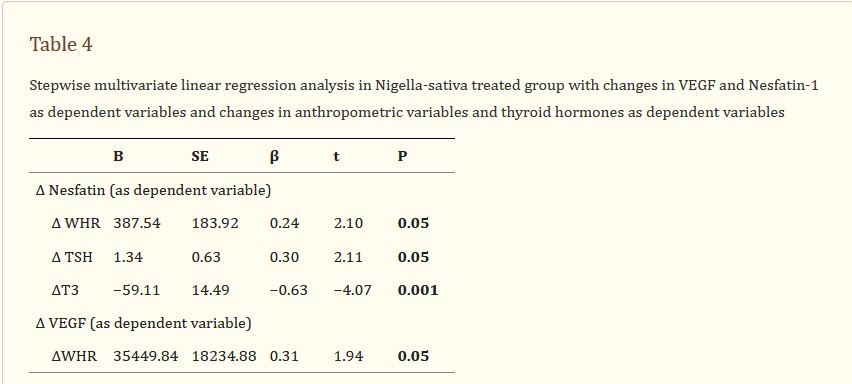
사진 설명을 입력하세요.
Table 4
Stepwise multivariate linear regression analysis in Nigella-sativa treated group with changes in VEGF and Nesfatin-1 as dependent variables and changes in anthropometric variables and thyroid hormones as dependent variables
WHR waist to hip ratio, TSH thyroid-stimulating hormone, T3 triiodothyronine, T4 thyroxine, VEGF vascular endothelial growth factor, B unstandardized coefficient, SE standard error, β standardized coefficient, t the student’s t distribution, P level of significance
표 4
VEGF와 Nesfatin-1의 변화를 종속변수로, 인체측정학 변수와 갑상선 호르몬의 변화를 종속변수로 한 Nigella-sativa 치료군의 단계적 다변량 선형 회귀 분석
WHR 허리 대 엉덩이 비율, TSH 갑상선 자극 호르몬, T3 트라이아이오도티로닌, T4 티록신, VEGF 혈관 내피 성장인자, Bunstandarded coefficient, SE standarded coefficient, βstandarded coefficient, 학생의 t분포, 유의수준
Discussion
In the current study we showed a meaningful impact of 8 weeks treatment with Nigella sativa on thyroid function, anthropometric features and serum VEGF concentrations in patients with Hashimoto’s thyroiditis. However changes in serum Nesfatin-1 concentrations were not significant. These findings were in accordance of findings of two animal studies; in one study by Khalawi AA [25] Nigella sativa oil improved hypothyroid status and decreased serum TSH concentrations in rats; in other animal study by Al-Asoom et al. [28] daily oral administration of 800 mg/kg Nigella sativa in male Wistar rats reduced serum thyroxine concentrations. However in our study, for the first time, we clearly demonstrated its beneficial role on improving thyroid function in human.
The seeds of Nigella sativa known as black seeds or black cumin have long been used in folk medicine in the middle and Far East as a traditional medicine for a wide range of disease including infections, obesity, hypertension and gastrointestinal problems [21]. Its most prominent constituent with well- known antioxidant, anti-inflammatory and anti-cancer properties is thyimoquinone [29]. Thyimoquinone has potential cytoprotective and anti-inflammatory effects; it has been reported that its anti-inflammatory effects are induced by up-regulated expression of heme-oxygenase-1 and suppression of the cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) expression in different cell lines [30]. Thyimoquinone also differentially modulated thyroid hormones and improved thyroid status in rats [31]. Therapeutic effects of Nigella sativa against hypothyroidism is mostly attributed to its antioxidant effects which have been proved in numerous studies [32–34]. It has also been suggested that Nigella sativa protects the hyperplasic changes of thyroid parenchyma in hypothyroid rats [25]. Accordingly, increment in T3 concentrations after treatment with Nigella sativa in the current study, has also been reported in the study by Ismail et al. [35] and the authors concluded that Nigella sativa could raise the lowered serum triiodothyronine concentration without changing the concentration of serum TSH because of its potential ability in repairing the thyroid gland and resynthesizing the thyroid hormone; therefore its therapeutic action could be in part due to antioxidant defense system. Accordingly, reduction of serum anti-TPO concentrations after treatment with Nigella sativa could be explained by its immunomodulatory effects approved previously by its protective roles against several autoimmune disease including type 1 diabetes mellitus and experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE) [36, 37]. The possible underlying mechanisms of immunomodulatory effects of Nigella sativa are reduced synthesis of auto-antibodies, reduced innate and acquired immune cell markers and reduction in transforming growth factor (TGF)-β and interleukin (IL)-23 concentrations [36–38].
논의
본 연구에서는 하시모토 갑상선염 환자의 갑상선 기능, 인체측정학적 특징 및 혈청 VEGF 농도에 대해 니겔라 사티바를 사용한 8주 치료의 의미 있는 영향을 보여주었다. 그러나 혈청 Nesfatin-1 농도의 변화는 유의하지 않았다. 이러한 발견은 두 가지 동물 연구의 결과에 따른 것이다. Khalawi AA [25] Nigella sativa 오일이 쥐의 갑상선 기능 저하 상태를 개선하고 혈청 TSH 농도를 감소시켰다. Al-Asoom 등의 다른 동물 연구에서. [28] 수컷 위스타 쥐에게 800 mg/kg 니겔라 사티바를 매일 경구 투여하여 혈청 티록신 농도를 감소시켰다. 그러나 우리의 연구에서, 우리는 처음으로 인간의 갑상선 기능을 향상시키는 데 그것의 유익한 역할을 분명히 보여주었다.
검은 씨앗 또는 검은 쿠민으로 알려진 니겔라 사티바의 씨앗은 감염, 비만, 고혈압, 위장 문제를 포함한 광범위한 질병에 대한 전통적인 약으로 중극동의 민간의학에서 오랫동안 사용되어 왔다[21]. 잘 알려진 항산화, 항염증 및 항암 특성을 가진 가장 두드러진 성분은 티모퀴논[29]이다. 티모퀴논의 항염증 효과는 헴-산소효소-1의 상향 조절된 발현과 다른 세포주에서의 시클로옥시게나제-2(COX-2) 발현 억제에 의해 유도된다고 보고되었다. 티모퀴논은 또한 쥐에서 갑상선 호르몬을 차등적으로 조절하고 갑상선 상태를 개선했다[31]. 갑상선 기능 저하증에 대한 니겔라 사티바의 치료 효과는 수많은 연구에서 입증된 항산화 효과에 주로 기인한다[32–34]. 또한 니겔라 사티바가 갑상샘 기능 저하 쥐에서 갑상샘 실질종의 과형성 변화를 보호한다고 제안되었다[25]. 따라서, 본 연구에서 Nigella sativa로 치료한 후 T3 농도가 증가한 것은 Ismail 등의 연구에서도 보고되었다. [35] 그리고 저자들은 Nigella sativa가 혈청 TSH의 농도를 변화시키지 않고 혈청 트라이아이오도티로닌의 낮은 농도를 증가시킬 수 있다고 결론내렸다. 왜냐하면 Nigella sativa가 갑상선을 복구하고 갑상선 호르몬을 재합성하는 잠재적 능력 때문이다. 따라서 그것의 치료 작용은 부분적으로 항산화 방어 시스템에 기인할 수 있다. 따라서 Nigella sativa를 사용한 치료 후 혈청 항TPO 농도의 감소는 제1형 당뇨병과 실험용 자가면역성 뇌수염(EAE)을 포함한 여러 자가면역질환에 대한 보호역할에 의해 이전에 승인된 면역조절 효과로 설명할 수 있다[36, 37]. Nigella sativa의 면역 조절 효과의 가능한 기본 메커니즘은 자가 항체의 합성 감소, 선천적 및 후천적 면역 세포 마커 감소, 변형 성장 인자(TGF)-β 및 인터류킨(IL)-23 농도의 감소이다[36–38].
VEGF is minimally expressed in normal human thyroid cells [39]; however in pathological situations, enhanced TSH concentrations, is a potent stimulator of VEGF secretion [11]. It has been shown that VEGF and one of its receptors, Flt-1, are present in epithelial cells of the thyroid, and VEGF contributes to the regulation of development and function of thyroid epithelial cells [10]. Higher VEGF concentrations are associated with increased risk of recurrence and decreased disease-free survival in papillary thyroid cancer [40]. Strong expression of VEGF has been reported in thyroiditis and thyroid carcinomas [41]; therefore it is a critical cytokine in tumor angiogenesis and will be a potent target of diagnosis and therapy. In the current study, Nigella sativa had a strong impact in reducing VEGF concentrations in Hashimoto’s thyroiditis. It is mostly because of anti-angiogenic effects of Nigella sativa and its major bioactive compound, thyimoquinone, which has been proven previously in different cancer cell lines [42, 43]. Moreover, in the current study, change in WHR was a significant positive predictor of changes in serum VEGF in Nigella sativa treated group. In fact, VEGF is a multifunctional cytokine and its elevated concentration has been reported previously in several metabolic disorders including type 2 diabetes mellitus and polycystic ovary syndrome. A positive association between serum VEGF and its different genomic variants with the components of metabolic syndrome including central obesity and waist to hip ratio has also been previously reported [44, 45]. This relationship arise from this fact that adipocytes, specially white adipose tissue cells, produce VEGF which may act as an angiogenic and vascular survival factor for the omental vasculature and has paracrine or systemic endocrine actions, these might hypothetically impact on adipose expansion or the vascular comorbidities of obesity related disease [46]. In this context, it is interesting that Randeva et al. could reported a strong correlation of serum VEGF with waist-to-hip ratio in a considerable cohort of individuals (χ 2 = 17.42; P < 0.001) [47], a measure that, is suggested to be a better marker of subclinical arteriosclerosis and endothelial dysfunction [48] which are common clinical consequences of Hashimoto’s thyroiditis [49, 50].
VEGF는 정상적인 인간 갑상선 세포에서 최소한으로 발현되지만 [39] 병리학적 상황에서는 향상된 TSH 농도가 VEGF 분비[11]의 강력한 자극제이다. VEGF와 그 수용체 중 하나인 Flt-1은 갑상선의 상피세포에 존재하며, VEGF는 갑상선 상피세포의 발달 및 기능 조절에 기여하는 것으로 나타났다[10]. VEGF 농도가 높을수록 유두 갑상선암의 재발 위험 증가와 무병 생존 감소와 관련이 있다[40]. VEGF의 강한 발현은 갑상선염과 갑상선암종에서 보고되었다[41]. 따라서 VEGF는 종양 혈관신생에서 중요한 사이토카인이며 진단 및 치료의 강력한 대상이 될 것이다. 본 연구에서 Nigella sativa는 하시모토 갑상선염의 VEGF 농도를 감소시키는 데 강한 영향을 미쳤다. 이는 대부분 Nigella sativa와 그 주요 생물학적 활성 화합물인 tyimoquinone의 항혈관신생 효과 때문이며, 이는 이전에 다른 암 세포주에서 입증되었다[42, 43]. 또한, 본 연구에서 WHR의 변화는 Nigella sativa 치료군에서 혈청 VEGF의 변화를 나타내는 유의미한 양성 예측 변수였다. 사실, VEGF는 다기능 사이토카인이며, 제2형 당뇨병 및 다낭성 난소 증후군을 포함한 여러 대사 장애에서 농도가 높아진 것으로 보고되었다. 혈청 VEGF와 다른 게놈 변이체 사이의 긍정적인 연관성은 중심 비만과 허리 대 엉덩이 비율을 포함한 대사 증후군의 구성 요소와 이전에 보고되었다[44, 45]. 이러한 관계는 지방 세포, 특히 백색 지방 조직 세포가 망막 혈관 구조에 혈관신생 및 혈관 생존 인자로 작용할 수 있고 파라클린 또는 전신 내분비 작용을 할 수 있는 VEGF를 생성한다는 사실에서 비롯되며, 이는 비만과 관련된 지방 확장 또는 혈관 이환에 가정적으로 영향을 미칠 수 있다.병이 나다[46]. 이러한 맥락에서, Randeva 등이 임상적으로 일반적인 임상적 결과인 아임상 동맥경화 및 내피 기능 장애[48]의 더 나은 마커로 제안되는 상당한 개인 코호트에서 혈청 VEGF와 허리 대 엉덩이 비율의 강한 상관관계를 보고할 수 있다는 것이 흥미롭다.하시모토 갑상선염의 장 [49, 50]
Weight reducing effects of Nigella sativa has been observed in previous studies; Zaoui A [51] reported a significant reduction in body weight in rats after 6 weeks treatment with Nigella sativa fixed oil (P < 0.001). In other study 3 month supplementation with 1.5 g per day of powdered Nigella sativa in central obese men significantly reduced body weight [52]. One suggested mechanism is increasing mean rates of satiety and fullness [53]; although, we did not observe any change in dietary energy or nutrient intakes after intervention. Other possible mechanisms are reduced lipid absorption, increased energy expenditure, decreased pre-adipocyte differentiation and proliferation, or decreased lipogenesis and increased lipolysis [54]. The suggested underlying mechanisms of the effects Nigella sativa and its major ingredient thymoquinone’s on thyroid health and body weight are summarized in Fig. 2.
Nigella sativa의 체중 감소 효과는 이전 연구에서 관찰되었습니다. Zaoui A[51]는 Nigella sativa 고정유로 6주 치료한 후 쥐의 체중 감소가 유의미하다고 보고했다(P < 0.001). 다른 연구에서는 중심 비만 남성의 경우 하루 1.5g의 니겔라 사티바 가루로 3개월 보충하면 체중[52]이 상당히 감소했다. 한 가지 제안된 메커니즘은 평균 포만감과 포만감을 증가시키는 것이다[53]. 그러나 개입 후 식이 에너지 또는 영양소 섭취의 변화는 관찰되지 않았다. 다른 가능한 메커니즘은 지질 흡수 감소, 에너지 소비 증가, 지방세포 전 분화 및 증식 감소 또는 지방 생성 감소 및 지방 분해 증가이다[54]. Nigella sativa와 그 주요 성분인 tymoquinone's가 갑상선 건강과 체중에 미치는 영향의 제안된 기본 메커니즘은 그림 2에 요약되어 있다.
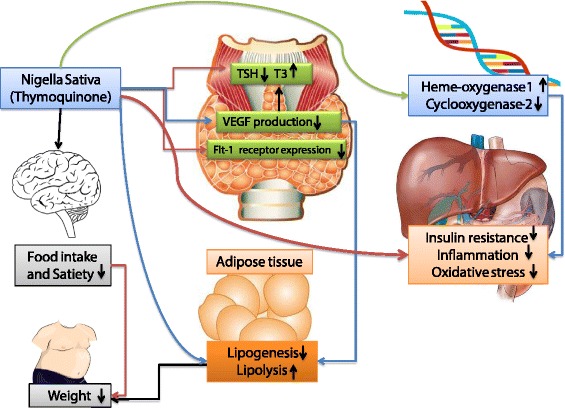
사진 설명을 입력하세요.
Hashimoto’s thyroiditis is more prevalent among females compared with males and women are up to 10 times more likely to develop the disease compared with men [55]. This strong female association remains unexplained although our hunch is that sex steroids have the critical role, as there is compelling evidence for such effects in animal models of many types of autoimmunity [56]. Other possible explanations include skewed X chromosome inactivation and fetal microchimerism [57]. Accordingly, the number of the female participants in the current study was more than men, but the gender distribution among two groups were equal. Therefore, the possible confounding effect of gender could be rule out. Moreover, the comparisons between all of the study parameters are adjusted for the possible confounding effects of age, gender and variable’s baseline values by ANCOVA.
In the current study serum Nesfatin-1 did not change after Nigella sativa supplementation in Hashimoto’s thyroiditis patients. The studies regarding the relationship between serum Nesfatin-1 concentrations and thyroid dysfunction are scarce and conflicting. One study in children demonstrated its reduced concentrations in children with untreated subclinical hypothyroidism [13]; while, other study by Sahin et al. [58] reported no difference in serum Nesfatin-1 concentrations in patients with hypothyroidism compared with healthy control group. Nesfatin-1 is colocalized with TRH and affects the membrane potential of TRH neurons in the paraventricular nucleus, which is known to be closely related to the regulation of thyroid function [15]. However we did not find any change in its concentrations after treatment with Nigella sativa. It could be due to relatively small sample size or treatment duration.
하시모토 갑상선염은 남성보다 여성에게서 더 흔하고 여성은 남성보다 최대 10배까지 발병할 가능성이 높다[55]. 많은 유형의 자가면역 동물 모델에서 그러한 효과에 대한 설득력 있는 증거가 있기 때문에 성 스테로이드가 중요한 역할을 한다는 우리의 예감이지만 이 강력한 여성 연관성은 설명되지 않고 있다[56]. 다른 가능한 설명은 왜곡된 X 염색체 불활성화와 태아 마이크로키머증을 포함한다[57]. 이에 따라 본 연구에서 여성 참여자 수는 남성보다 많았으나 두 집단 간의 성 분포는 동일하였다. 따라서 성별의 가능한 교란 효과는 배제될 수 있다. 또한 모든 연구 매개 변수 간의 비교는 ANCOVA에 의해 연령, 성별 및 변수의 기준선 값의 가능한 교란 효과에 대해 조정된다.
현재 연구에서 Nesfatin-1은 하시모토의 갑상선염 환자에서 Nigella sativa 보충 후에도 변하지 않았다. 혈청 네스파틴-1 농도와 갑상선 기능 장애 사이의 관계에 대한 연구는 드물고 모순적이다. 아동에 대한 한 연구는 치료되지 않은 아임상 갑상선 기능 저하증을 가진 아동에서 농도가 감소함을 입증했다[13]. 반면, 사힌 등의 다른 연구는. [58]은 건강한 대조군과 비교하여 갑상선 기능 저하증 환자의 혈청 Nesfatin-1 농도의 차이가 보고되지 않았다. Nesfatin-1은 TRH와 함께 국소화되어 있으며, 갑상선 기능 조절과 밀접한 관련이 있는 것으로 알려진 부심실 핵에서 TRH 뉴런의 막 전위에 영향을 미친다[15]. 그러나 Nigella sativa로 치료한 후 농도 변화는 발견되지 않았다. 비교적 작은 검체 크기 또는 처리 기간 때문일 수 있다.
Conclusions
We have demonstrated beneficial effects of Nigella sativa in improving thyroid status, reducing VEGF and body weight in patients with Hashimoto’s thyroiditis. Although no significant change in serum Nesfatin-1 concentrations has been observed, change in anthropometric variables and thyroid hormones were significant predictors of changes in serum Nesfatin-1 concentrations.
결론들
하시모토 갑상선염 환자의 갑상선 상태를 개선하고 VEGF와 체중을 줄이는 데 니겔라 사티바의 유익한 효과를 입증했다. 혈청 Nesfatin-1 농도의 유의미한 변화는 관찰되지 않았지만, 인체측정학 변수와 갑상선 호르몬의 변화는 혈청 Nesfatin-1 농도 변화의 유의미한 예측 변수였다.
Acknowledgement
The current research was financially supported by a grant from Tabriz University of Medical Sciences.
승인
현재의 연구는 타브리즈 의과대학의 보조금에 의해 재정적으로 지원되었다.
Abbreviations
BMI Body mass index
HC Hip circumference
T3 Triiodotyronine
T4 Thyroxine
TG-Ab Thyroglobulin antibody
TPO-Ab Thyroid peroxidase antibody
TRH Thyrotropin releasing hormone
TSH Thyroid stimulating hormone
VEGF Vascular endothelial growth factor
WC Waist circumference
WHR Waist to hip ratio
약어
BMI 체질량지수
HC 힙 둘레
T3 트리오도티로닌
T4 티록신
TG-Ab 티로글로불린 항체
TPO-Ab 갑상선 과산화효소 항체
TRH 티로트로핀 분비 호르몬
TSH 갑상선 자극 호르몬
VEGF 혈관내피증식인자
WC 허리둘레
WHR 허리 대 엉덩이 비율
※ 긴 글을 끝까지 읽어주셔서 감사합니다.
저 역시 전문가가 아니기 때문에 고객님들의 문의가 들어오면 가급적 많은 정보를 바탕으로 설명을 드리고자 합니다만 보시다 시피 아직까지 블랙씨드에 대하여 인체에 직접적으로 실험을 하고 나온 결과들이 많지 않기에 주로 동물실험 및 세포실험을 통하여 그 기능과 효능에 대하여 짐작만 하고 있을 뿐입니다.
위 자료의 내용을 곧이 곧대로 해석하여 이해하지 마시고... 적당히 블랙씨드가 갑상선염에 효과가 있다 정도로만 해석하시면 될 것 같습니다.
언제 또 자료를 올릴 지는 모르겠습니다만... 다음 자료는 블랙씨드와 요산수치에 대한 글이 될 것 같습니다.
감사합니다.
'게시판' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 광범위한 질병에 대한 유망한 자연 치료법 (0) | 2024.06.06 |
|---|---|
| Nigella sativa (Black Seed, 블랙씨드)가 관절염 및 통풍 질환에 미치는 영향 (0) | 2024.06.06 |
| 널리 사용되는 식품 첨가제인 Nigella sativa(블랙커민씨드)의 항암 특성에 대한 최근의 진보 (0) | 2024.06.06 |
| 블랙씨드 오일의 놀라운 건강상의 10가지 이점 (0) | 2024.06.06 |
| 블랙씨드 오일 섭취시 주의해야 할 점 (0) | 2024.06.06 |