오늘은 미국 국립 생명공학 정보 센터 (National Center for Biotechnology Information)에 게제된 "제2형 당뇨병, 심혈관 질환 및 류마티스 관절염 질환을 조절하는 니겔라 사티바: 분자적 측면"에 대한 자료를 공유해 드리고자 합니다.
원본의 출처는 아래와 같습니다.

Oxidative stress is an important factor in the etiology of several chronic diseases that include cardiovascular disease (CVD), Type 2 diabetes (T2D), and rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Oxidative stress can lead to inflammation, and this can contribute to ...
www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
Nigella sativa in controlling Type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular, and rheumatoid arthritis diseases: Molecular aspects
제2형 당뇨병, 심혈관 질환 및 류마티스 관절염 질환을 조절하는 니겔라 사티바(블랙씨드) : 분자적 측면
Vahid Hadi,1,2 Naseh Pahlavani,3,4 Mahsa Malekahmadi,5 Elyas Nattagh-Eshtivani,1,6 Jamshid Gholizadeh Navashenaq,7,8 Saeid Hadi,2,9 Gordon A Ferns,10 Majid Ghayour-Mobarhan,11,12 Gholamreza Askari,13 and Abdolreza Norouzy1
Author information Article notes Copyright and License information PMC Disclaimer
Abstract (개요)
Oxidative stress is an important factor in the etiology of several chronic diseases that include cardiovascular disease (CVD), Type 2 diabetes (T2D), and rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Oxidative stress can lead to inflammation, and this can contribute to these chronic diseases. Reducing inflammation and oxidative stress may, therefore, be useful in the prevention and treatment of these conditions. One of the treatment options for chronic diseases is the use of traditional medicine and herbs, such as Nigella sativa. This is one of the herbs that have recently been assessed for its ability to reduce inflammation and oxidative stress. We have reviewed the reported effects of N. sativa on risk factors of chronic diseases (CVD, DM, and RA) with emphasis on molecular and cellular mechanisms in controlling inflammation and oxidative stress. Various mechanisms have been proposed to contribute to the beneficial properties of N. sativa, including a reduction of lipid peroxidation via its antioxidant properties; agonist of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma in adipose tissue; activation of AMP-activated protein kinase, increased antioxidants, inhibition of nuclear factor-kappa B pathway; increased in interleukin-10 expression, CD4+ T-cell percentage, T regulatory cell percentage (CD4+ CD25+ T-cell) in peripheral blood, and CD4+/CD8+ ratio, but to prove this claim, it is necessary to conduct experimental and well-designed clinical trial studies with a larger sample size on the effects of N. sativa on these chronic diseases.
산화 스트레스는 심혈관 질환(CVD), 제2형 당뇨병(T2D), 류마티스 관절염(RA)을 비롯한 여러 만성 질환의 원인에 중요한 요인입니다. 산화 스트레스는 염증을 유발할 수 있으며, 이는 이러한 만성 질환의 원인이 될 수 있습니다. 따라서 염증과 산화 스트레스를 줄이면 이러한 질환의 예방과 치료에 도움이 될 수 있습니다. 만성 질환의 치료 옵션 중 하나는 니겔라 사티바와 같은 전통 의학 및 허브의 사용입니다. 니겔라 사티바는 최근 염증과 산화 스트레스를 줄이는 능력에 대해 평가된 허브 중 하나입니다. 우리는 염증과 산화 스트레스를 조절하는 분자 및 세포 메커니즘에 중점을 두고 만성 질환(CVD, DM, RA)의 위험 요인에 대한 N. sativa의 보고된 효과를 검토했습니다. N. sativa의 유익한 특성에 기여하는 다양한 메커니즘이 제안되었습니다. N. sativa의 항산화 특성을 통한 지질 과산화 감소, 지방 조직에서 퍼옥시좀 증식인자 활성화 수용체 감마의 작용제, AMP 활성화 단백질 키나제 활성화, 항산화 물질 증가, 핵 인자-카파 B 경로 억제 등 다양한 메커니즘이 제안되었습니다; 인터루킨-10 발현, CD4+ T세포 비율, 말초 혈액의 T 조절 세포 비율(CD4+ CD25+ T세포), CD4+/CD8+ 비율 증가, 그러나 이러한 주장을 증명하기 위해서는 N. sativa가 이러한 만성 질환에 미치는 영향에 대해 더 큰 표본 규모로 실험적이고 잘 설계된 임상 시험 연구를 수행해야 합니다.
Keywords: Chronic disease, inflammation, Nigella sativa, oxidative stress
키워드: 만성 질환, 염증, 니겔라 사티바, 산화 스트레스
Introduction (도입)
Chronic diseases may be defined as a long-term illness with long treatment period that cannot currently be prevented by vaccines, or fully cured by medication and also causes physical changes in the body and reduces its performance.[1] According to the Centers for Disease Control (CDC) definition, cardiovascular disease (CVD), Type 2 diabetes (T2D), and rheumatoid arthritis (RA) are common chronic diseases globally.[1,2] CVD is associated with dysfunction of the heart and blood vessels and comprises disorders such as coronary heart disease and hypertension.[3] It has been estimated that the prevalence of hypertension and CVD reaches about 30% of the world's population by the year 2025.[4,5,6] T2D is the most common type of diabetes, accounting for 90% of all diabetes cases.[7] The number of people with T2D in the world was estimated to be approximately 125 million in 1997 and is expected to reach 300 million by 2025, and on average, the prevalence among adults is 8.5%.[8,9] RA is an autoimmune chronic disease that affects the small joints of the human body and affects approximately 1% of the population and is usually associated with severe disability.[10] Based on the National Health Council (NHC) reports, the burden of the cost of chronic diseases annually in the United States is about $ 1.3 trillion for seven common chronic diseases and now about 78% of total health care spending in the United States is spent on chronic diseases, and this trend is increasing.[11] It has been widely accepted that persistent oxidative stress leads to chronic inflammation and this inflammation can be effective in many chronic diseases such as CVD, T2D, and RA;[12] therefore, it is possible that reducing the level of inflammation and oxidative stress may ameliorate these diseases. One of the treatment options for chronic diseases is the use of traditional medicine and herbs, and it has been shown to be used in both prevention and treatment.[13] In general, the consumption of medicinal plants is increasing in different countries due to the evidence of the positive effects as well as the low side effects and availability of these plants.[14,15,16] Nigella sativa is one of the herbs that have recently been used to reduce inflammation and oxidative stress in various chronic diseases.[17]
만성 질환은 현재 백신으로 예방할 수 없거나 약물로 완전히 치료할 수 없고 치료 기간이 길며 신체에 신체적 변화를 일으키고 기능을 저하시키는 장기적인 질병으로 정의할 수 있습니다.[1] 미국 질병통제센터(CDC)의 정의에 따르면 심혈관 질환(CVD), 제2형 당뇨병(T2D), 류마티스 관절염(RA)은 전 세계적으로 흔한 만성 질환입니다. [1,2] CVD는 심장 및 혈관의 기능 장애와 관련이 있으며 관상동맥 심장 질환 및 고혈압과 같은 질환으로 구성됩니다.[3] 2025년까지 고혈압 및 CVD의 유병률은 전 세계 인구의 약 30%에 달할 것으로 추정되고 있습니다. [4,5,6] 제2형 당뇨병은 가장 흔한 당뇨병 유형으로 전체 당뇨병의 90%를 차지합니다.[7] 전 세계 제2형 당뇨병 환자 수는 1997년에 약 1억 2,500만 명으로 추정되며 2025년에는 3억 명에 이를 것으로 예상되며, 성인 유병률은 평균 8. 5%.[8,9] RA(류마티스 관절염)는 인체의 작은 관절에 영향을 미치는 자가면역성 만성 질환으로 인구의 약 1%가 앓고 있으며 일반적으로 중증 장애와 관련이 있습니다.[10] 미국 국립보건위원회(NHC) 보고서에 따르면 미국에서 매년 만성 질환으로 인한 비용 부담은 약 1조 달러에 달합니다. 7가지 흔한 만성 질환에 3조 달러, 현재 미국 전체 의료비 지출의 약 78%가 만성 질환에 지출되고 있으며 이러한 추세는 증가하고 있습니다.[11] 지속적인 산화 스트레스는 만성 염증을 유발하고 이러한 염증은 CVD(심혈관 질환), T2D(제2형 당뇨병), RA 등 많은 만성 질환에 영향을 미칠 수 있으며[12] 따라서 염증과 산화 스트레스 수준을 줄이면 이러한 질환을 개선할 수 있다는 것이 널리 알려져 있습니다. 만성 질환의 치료 옵션 중 하나는 전통 의학 및 허브의 사용이며 예방과 치료 모두에 사용되는 것으로 나타났습니다.[13] 일반적으로 약용 식물의 긍정적 인 효과와 낮은 부작용 및 가용성에 대한 증거로 인해 여러 국가에서 약용 식물의 소비가 증가하고 있습니다.[14,15,16] 니겔라 사티바는 최근 다양한 만성 질환에서 염증과 산화 스트레스를 줄이기 위해 사용되는 허브 중 하나입니다.
N. sativa is also known as black seed, black cumin, habbatus sauda, and black caraway seed. It is cultivated in countries such as India, Pakistan, and some parts of Iran. The plant is a local herb in southern Europe, North Africa, and Asia.[18,19,20,21] N. sativa, as a 1-year-old plant, has flowers whose stem is covered with very delicate fluff and grows to a height of 20–30 cm; this plant's flowers are solitary and pale blue or white with 5 petals, the fruits are shaped like a large capsule containing 3–7 follicles, and the seeds in each follicle are black in color and have a bitter, spicy flavor[22] [Figure 1].
N. 사티바는 블랙씨드, 블랙 커민, 하바투스 사우다, 블랙 캐러웨이 씨앗으로도 알려져 있습니다. 인도, 파키스탄 및 이란의 일부 지역에서 재배됩니다. 이 식물은 남부 유럽, 북아프리카 및 아시아의 지역 허브입니다.[18,19,20,21] N. sativa는 1년생 식물로 줄기가 매우 섬세한 보풀로 덮여 있고 높이가 20-30cm까지 자라는 꽃이 있으며,이 식물의 꽃은 단독으로 피고 옅은 파란색 또는 흰색이며 꽃잎이 5 개 있고 열매는 3-7 개의 난포가 들어있는 큰 캡슐 모양이며 각 난포의 씨앗은 검은 색이며 쓴맛이 있고 매운 맛이납니다[22] [그림 1] [그림 1].

Figure 1
Nigella sativa plant: Fruits, leaf, and flowers
그림 1
니겔라 사티바 식물: 과일, 잎, 꽃
N. sativa has been reported to contain more than 100 chemical compounds and has many reported therapeutic effects due to these compounds. N. sativa oil contains average, 35.6%–41.6% fat (constant oil), 22.7% protein, 32% carbohydrate, and 0.5%–1.6% essential fatty acid. The major fatty acid in this plant is linoleic acid (about 57.3% of fixed oil).[23,24] It also contains other compounds such as crude fiber, reducing sugars, mucilage, resin, alkaloids, sterols, tannins, flavonoids, saponins, minerals (such as Fe, zinc, Na, phosphorus, and calcium), and vitamins (C, B1, B3, B6, and B9 as water-soluble vitamins and A and E as a couple of fat-soluble vitamins).[24,25] The biological activity of N. sativa is attributed to the following proportions of forming components: volatile oils, such as thymoquinone (TQ) (30%–48%), P-cymene (7%–15%), carvacrol (6%–12%), 4-terpineol (2%–7%), trans-anethole (1%–4%), and sesquiterpene longifolene (1%–8%). A combination of four monoterpenes (d-limonene (carvone), carvone, pinene-α, and p-cymene), TQ, and its derivatives are the most pharmacologically active compounds.[24,26,27] TQ is not only a type of inhibitor for chemically reactive species containing oxygen such as superoxide and hydroxyl radicals but also inhibits leukotriene C4 and B4 production in humans and has anti-inflammatory effects.[27,28]
니겔라 사티바에는 100가지 이상의 화합물이 함유되어 있는 것으로 보고되었으며, 이러한 화합물로 인한 치료 효과에 대한 보고도 많습니다. 니겔라 사티바 오일은 평균 35.6%-41.6%의 지방(유지방), 22.7%의 단백질, 32%의 탄수화물, 0.5%-1.6%의 필수 지방산을 함유하고 있습니다. 이 식물의 주요 지방산은 리놀레산(고정유의 약 57.3%)입니다.[23,24] 또한 조섬유, 환원당, 점액질, 수지, 알칼로이드, 스테롤, 탄닌, 플라보노이드, 사포닌, 미네랄(Fe, 아연, Na, 인, 칼슘 등), 비타민(수용성 비타민인 C, B1, B3, B6, B9와 지용성 비타민인 A와 E) 등의 기타 화합물을 함유합니다. [24,25] N. sativa의 생물학적 활성은 티모퀴논(TQ)(30%-48%), P-시멘(7%-15%), 카르바크롤(6%-12%), 4-테르피네올(2%-7%), 트랜스-아네톨(1%-4%), 세스키테르펜 롱이폴렌(1%-8%) 등 휘발성 오일의 형성 비율에 기인합니다. 네 가지 모노테르펜(d-리모넨(카르본), 카르본, 피넨-α, p-시멘)의 조합인 TQ와 그 유도체는 가장 약리 활성도가 높은 화합물입니다.[24,26,27] TQ는 슈퍼옥사이드 및 하이드록실 라디칼과 같은 산소를 포함하는 화학적 반응성 종의 억제제일 뿐만 아니라 인체에서 류코트리엔 C4 및 B4 생성을 억제하고 항염 효과가 있습니다.[27,28]
Recent studies have shown that N. sativa can be helpful and effective in the prevention and treatment of some chronic diseases, such as asthma, liver and kidney disease, influenza, and gastrointestinal problems.[21,29] Previous studies reported that N. sativa was used as antihypertensive, liver tonics, diuretics, antidiarrheal, appetite stimulant, analgesics, digestive, antibacterial, and in skin disorders,[30] and also, its effects on neurological and mental illness, cardiovascular disorders, cancer, diabetes, and inflammatory conditions have been shown.[31] Effects of an aqueous extract from N. sativa on glucose tolerance and body weight in rats were studied by Meddan et al.[32] In a similar study, N. sativa was reported to reduce the risk of CVD in diabetic patients.[33] Some studies have also shown the anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects of N. sativa in RA.[34]
최근 연구에 따르면 천식, 간 및 신장 질환, 인플루엔자, 위장 문제와 같은 일부 만성 질환의 예방과 치료에 도움이 되고 효과적일 수 있다고 합니다[21,29] 이전 연구에서는 N. sativa는 항 고혈압제, 간 강장제, 이뇨제, 지사제, 식욕 자극제, 진통제, 소화제, 항균제 및 피부 질환에 사용되었으며[30] 신경 및 정신 질환, 심혈관 질환, 암, 당뇨병 및 염증 질환에 대한 효과도 나타났습니다. [31] 쥐의 포도당 내성과 체중에 대한 N. sativa 수성 추출물의 효과는 Meddan 등에 의해 연구되었습니다.[32] 유사한 연구에서 N. sativa는 당뇨병 환자의 CVD 위험을 줄이는 것으로 보고되었습니다.[33] 일부 연구에서는 RA에서 N. sativa의 항 염증 및 진통 효과도 보여주었습니다.[34]
Despite the effects of N. sativa on some chronic disease risk factors in previous studies, the exact mechanism of these effects has not been identified and the results of some studies have been inconsistent. Therefore, this study aims to review the possible molecular and cellular effects of N. sativa on inflammation, oxidative stress, and other related risk factors of chronic diseases (CVD, T2D, and RA).
이전 연구에서 일부 만성 질환 위험 인자에 대한 N. sativa의 효과에도 불구하고 이러한 효과의 정확한 메커니즘은 밝혀지지 않았으며 일부 연구 결과는 일관되지 않았습니다. 따라서 본 연구에서는 염증, 산화 스트레스 및 기타 만성 질환(CVD, T2D 및 RA)의 관련 위험 요인에 대한 N. sativa의 가능한 분자 및 세포 효과를 검토하는 것을 목표로 합니다.
SEARCH STRATEGY (검색 전략)
Laboratory animal studies
실험실 동물 연구
Three doses of hydroalcoholic extract of N. sativa (200, 400, and 600 mg/kg) were injected intraperitoneally in hypertensive rats showed a protective effect on blood pressure (BP) after 30 min of injection that was induced by TQ and its effects on angiotensin II.[35] In another study, improvements of cardiovascular risk factors including body weight, red blood cell and white blood cell, lipid profile (triglyceride [TG], low-density lipoprotein [LDL], and high-density lipoprotein [HDL]) and immune response (IgM and IgG), total antioxidant capacity, and malondialdehyde (MDA) after 8-week supplementation with N. sativa seed at doses of 300 and 600 g/kg in rabbits were proved.[36] This effect was dose dependent. The cardioprotective effects of N. sativa are summarized in Table 1.
고혈압 쥐에 세 가지 용량의 하이드로알코올 추출물(200, 400, 600 mg/kg)을 복강 내 주사한 결과, 주사 30분 후 혈압(BP)에 대한 보호 효과가 나타났으며, 이는 TQ에 의해 유도된 혈압과 안지오텐신 II에 미치는 영향에 대한 보호 효과가 있었습니다. [35] 또 다른 연구에서는 체중, 적혈구 및 백혈구, 지질 프로필(트리글리세라이드[TG], 저밀도 지단백질[LDL], 고밀도 지단백질[HDL]), 면역 반응(IgM 및 IgG), 총 항산화 능력, 말론디알데히드(MDA) 등 심혈관 위험 요인이 8주 동안 N. 사티바 씨앗을 토끼에게 300 및 600g/kg 용량으로 8주 동안 보충한 결과[36] 이 효과는 용량에 따라 달라졌습니다. N. sativa의 심장 보호 효과는 표 1에 요약되어 있습니다.
Table 1
Effects of Nigella sativa on cardiovascular, diabetes, and rheumatoid arthritis risk factors in experimental studies
|
Author (year)
|
Country (reference number)
|
n
|
Type and dose of N.S administered
|
Duration
|
Outcome measures
|
|
Enayatfard et al. (2019)[35]
|
Iran
|
21 hypertensive rats
|
200, 400, and 600 mg/kg N.S
|
Once injection
|
Dose-dependent reduction in systolic blood pressure, mean arterial pressure, and heart rate
|
|
El-Gindy et al. (2019)[36]
|
Egypt
|
54 growing V-line unsexed rabbits
|
300 or 600 mg of N.S seed/kg
|
8 weeks
|
Significantly improved body weight, ↑RBCs and WBCs ↑IgG and IgM immune responses, ↓ serum total lipids, TG, LDL, and MDA, and ↑HDL and total antioxidant capacity.
|
|
Ahmed and Hassanein (2013)[94]
|
Egypt
|
45 Albino rats
|
N.S oil (4 ml/kg) orally
|
Once administration
|
↓heart rate, ST-segment change, pro-inflammatory cytokines, oxidative stress, and cardiac tissue damage
|
|
Randhawa (2013)[95]
|
India
|
16 Wistar albino rats
|
0.2 ml/kg/day, intraperitoneally
|
6 weeks
|
↓blood pressure, oxidative injury, improved left ventricular function
|
|
Babaei Bonab and Tofighi (2019)[96]
|
Iran
|
35 male Wistar rats with T2M
|
400mg/kg/day
|
8 weeks
|
Improvement in lipid profile (LDL, HDL, TC, and TG), FBG, HbA1c, and insulin resistance
|
|
Ahmad and Alkreathy (2018)[97]
|
Saudi Arabia
|
48 male Albino Wistar rats
|
2 ml/kg, p.o
|
7 days
|
Improvement in lipid profile (TC, LDL, HDL, and TG)
|
|
Muneera et al. (2015)[98]
|
Pakistan
|
30 Sprague Dawley rats
|
1000mg/kg/day
|
6 weeks
|
Improvement in the lipid profile of rats
|
|
Al-Hader et al. (1993)[99]
|
Jordan
|
Diabetic rabbits
|
50 mg/kg volatile oil extract of N.S
|
2, 4, and 6 h
|
Showed significant decreases in FBG levels
|
|
Meral et al. (2001)[44]
|
Turkey
|
15 New Zealand male rabbits
|
20 ml/kg aqueous extract of N.S
|
2 months
|
↑GSH and ceruloplasmin concentrations
↓MDA and glucose levels |
|
El-Dakhakhny et al. (2002)[54]
|
Egypt
|
Diabetic rats
|
0.4g/kg N.S oil
|
2, 4, and 6 weeks
|
↓blood glucose concentration
|
|
Kanter et al. (2003)[59]
|
Turkey
|
46 male Wistar rats
|
0.2 ml/kg/day volatile oil of N.S
|
4 weeks
|
↓GSH, glucose level, and serum NO ↑Insulin level
|
|
Fararh et al. (2004)[74]
|
Japan
|
Male Syrian hamsters
|
400 mg/kg body weight/day of N.S oil
|
4 weeks
|
↓total glycated hemoglobin
|
|
Rchid et al. (2004)[61]
|
-
|
Rat pancreatic cells
|
0.01, 0.1, 1, and 5 mg/ml whole, basic, and acidic subfractions of N.S
|
30 min
|
A significant stimulatory effect on insulin release has been observed
|
|
Mansi et al. (2005)[55]
|
Jordan
|
Diabetic rats
|
20 ml/kg/day aqueous extract of N.S
|
15 days
|
↑Insulin level and ↓Glucose level
|
|
Mansi (2006)[100]
|
Jordan
|
Diabetic rats
|
20 ml/kg aqueous extract of N.S
|
3 weeks
|
↑Insulin level
|
|
Kaleem et al. (2006)[101]
|
India
|
Wister rats
|
300 mg/kg/day ethanol extract of N.S
|
4 weeks
|
↑Catalase, SOD and insulin levels ↓Lipid peroxidation, GPX and glutathione ↓Body weight
|
|
Houcher et al. (2007)[56]
|
Algeria
|
Diabetic rats
|
810 mg/kg/day 2.5 ml/kg/day methanol extract of N.S and N.S oil
|
25 days
|
↓Glucose level
↑TAC |
|
Kanter (2008)[58]
|
Turkey
|
diabetic rats
|
N.S in a dose of 400 mg/kg body weight and TQ 50 mg/kg body weight once a day
|
12 weeks
|
↓Serum glucose
|
|
AL-Logmani (2009)[102]
|
Saudi Arabia
|
40 diabetic male Wistar rats
|
N.S oil
|
3 weeks
|
↓Blood glucose
|
|
Meddah et al. (2009)[59]
|
Morocco
|
Rat jejunum
|
In vitro: 0.1 pg/ml to 100 ng/ml
In vivo: 2g/kg |
6 weeks
|
In vivo: glucose tolerance and body weight improvement
In vitro: inhibition of glucose absorption |
|
Benhaddou-Andaloussi et al. (2010)[103]
|
Morocco
|
C2C12 skeletal muscle cells and 3T3-L1 adiposities
|
Ethanol extract of N.S
|
18 h
|
↑Glucose uptake in skeletal cells and adiposities
|
|
Fararh et al. (2010)[53]
|
Egypt
|
Diabetic rats
|
50 mg/kg/day TQ
|
20 days
|
↓ Plasma glucose, TC, TG
↑ Insulin concentration |
|
Abdelmeguid et al. (2010)[62]
|
Egypt
|
Diabetic rats
|
2 mL⁄kg, i.p., 5% N. S
Extract 0.2 mL⁄kg, i.p, N.S oil, or 3 mg⁄mL, i.p., TQ |
30 days
|
↓ glucose and improve serum insulin levels
|
|
Salama (2011)[52]
|
Saudi Arabia
|
Diabetic rats
|
500 mg/kg N.S oil
|
4 weeks
|
↓Glucose concentration
↑insulin, c-peptide, and TAC |
|
Al-Logmani and Zari (2011)[104]
|
Saudi Arabia
|
Diabetic Wistar rats
|
Diet containing 5% N.S oil
|
7 weeks
|
N. sativa oil decreased blood glucose levels
|
|
Alimohammadi et al. (2013)[105]
|
Iran
|
Diabetic rats
|
5, 10, and 20 mg/kg hydroalcoholic N.S extract
|
32 days
|
5 mg/kg: ↓FBS
↑Insulin secretion |
|
Mohamed et al. (2015)[51]
|
Saudi Arabia
|
Nonalcoholic fatty liver in obese diabetic albino rats
|
100mg/kg aqueous extract of N.S seed
|
4 weeks
|
↓FBS
↓TG, TC |
|
Asaduzzaman et al. (2015)[106]
|
Bangladesh
|
Diabetic rats
|
300 mg/kg body weight of ethanol extract of N.S
|
28 days
|
↓TG, TC, LDL, and FBG
↑HDL |
|
Al-Trad et al. (2016)[107]
|
Jordan
|
Experimental diabetic rats
|
50 mg/kg TQ and 2 mL/kg N.S oil
|
10 weeks
|
N.S oil or TQ significantly reduced blood glucose level compared with that in untreated diabetic rats
|
|
Umar et al. (2012)[75]
|
India
|
Three groups of six Wistar albino rats each with collagen-induced arthritis
|
5 mg/ kg TQ PO
|
21 days
|
↓ IL-1β, IL-6, TNF-α, IFN- γ, PGE2, articular elastase, myeloperoxidase, lipoxygenase, and NO
↑IL-10, SOD, GPX, and catalase |
|
Vaillancourt et al. (2011)[76]
|
Canada
|
24 female Lewis rats with lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced arthritis
|
5 mg/ kg TQ PO
|
7 days
|
↓ LPS-induced IL-1β, TNF-α, MMP-13, Cox-2, and PGE2
|
|
Tekeoglu et al. (2006)[108]
|
Turkey
|
Five groups of seven Wistar albino rats each with collagen-induced arthritis
|
2.5 mg/kg and 5 mg/kg TQ PO
|
7 days
|
↓ TNF-α and IL-1β
|
|
Mohamed et al. (2003)[109]
|
Canada
|
24 mice with inducing inflammation
|
1 mg/kg TQ iv
|
5 days and 12 days
|
Mice received TQ at day 12: Higher levels of GSH
Significant reduction of symptoms of inflammation |
|
Faisal et al. (2015)[110]
|
Pakistan
|
32 rats with collagen-induced arthritis
|
2mg/kg/day TQ by i.p injection
|
15 days
|
↓ in clinical score of inflammation and differentiation leucocyte counts
|
|
Zhong (2017)
|
China
|
60 rabbit osteoarthritis model
|
1mg/kg/day TQ by intra-articular injection
|
9 weeks
|
↓ in MMP-13 mRNA and cartilage lesions
|
|
Chen et al. (2010)[111]
|
China
|
20 rabbit osteoarthritis model
|
10 µmol/L TQ
intra-articular injection |
4 weeks
|
Inhibited NF-kB p65
↓ IL-1β Suppressed the MMP-1, MMP-3, and MMP-13 gene expression |
.S=Nigella sativa; TQ=thymoquinone; i.p=intraperitoneal; RBC=Red blood cells; WBC=White blood cells; TG=Triglyceride; TC=Total cholesterol; LDL=Low-density lipoprotein; HDL=High-density lipoprotein; MDA=Malondialdehyde; IgG=Immunoglobulin G; IgM=Immunoglobulin M; FBG=Fasting blood glucose; HbA1C=Glycated hemoglobin; IL-1β=Interleukin-1 beta; IL-6=Interleukin-6; TNF-α=Tumor necrosis factor-alpha; IFN- γ=Interferon-gamma; PGE2=Prostaglandin E2; GSH=Glutathione; NO=Nitric oxide, GPX=Glutathione peroxidase; TAC=Total antioxidant capacity; IL-10=Interleukin-10; LPS=Lipopolysaccharide; MMP=Matrix metalloproteinase; Cox-2=Cyclooxygenase 2; NFkB= Nuclear factor-κB
표 1
실험 연구에서 Nigella sativa 가 심혈관, 당뇨병 및 류마티스 관절염 위험 요인에 미치는 영향
|
저자(연도)
|
국가(참조번호)
|
N
|
투여되는 NS의 종류와 용량
|
지속
|
결과 측정
|
|
Enayatfardet al . (2019)[ 35 ]
|
이란
|
고혈압 쥐 21마리
|
200, 400, 600mg/kg NS
|
한번 주사하면
|
수축기 혈압, 평균 동맥압, 심박수의 용량 의존적 감소
|
|
El-Gindyet al . (2019)[ 36 ]
|
이집트
|
V라인 성별이 없는 토끼 54마리 키우기
|
NS 종자 300 또는 600mg/kg
|
8주
|
체중, ↑RBC 및 WBC ↑IgG 및 IgM 면역 반응, ↓ 혈청 총 지질, TG, LDL 및 MDA, ↑HDL 및 총 항산화 능력이 크게 향상되었습니다.
|
|
아흐메드와 하사네인(2013)[ 94 ]
|
이집트
|
알비노 쥐 45마리
|
NS 오일(4ml/kg) 경구 섭취
|
한번 투여
|
↓심박수, ST분절 변화, 염증성 사이토카인, 산화 스트레스, 심장 조직 손상
|
|
란다와(2013)[ 95 ]
|
인도
|
위스타 알비노 쥐 16마리
|
0.2 ml/kg/일, 복강내
|
6주
|
↓혈압, 산화 손상, 좌심실 기능 개선
|
|
바바이 보나브와 토피기(2019)[ 96 ]
|
이란
|
T2M을 사용하는 수컷 Wistar 쥐 35마리
|
400mg/kg/일
|
8주
|
지질 프로필(LDL, HDL, TC 및 TG), FBG, HbA1c 및 인슐린 저항성 개선
|
|
아마드와 알크리시(2018)[ 97 ]
|
사우디 아라비아
|
수컷 알비노 위스타 쥐 48마리
|
2ml/kg, 포
|
7 일
|
지질 프로필(TC, LDL, HDL, TG) 개선
|
|
Muneeraet al . (2015)[ 98 ]
|
파키스탄
|
스프라그 다울리 쥐 30마리
|
1000mg/kg/일
|
6주
|
쥐의 지질 프로필 개선
|
|
Al-Haderet al . (1993)[ 99 ]
|
요르단
|
당뇨병 토끼
|
NS의 휘발성 오일 추출물 50mg/kg
|
2, 4, 6시간
|
FBG 수준이 크게 감소한 것으로 나타났습니다.
|
|
Meralet al . (2001)[ 44 ]
|
터키
|
뉴질랜드 수컷 토끼 15마리
|
NS수성추출물 20ml/kg
|
2 개월
|
↑GSH 및 세룰로플라스민 농도
↓MDA 및 포도당 수치 |
|
El-Dakhakhnyet al . (2002)[ 54 ]
|
이집트
|
당뇨병 쥐
|
0.4g/kg NS 오일
|
2주, 4주, 6주
|
↓혈당 농도
|
|
Kanteret al . (2003)[ 59 ]
|
터키
|
수컷 Wistar 쥐 46마리
|
NS의 0.2 ml/kg/일 휘발성 오일
|
4 주
|
↓GSH, 포도당 수치, 혈청 NO ↑인슐린 수치
|
|
Fararhet al . (2004)[ 74 ]
|
일본
|
수컷 시리아 햄스터
|
NS 오일 400 mg/kg 체중/일
|
4 주
|
↓총당화혈색소
|
|
Rchidet al . (2004)[ 61 ]
|
-
|
쥐 췌장 세포
|
NS의 0.01, 0.1, 1 및 5mg/ml 전체, 염기성 및 산성 소분획
|
30 분
|
인슐린 방출에 대한 상당한 자극 효과가 관찰되었습니다.
|
|
Mansiet al . (2005)[ 55 ]
|
요르단
|
당뇨병 쥐
|
NS수성추출물 20ml/kg/일
|
15 일
|
↑인슐린 수치 및 ↓포도당 수치
|
|
만시(2006)[ 100 ]
|
요르단
|
당뇨병 쥐
|
NS수성추출물 20ml/kg
|
3 주
|
↑인슐린 수치
|
|
Kaleemet al . (2006)[ 101 ]
|
인도
|
등나무쥐
|
NS의 에탄올 추출물 300 mg/kg/day
|
4 주
|
↑카탈라아제, SOD 및 인슐린 수치 ↓지질 과산화, GPX 및 글루타티온 ↓체중
|
|
Houcheret al . (2007)[ 56 ]
|
알제리
|
당뇨병 쥐
|
810 mg/kg/day NS 및 NS 오일의 메탄올 추출물 2.5 ml/kg/day
|
25일
|
↓포도당 수치
↑TAC |
|
칸터(2008)[ 58 ]
|
터키
|
당뇨병 쥐
|
NS는 체중 kg당 400mg, TQ는 체중 kg당 50mg을 1일 1회 투여합니다.
|
12주
|
↓혈청 포도당
|
|
AL-로그마니(2009)[ 102 ]
|
사우디 아라비아
|
당뇨병이 있는 수컷 Wistar 쥐 40마리
|
NS 오일
|
3 주
|
↓혈당
|
|
Meddahet al . (2009)[ 59 ]
|
모로코
|
쥐 공장
|
시험관 내 : 0.1 pg/ml ~ 100 ng/ml
생체 내 : 2g/kg |
6주
|
In vivo : 당내성 및 체중 개선
In vitro : 포도당 흡수 억제 |
|
Benhaddou-Andaloussiet al . (2010)[ 103 ]
|
모로코
|
C2C12 골격근 세포 및 3T3-L1 지방과다증
|
NS의 에탄올 추출물
|
18시간
|
↑골격세포 및 지방과다증의 포도당 흡수
|
|
Fararhet al . (2010)[ 53 ]
|
이집트
|
당뇨병 쥐
|
50mg/kg/일 TQ
|
20 일
|
↓ 혈장 포도당, TC, TG
↑ 인슐린 농도 |
|
Abdelmeguidet al . (2010)[ 62 ]
|
이집트
|
당뇨병 쥐
|
2 mL⁄kg, ip, 5% N. S
추출물 0.2 mL⁄kg, ip, NS 오일 또는 3 mg⁄mL, ip, TQ |
30 일
|
↓ 혈당 및 혈청 인슐린 수치 개선
|
|
살라마 (2011)[ 52 ]
|
사우디 아라비아
|
당뇨병 쥐
|
500mg/kg NS 오일
|
4 주
|
↓포도당 농도
↑인슐린, c-펩타이드, TAC |
|
알 로그마니와 자리(2011)[ 104 ]
|
사우디 아라비아
|
당뇨병에 걸린 Wistar 쥐
|
5% NS 오일을 함유한 다이어트
|
7주
|
N. 사티 바 오일은 혈당 수치를 감소시켰습니다
|
|
Alimohammadiet al . (2013)[ 105 ]
|
이란
|
당뇨병 쥐
|
5, 10 및 20mg/kg 하이드로알코올성 NS 추출물
|
32일
|
5mg/kg: ↓FBS
↑인슐린 분비 |
|
Mohamedet al . (2015)[ 51 ]
|
사우디 아라비아
|
비만 당뇨병 흰둥이 쥐의 비알코올성 지방간
|
NS 종자 수추출물 100mg/kg
|
4 주
|
↓FBS
↓TG, TC |
|
Asaduzzamanet al . (2015)[ 106 ]
|
방글라데시
|
당뇨병 쥐
|
NS의 에탄올 추출물 300 mg/kg 체중
|
28일
|
↓TG, TC, LDL 및 FBG
↑HDL |
|
Al-Tradet al . (2016)[ 107 ]
|
요르단
|
실험용 당뇨병 쥐
|
50mg/kg TQ 및 2mL/kg NS 오일
|
10주
|
NS 오일 또는 TQ는 치료받지 않은 당뇨병 쥐의 혈당 수치와 비교하여 혈당 수치를 크게 감소시켰습니다.
|
|
Umaret al . (2012)[ 75 ]
|
인도
|
콜라겐 유발 관절염을 앓고 있는 Wistar 알비노 쥐 6마리로 구성된 세 그룹
|
5mg/kg TQPO
|
21일
|
↓ IL-1β, IL-6, TNF-α, IFN-γ, PGE2, 관절 엘라스타제, 골수과산화효소, 리폭시게나제 및 NO ↑
IL-10, SOD, GPX 및 카탈라제 |
|
Vaillancourtet al . (2011)[ 76 ]
|
캐나다
|
지질다당류(LPS) 유발 관절염이 있는 24마리의 암컷 Lewis 쥐
|
5mg/kg TQPO
|
7 일
|
↓ LPS로 유도된 IL-1β, TNF-α, MMP-13, Cox-2, PGE2
|
|
Tekeogluet al . (2006)[ 108 ]
|
터키
|
콜라겐 유발 관절염을 앓고 있는 Wistar 알비노 쥐 7마리로 구성된 5개 그룹
|
2.5mg/kg 및 5mg/kg TQ PO
|
7 일
|
↓ TNF-α와 IL-1β
|
|
Mohamedet al . (2003)[ 109 ]
|
캐나다
|
염증을 유발한 쥐 24마리
|
1mg/kg TQ iv
|
5일과 12일
|
12일차에 TQ를 받은 마우스: 더 높은 수준의 GSH
염증 증상의 현저한 감소 |
|
Faisalet al . (2015)[ 110 ]
|
파키스탄
|
콜라겐 유발 관절염이 있는 쥐 32마리
|
IP 주사에 의한 2mg/kg/day TQ
|
15 일
|
↓ 염증 및 분화 백혈구 수의 임상 점수에서
|
|
종 (2017)
|
중국
|
60 토끼 골관절염 모델
|
관절내 주사로 1mg/kg/day TQ
|
9주
|
↓ MMP-13 mRNA 및 연골 병변에서
|
|
Chenet al . (2010)[ 111 ]
|
중국
|
20 토끼 골관절염 모델
|
10 µmol/L TQ
관절내 주사 |
4 주
|
NF-kB p65 억제
↓ IL-1β MMP-1, MMP-3, MMP-13 유전자 발현 억제 |
NS= 니겔라 사티바 ; TQ=티모퀴논; ip=복강내; RBC=적혈구; WBC=백혈구; TG=트리글리세리드; TC=총 콜레스테롤; LDL=저밀도 지단백질; HDL=고밀도 지단백질; MDA=말론디알데히드; IgG=면역글로불린 G; IgM=면역글로불린 M; FBG=공복 혈당; HbA1C=당화혈색소; IL-1β=인터루킨-1 베타; IL-6=인터루킨-6; TNF-α=종양괴사인자-알파; IFN-γ=인터페론-감마; PGE2=프로스타글란딘 E2; GSH=글루타티온; NO=산화질소, GPX=글루타티온 퍼옥시다제; TAC=총 항산화 능력; IL-10=인터루킨-10; LPS=지질다당류; MMP=매트릭스 메탈로프로테이나제; Cox-2=사이클로옥시게나제 2; NFkB= 핵인자-κB
Clinical studies (임상 연구)
Clinical trials in human subjects showed similar results. Sabzghabaee et al.[37] have reported that 2 g/d N. sativa for 4 weeks in hyperlipidemic patients significantly reduced total cholesterol (TC), TG, and LDL compared to control group [Table 2]. Furthermore, 500 mg/d N. sativa in metabolic syndrome patients decreased systolic and diastolic BP and LDL-cholesterol (LDL-C) compared to control group.[38]
인간을 대상으로 한 임상 시험에서도 비슷한 결과가 나타났습니다. Sabzghabaee 등[37]은 고지혈증 환자에게 4주간 2g/d N. sativa를 투여한 결과, 대조군에 비해 총 콜레스테롤(TC), TG 및 LDL이 유의하게 감소했다고 보고했습니다[표 2]. 또한 대사증후군 환자에게 500 mg/d N. sativa를 투여하면 대조군에 비해 수축기 및 이완기 혈압과 LDL-콜레스테롤(LDL-C)이 감소했습니다[38].
Table 2
Effects of Nigella sativa on cardiovascular, diabetes, and rheumatoid arthritis risk factors in clinical trial studies
|
Cardiovascular risk factors
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Author (year)
|
Country (reference number)
|
Study design (sex)
|
Participant numbers
|
Type and dose of N.S administered
|
Duration (mean age of subjects)
|
Outcome measures
|
|
Darand et al. (2019)[112]
|
Iran
|
RCT (male/female)
|
50 patients with NAFLD
|
2 g/day
|
12 weeks
|
↓serum glucose and serum insulin
↑quantitative insulin sensitivity |
|
Sabzghabaee et al. (2012)[37]
|
Iran
|
RCT (male/female)
|
88 Hyperlipidemia patients
|
2 g/d (capsule contained N.S crushed seeds)
|
4 weeks
|
↓TC, TG, and LDL, no significant difference in HDL, FBG
|
|
Dehkordi and Kamkhah (2008)[113]
|
Iran
|
RCT (male/female)
|
Patients with mild hypertension
|
Two test groups received 100 and 200 mg of N.S extract twice a day
|
8 weeks
|
Significant dose-dependent decline in the levels of TC, TG, LDL, systolic and diastolic blood pressure
|
|
Najimi et al. (2013)[38]
|
India
|
Open labeled RCT (male/female)
|
90 patients of metabolic syndrome
|
500 mg capsule of N.S per day
|
8 weeks
|
Significant improvement with reference to systolic and diastolic blood pressure and LDL-cholesterol, no significant difference in HDL, TG
|
|
Ibrahim et al. (2014)[114]
|
Malaysia
|
RCT (female)
|
37 hyperlipidemic menopausal women
|
500 mg capsule of N.S per day
|
2 months
|
↓ TC, LDL and TG, and increased HDL and FBG. No significant difference in diastolic and systolic blood pressure
|
|
Tasawar et al. (2011)[115]
|
Pakistan
|
RCT (male/female)
|
80 patients with coronary artery diseases
|
500 mg capsule of N.S per day
|
6 months
|
↓TC, LDL, VLDL, and TG
↑HDL-C |
|
Bamosa et al. (1997)[116]
|
Saudi Arabia
|
CT (male)
|
16 male adolescents
|
2 capsules of 500 mg N.S twice daily
|
2 weeks
|
↓ glucose
No significant difference for TG change |
|
Farzaneh et al. (2014)[117]
|
Iran
|
RCT (female)
|
20 sedentary overweight females
|
3 capsules of 500 mg N.S daily
|
8 weeks
|
↓TC, LDL, TG, and body mass index, and ↑HDL-C
|
|
Najimi et al. (2008)[118]
|
India
|
CT (male/female)
|
60 patients of metabolic syndrome
|
N.S oil 2.5 ml twice daily
|
6 weeks
|
↑TC, LDL, FBG
No effect on TG, HDL, postprandial glucose, body weight, BMI, and waist circumference |
|
Mahdavi et al. (2015)[119]
|
Iran
|
RCT (female)
|
90 obese women
|
3 g per day (1 g before each meal) N.S oil
|
8 weeks
|
↓VLD, TG, and BMI
No effect on HDL, TC, and LDL |
|
Rashidmayvan et al. (2019)[66]
|
Iran
|
RCT (male/female)
|
44 patients with NAFLD
|
N.S oil
|
8 weeks
|
↓FBS, TG, TC, LDL, VLDL, AST and ALT, hs-CRP, IL-6, TNF-α
↑HDL-C N.S oil had no significant effect on serum levels of insulin, blood pressure, and GGT |
|
Pelegrin et al. (2019)[69]
|
France
|
Pilot RCT (male)
|
30 healthy male volunteers
|
N.S powder (1 g/day)
|
4 weeks
|
↓TC, LDL
|
|
Farhangi et al. (2018)[120]
|
Iran
|
RCT (male/female)
|
40 patients with Hashimoto’s thyroiditis
|
2 g N.S powder per day
|
8 weeks
|
↓ BMI, LDL, and TG
↑ HDL |
|
Bhatti et al. (2016)[121]
|
Pakistan
|
CT (male/female)
|
60 hyperlipidemic smokers
|
1 g of N.S (kalonji) seed
|
30 days
|
↓TC, LDL, and TG, ↑ HDL
|
|
|
||||||
|
Diabetes risk factors
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Bamosa et al. (2010)[64]
|
Saudi Arabia
|
RCT (male/female)
|
94 patients with T2D
|
Capsules containing N.S (1, 2, and 3 g/day)
|
12 weeks
|
↓ FBS, 2hPG, and HbA1c
|
|
Kaatabi et al. (2012)[122]
|
Saudi Arabia
|
94 diabetic patients
|
CT (F)
|
1, 2, and 3 g/day of powdered N.S
|
12 weeks
|
1gr: ↑HDL-C
2gr: ↑ HDL; ↓TC, TG, and LDL-C; 3gr: ↑HDL; ↓ TC, TG, and LDL-C |
|
Hosseini et al. (2013)[123]
|
Iran
|
RCT (male/female)
|
70 patients with T2D
|
5 ml/day N.S oil
|
12 weeks
|
↓FBS, 2hPG, BMI
|
|
Mirmiran et al. (2015)[68]
|
Iran
|
RCT (male/female)
|
43 patients with T2D
|
1000 mg extract of black seed oil
|
8 weeks
|
↓FBS, LDL, total cholesterol, and LDL/HDL
|
|
Heshmati et al. (2015)[124]
|
Iran
|
RCT (male/female)
|
72 patients with
|
3 g/day N.S oil or soft gel capsules
|
12 weeks
|
↓FBS, HbA1c, ↓LDL-C, and TG
|
|
Farhangi et al. (2018)[120]
|
Iran
|
RCT
male/female) |
40 patients with Hashimoto’s thyroiditis
|
2 g N.S powder per day
|
8 weeks
|
↓BMI
↑HDL ↓Serum concentrations of LDL and tri-TG |
|
Rashidmayvan et al. (2019)[66]
|
Iran
|
RCT
(male/female) |
44 patients with NAFLD
|
1000 mg N.S oil per day
|
8 weeks
|
↓ FBS level
↓TG, TC, LDL, VLDL ↑ HDL |
|
Pelegrin et al. (2019)[69]
|
France
|
Pilot RCT (male)
|
30 healthy male volunteers
|
N.S powder (1 g/day)
|
4-weeks
|
Ineffective on glucose-induced insulin secretion and insulin sensitivity
|
|
|
||||||
|
Rheumatoid arthritis risk factors
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Hadi et al. (2016)[77]
|
Iran
|
RCT (female)
|
45 patients with rheumatoid arthritis
|
two capsules 500 mg/day N.S oil
|
8 weeks
|
↓ MDA, NO
↑ Serum level of IL-10 |
|
Kheirouri et al. (2016)[91]
|
Iran
|
RCT (female)
|
45 patients with rheumatoid arthritis
|
two capsules 500 mg/day N.S oil
|
8 weeks
|
↓ hs-CRP level, cytotoxic T-cells (CD8+), DAS-28 score, and an improved number of swollen joints.
↓ Serum level of CD4+ T-cell percentage, T regulatory cell percentage (CD4+CD25+ T-cell) and CD4+/CD8+ ratio |
|
Gheita and Kenawy (2012)[78]
|
Egypt
|
RCT (female)
|
40 patients with rheumatoid arthritis
|
Two capsules 500 mg/day N.S oil
|
4 weeks
|
↓DAS-28, joint inflammation, and morning stiffness
|
|
Kooshki et al. (2016)[125]
|
Iran
|
RCT (male/female)
|
40 elderly patients with knee osteoarthritis
|
Topical application of 3cc N.S oil on knee
|
3 weeks
|
Pain reduction in the black seed group was greater than that of the acetaminophen group
|
N.S=Nigella sativa; RCT=Randomized controlled trial; TG=Triglyceride; TC=Total cholesterol; LDL=Low-density lipoprotein; HDL=High-density lipoprotein; VLDL=Very-lowdensity lipoprotein; FBG=Fasting blood glucose; BMI=Body mass index; AST=Aspartate aminotransferase; ALT=Alanine aminotransferase; GGT=Gamma-glutamyltransferase; hs-CRP; high-sensitive C-reactive protein; IL-6=Interleukin-6; TNF-α=Tumor necrosis factor-α; T2D=Type 2 diabetes; FBS=Fasting blood sugar; 2hPG=2-h postprandially glucose; HbA1c=Glycosylated hemoglobin; NAFLD=Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease; MDA=Malondialdehyde; NO=Nitric oxide; DAS-28=Disease Activity Score-28
표 2
임상 시험 연구에서 Nigella sativa가 심혈관, 당뇨병 및 류마티스 관절염 위험 요인에 미치는 영향
|
심혈관 위험 요인
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
저자(연도)
|
국가(참조번호)
|
연구 설계(성별)
|
참가자 수
|
투여되는 NS의 종류와 용량
|
기간(피험자의 평균 연령)
|
결과 측정
|
|
Darandet al . (2019)[ 112 ]
|
이란
|
RCT(남성/여성)
|
NAFLD 환자 50명
|
2g/일
|
12주
|
↓혈청 포도당 및 혈청 인슐린
↑정량적 인슐린 민감도 |
|
Sabzghabaeeet al . (2012)[ 37 ]
|
이란
|
RCT(남성/여성)
|
88 고지혈증 환자
|
2 g/d (NS 분쇄 씨앗이 함유된 캡슐)
|
4 주
|
↓TC, TG, LDL, HDL, FBG에는 큰 차이 없음
|
|
데코르디와 캄카(2008)[ 113 ]
|
이란
|
RCT(남성/여성)
|
경증 고혈압 환자
|
두 테스트 그룹에는 NS 추출물 100mg과 200mg을 하루에 두 번씩 투여받았습니다.
|
8주
|
TC, TG, LDL, 수축기 및 확장기 혈압 수준의 현저한 용량 의존적 감소
|
|
Najimiet al . (2013)[ 38 ]
|
인도
|
공개 라벨 RCT(남성/여성)
|
대사증후군 환자 90명
|
하루에 NS 500mg 캡슐
|
8주
|
수축기 혈압과 확장기 혈압, LDL-콜레스테롤을 기준으로 상당한 개선, HDL, TG는 큰 차이 없음
|
|
Ibrahimet al . (2014)[ 114 ]
|
말레이시아
|
RCT(여)
|
고지혈증 갱년기 여성 37명
|
하루에 NS 500mg 캡슐
|
2 개월
|
↓ TC, LDL 및 TG, HDL 및 FBG 증가. 이완기 혈압과 수축기 혈압에는 큰 차이가 없습니다.
|
|
Tasawaret al . (2011)[ 115 ]
|
파키스탄
|
RCT(남성/여성)
|
관상동맥질환 환자 80명
|
하루에 NS 500mg 캡슐
|
6 개월
|
↓TC, LDL, VLDL, TG
↑HDL-C |
|
Bamosaet al . (1997)[ 116 ]
|
사우디 아라비아
|
CT(남)
|
남자 청소년 16명
|
1일 2회 500mg NS 2캡슐
|
이주
|
↓ 포도당
TG 변화에 유의미한 차이 없음 |
|
Farzanehet al . (2014)[ 117 ]
|
이란
|
RCT(여)
|
앉아서 생활하는 과체중 여성 20명
|
매일 500mg NS 캡슐 3개
|
8주
|
↓TC, LDL, TG, 체질량지수, ↑HDL-C
|
|
Najimiet al . (2008)[ 118 ]
|
인도
|
CT(남성/여성)
|
대사증후군 환자 60명
|
NS 오일 2.5ml 하루 2회
|
6주
|
↑TC, LDL, FBG
TG, HDL, 식후 혈당, 체중, BMI, 허리둘레에는 영향 없음 |
|
Mahdaviet al . (2015)[ 119 ]
|
이란
|
RCT(여)
|
90명의 비만 여성
|
1일 3g(매 식사 전 1g) NS 오일
|
8주
|
↓VLD, TG, BMI
HDL, TC, LDL에는 영향 없음 |
|
Rashidmayvanet al . (2019)[ 66 ]
|
이란
|
RCT(남성/여성)
|
NAFLD 환자 44명
|
NS 오일
|
8주
|
↓FBS, TG, TC, LDL, VLDL, AST 및 ALT, hs-CRP, IL-6, TNF-α
↑HDL-C N.S 오일은 혈청 인슐린 수치, 혈압 및 GGT에 큰 영향을 미치지 않았습니다. |
|
Pelegrinet al . (2019)[ 69 ]
|
프랑스
|
파일럿 RCT(남)
|
건강한 남성 자원봉사자 30명
|
NS분말(1g/일)
|
4 주
|
↓TC, LDL
|
|
Farhangiet al . (2018)[ 120 ]
|
이란
|
RCT(남성/여성)
|
하시모토 갑상선염 환자 40명
|
하루 2g NS 파우더
|
8주
|
↓ BMI, LDL, TG
↑ HDL |
|
Bhattiet al . (2016)[ 121 ]
|
파키스탄
|
CT(남성/여성)
|
고지혈증 흡연자 60명
|
NS(칼론지) 종자 1g
|
30 일
|
↓TC, LDL, TG, ↑ HDL
|
|
|
||||||
|
당뇨병 위험 요인
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Bamosaet al . (2010)[ 64 ]
|
사우디 아라비아
|
RCT(남성/여성)
|
제2형 당뇨병 환자 94명
|
NS가 함유된 캡슐(1일 1, 2, 3g)
|
12주
|
↓ FBS, 2hPG 및 HbA1c
|
|
Kaatabiet al . (2012)[ 122 ]
|
사우디 아라비아
|
당뇨병 환자 94명
|
CT(여)
|
분말 NS 1, 2, 3g/일
|
12주
|
1gr: ↑HDL-C
2gr: ↑HDL; ↓TC, TG 및 LDL-C; 3gr: ↑HDL; ↓ TC, TG, LDL-C |
|
Hosseiniet al . (2013)[ 123 ]
|
이란
|
RCT(남성/여성)
|
제2형 당뇨병 환자 70명
|
NS 오일 5ml/일
|
12주
|
↓FBS, 2hPG, BMI
|
|
Mirmiranet al . (2015)[ 68 ]
|
이란
|
RCT(남성/여성)
|
제2형 당뇨병 환자 43명
|
블랙 씨드 오일 추출물 1000mg
|
8주
|
↓FBS, LDL, 총 콜레스테롤, LDL/HDL
|
|
Heshmatiet al . (2015)[ 124 ]
|
이란
|
RCT(남성/여성)
|
환자 72명
|
NS 오일 또는 소프트 젤 캡슐 3g/일
|
12주
|
↓FBS, HbA1c, ↓LDL-C, TG
|
|
Farhangiet al . (2018)[ 120 ]
|
이란
|
RCT
남성/여성) |
하시모토 갑상선염 환자 40명
|
하루 2g NS 파우더
|
8주
|
↓BMI
↑HDL ↓ LDL 및 tri-TG 의 혈청 농도 |
|
Rashidmayvanet al . (2019)[ 66 ]
|
이란
|
RCT
(남성/여성) |
NAFLD 환자 44명
|
하루 1000mg NS 오일
|
8주
|
↓ FBS 수준
↓TG, TC, LDL, VLDL ↑ HDL |
|
Pelegrinet al . (2019)[ 69 ]
|
프랑스
|
파일럿 RCT(남)
|
건강한 남성 자원봉사자 30명
|
NS분말(1g/일)
|
4 주
|
포도당 유발 인슐린 분비 및 인슐린 감수성에는 효과가 없습니다.
|
|
|
||||||
|
류마티스관절염 위험인자
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Hadiet al . (2016)[ 77 ]
|
이란
|
RCT(여)
|
류마티스 관절염 환자 45명
|
2캡슐 500mg/일 NS 오일
|
8주
|
↓ MDA, NO
↑ IL-10의 혈청 수준 |
|
Kheirouriet al . (2016)[ 91 ]
|
이란
|
RCT(여)
|
류마티스 관절염 환자 45명
|
2캡슐 500mg/일 NS 오일
|
8주
|
↓ hs-CRP 수준, 세포독성 T 세포(CD8+), DAS-28 점수 및 관절 부기 수가 개선되었습니다.
↓ CD4+ T 세포 비율, T 조절 세포 비율(CD4+CD25+ T 세포) 및 CD4+/CD8+ 비율의 혈청 수준 |
|
게이타와 케나위(2012)[ 78 ]
|
이집트
|
RCT(여)
|
류마티스 관절염 환자 40명
|
2캡슐 500mg/일 NS 오일
|
4 주
|
↓DAS-28, 관절염증, 아침강직
|
|
Kooshkiet al . (2016)[ 125 ]
|
이란
|
RCT(남성/여성)
|
무릎 골관절염을 앓고 있는 노인 환자 40명
|
3cc NS 오일을 무릎에 국소 도포
|
3 주
|
아세트아미노펜 그룹보다 블랙씨드 그룹의 통증 감소 효과가 더 컸습니다.
|
NS= 니겔라 사티바 ; RCT=무작위 대조 시험; TG=트리글리세리드; TC=총 콜레스테롤; LDL=저밀도 지단백질; HDL=고밀도 지단백질; VLDL=초저밀도 지질단백질; FBG=공복 혈당; BMI=체질량지수; AST=아스파르트산 아미노트랜스퍼라제; ALT=알라닌 아미노트랜스퍼라제; GGT=감마-글루타밀전이효소; hs-CRP; 고감도 C-반응성 단백질; IL-6=인터루킨-6; TNF-α=종양괴사인자-α; T2D=제2형 당뇨병; FBS=공복 혈당; 2hPG = 식후 2시간 포도당; HbA1c=당화된 헤모글로빈; NAFLD=비알코올성 지방간 질환; MDA=말론디알데히드; NO=산화질소; DAS-28=질병 활동 점수-28
Effect on lipid profile (지질 프로필에 미치는 영향)
Improvements in serum lipid profile were investigated in human and animal studies. The meta-analysis on the effect of N. sativa on lipid profiles indicated that the levels of TC and LDL-C dropped significantly.[39,40] Sahebkar et al. showed significant reductions in serum TG.[40] Daryabeygi-Khotbehsara et al.[39] found that N. sativa seed oil reduced serum TG, while seed powder increased TG levels what may be a consequence for different preparation processes of crushed seeds and extracted oil in addition to chemical composition.[39] Another systematic review revealed that N. sativa supplementation might be effective in glycemic control, but its effects on anthropometric parameters and lipid profile were controversial.[41]
혈청 지질 프로필의 개선은 인간 및 동물 연구에서 조사되었습니다. 지질 프로필에 대한 N. sativa의 영향에 대한 메타 분석에 따르면 TC 및 LDL-C 수치가 크게 감소한 것으로 나타났습니다.[39,40] Sahebkar 등은 혈청 TG가 크게 감소한 것으로 나타났습니다.[40] Daryabeygi-Khotbehsara 등[39]은 N. sativa 종자유는 혈청 TG를 감소시킨 반면 종자 분말은 TG 수치를 증가 시켰는데, 이는 화학 성분 외에도 분쇄 된 종자와 추출 된 오일의 다른 준비 공정에 대한 결과 일 수 있습니다.[39] 또 다른 체계적인 검토에 따르면 N. sativa 보충제는 혈당 조절에 효과적 일 수 있지만 인체 계측 매개 변수와 지질 프로필에 미치는 영향은 논란의 여지가 있습니다.[41]
The effects of N. sativa on lipid profile may be related to its antioxidant properties,[42] and its agonist effects on peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPAR-γ),[43] reducing lipid peroxidation,[42] upregulation of the LDL receptor in the hepatocytes subsequently, cholesterol removal, and suppression of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A reductase (HMG-CoA R) gene and cholesterol synthase.[44]
지질 프로필에 대한 N. 사티바가 지질 프로필에 미치는 영향은 항산화 특성,[42] 과산화지질 과산화 감소,[43] 간세포에서 LDL 수용체의 상향 조절, 콜레스테롤 제거, 3-하이드록시-3-메틸글루타릴-코엔자임 A 환원효소(HMG-CoA R) 유전자 및 콜레스테롤 합성효소의 억제[44] 등의 작용과 관련이 있을 것으로 보입니다.
Effect on blood pressure (혈압에 미치는 영향)
N. sativa lowers BP sharply according to meta-analysis.[45] This may be connected to some factors such as diuretic effect, calcium channel-blocking properties, and cardiac depressant effect of N. sativa that are likely related to various components of N. sativa involved in this effect, including TQ, and fatty acids that contain substantial quantities of linoleic, oleic, and arachidonic acids, nigellicine, flavonoids, trans-anethole, p-cymene, α-pinene, limonene, carvone, and soluble fiber[41,46] volatile oils extracted from N. sativa and TQ may directly or indirectly reduce both BP and heart rate, by their serotoninergic and muscarinic properties.[47] N. sativa compounds are also reported to have endothelium-independent relaxation effects that may be due to suppression of Ca2+ release from the sarcoplasmic reticulum across the smooth muscle cell membrane and reduction of Ca2+ sensitivity and influx.[48] Furthermore, N. sativa may reduce BP by its diuretic effects and regulate the electrolytes and water content, and also control of blood volume; subsequently, cardiac output is reduced, an important regulator of BP.[49] Figure 2 shows the potential mechanisms of the effect of N. sativa on CVD.
메타 분석에 따르면 N. sativa는 혈압을 급격히 낮춥니다.[45] 이는 이뇨 효과, 칼슘 채널 차단 특성, 심장 억제 효과와 같은 일부 요인과 관련이 있을 수 있으며, 이는 N. sativa의 다양한 성분과 관련이 있을 가능성이 높습니다. 상당한 양의 리놀레산, 올레산 및 아라키돈산, 니겔리신, 플라보노이드, 트랜스 아네톨, p- 시멘, α- 피넨, 리모넨, 카르본 및 수용성 섬유질을 포함하는 지방산[41,46] N. sativa 및 TQ에서 추출한 휘발성 오일은 세로토닌 및 무스카린 특성에 의해 혈압과 심박수를 직접 또는 간접적으로 감소시킬 수 있습니다. [47] N. sativa 화합물은 또한 평활근 세포막을 가로지르는 소포체로부터의 Ca2+ 방출 억제와 Ca2+ 민감도 및 유입 감소로 인한 내피 독립적 이완 효과를 갖는 것으로 보고되었습니다. sativa는 이뇨 효과로 혈압을 낮추고 전해질과 수분 함량을 조절하고 혈액량을 조절할 수 있으며 결과적으로 혈압의 중요한 조절자인 심박출량이 감소합니다.[49] 그림 2는 N. sativa가 CVD에 미치는 영향의 잠재적 메커니즘을 보여줍니다.

Figure 2
Potential mechanisms of the effect of N. sativa on cardiovascular disease. PPAR-γ = Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma; LDL receptor = Low-density lipoprotein receptor; HMG-CR = 3-Hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A reductase
그림 2
심혈관 질환에 대한 N. sativa의 영향의 잠재적 메커니즘. PPAR-γ = 퍼옥시좀 증식 촉진제 활성화 수용체 감마; LDL 수용체 = 저밀도 지단백질 수용체; HMG-CR = 3-하이드록시-3-메틸글루타릴-코엔자임 A 환원효소
EFFECTS OF NIGELLA SATIVA IN TYPE 2 DIABETES (제2형 당뇨병에 대한 니겔라 사티바의 효과)
Laboratory animal studies
실험실 동물 연구
T2D mellitus is marked by hyperglycemia, dyslipidemia and increased oxidative markers that may be caused insulin resistance, and finally, overt diabetes.[50] Seeds of N. sativa have been used as a natural treatment for various diseases. Hypoglycemic, hypolipidemic, and antioxidant effects of N. sativa have been reported.[51,52,53] Numerous studies have been done in diabetic animal models. El-Dakhakhny et al. have shown that 0.4 g/kg N. sativa oil significantly diluted blood glucose concentration in diabetic rats after 6 weeks.[54] Insulin levels in diabetic rats treated with a dose of 20 ml/kg aqueous extract of N. sativa rose after 15 days.[55] Houcher et al. reported that intraperitoneally, a daily dosage of 810 mg/kg methanol extract and 2.5 ml/kg of N. sativa oil not only lowered glucose but also increased total antioxidant capacity levels in diabetic rats after treated for 25 days.[56] Kantar et al. showed that 50 mg/kg TQ administered orally grew both energy metabolism and insulin levels in diabetic rats after 20 days of insertion.[57,58,59] These studies also showed that a single daily dosage of 400 mg/kg and 50 mg/kg body weight N. sativa and TQ, respectively, administered orally in diabetic rats decreased serum glucose after the intervention.[58] Salama et al. in an animal study reported that oral 500 mg/kg N. sativa oil increased serum C-peptide, insulin, and total antioxidant capacity (TAC) concentration and decreased glucose level in a diabetic rat model.[52] Some studies assert that these antidiabetic properties of N. sativa are due to insulinotropic action,[60,61] hepatic gluconeogenesis inhibition, and its antioxidant effects.[52,56,62,63] Many studies have been done to confirm the properties of N. sativa on insulin sensitivity and release.[55] Several attempts have been worked on N. sativa, and they suggest that this plant improves insulin sensitivity by preventing the severity of oxidative stress. Insulin secretory effects of N. sativa have been probed on in vitro isolated rat pancreatic islets and saw that the secretion of insulin is increased in the presence of N. sativa. Table 1 summarizes the effects of N. sativa on diabetes in experimental studies.
제2형 당뇨병은 고혈당증, 이상지질혈증, 인슐린 저항성을 유발할 수 있는 산화 표지자의 증가, 그리고 최종적으로 명백한 당뇨병을 특징으로 합니다.[50] N. sativa 씨앗은 다양한 질병의 자연 치료제로 사용되어 왔습니다. 저혈당, 고지혈증 및 항산화 효과가 보고되었습니다.[51,52,53] 당뇨병 동물 모델에서 수많은 연구가 수행되었습니다. 엘-다카크니(El-Dakhakhny) 등은 0.4g/kg의 N. sativa 오일이 6주 후 당뇨병 쥐의 혈당 농도를 유의하게 희석시켰다고 밝혔습니다.[54] N. sativa 수성 추출물 20ml/kg을 투여한 당뇨병 쥐의 인슐린 수치는 15일 후 상승했습니다.[55] 후처(Houcher) 등은 복강 내로 810 mg/kg의 메탄올 추출물과 2.5ml/kg의 N. sativa 오일을 매일 투여한 결과, 당뇨병 쥐의 혈당 농도가 감소했다고 보고했습니다. N. sativa 오일을 25일간 처리한 후 당뇨병 쥐의 포도당을 낮출 뿐만 아니라 총 항산화 능력 수준을 증가시켰다고 보고했습니다.[56] Kantar 등은 경구 투여한 50mg/kg TQ가 20일 후 당뇨병 쥐의 에너지 대사와 인슐린 수치를 모두 증가시켰다고 밝혔습니다.[57,58,59] 이 연구에서는 또한 400 mg/kg과 50 mg/kg의 체중당 N. sativa와 TQ를 각각 당뇨병 쥐에 경구 투여하면 개입 후 혈청 포도당이 감소했습니다.[58] 살라마 등은 동물 연구에서 경구 500 mg/kg N. sativa 오일이 당뇨병 쥐 모델에서 혈청 C-펩티드, 인슐린 및 총 항산화 능력(TAC) 농도를 증가시키고 포도당 수준을 감소시켰다고 보고했습니다.[52] 일부 연구에서는 이러한 항당뇨 특성이 N. sativa의 항당뇨 특성 때문이라고 주장합니다. N. sativa의 이러한 항당뇨병 특성은 인슐린 유사 작용,[60,61] 간 포도당 생성 억제 및 항산화 효과에 기인한다고 주장합니다.[52,56,62,63] 인슐린 감수성 및 방출에 대한 N. sativa의 특성을 확인하기 위해 많은 연구가 수행되었습니다.[55] N. sativa에 대한 여러 시도가 이루어졌으며 이 식물은 산화 스트레스의 심각성을 예방하여 인슐린 감수성을 향상시키는 것으로 제안합니다. 시험관 내에서 분리 된 쥐의 췌장도에서 N. sativa의 인슐린 분비 효과를 조사한 결과 N. sativa가 있으면 인슐린 분비가 증가하는 것을 확인했습니다. 표 1은 실험 연구에서 N. sativa가 당뇨병에 미치는 영향을 요약한 것입니다.
Clinical studies (임상 연구)
There have been several clinical studies that have evaluated the effects of oral N. sativa supplementation in different subject groups. Bamosa et al. in a clinical trial on 94 patients with diabetes showed that 2 g/day of N. sativa seed supplementation decreased fasting blood glucose (FBG), 2 h postprandially glucose, glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c), and insulin resistance after 12 weeks.[64] Hosseini et al. have reported a significant decrease in FBG, 2 h postprandial glucose, and HbA1c in 70 patients with T2D consuming (5 ml/day for 12 weeks) N. sativa oil.[65] The hypolipidemic and hypoglycemic effects of N. sativa oil (1000 mg/day for 8 weeks) were confirmed by Rashidmayvan et al. in a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial performed in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver.[66] Najmi et al. have been reported that the administration of N. sativa oil (2.5 mL twice a day for 6 weeks) to patients with metabolic syndrome significantly decreased FBG and LDL and increased HDL levels.[67] Hadi et al. in a clinical trial study investigated the effect 1000 mg/days extract of N. sativa oil supplementation on 43 patients with T2D. The results after 12-week supplementation of N. sativa oil have been shown a significant reduction in serum level of fasting blood sugar, HbA1c, LDL-C, and TG.[68] Table 2 summarizes clinical trials that evaluated the effects of N. sativa supplementation on healthy and patient subjects.
여러 피험자 그룹에서 경구용 N. sativa 씨앗 보충제의 효과를 평가한 여러 임상 연구가 있었습니다. 94명의 당뇨병 환자를 대상으로 한 임상 시험에서 바모사(Bamosa) 등은 하루 2g의 N. sativa 종자 보충제를 복용한 결과 12주 후 공복 혈당(FBG), 식후 2시간 혈당, 당화혈색소(HbA1c) 및 인슐린 저항성이 감소했다고 밝혔습니다. [64] 호세이니(Hosseini) 등은 70명의 T2D 환자에서 (12주 동안 5ml/일) N. sativa 오일을 섭취한 결과 FBG, 식후 2시간 혈당, HbA1c가 유의하게 감소했다고 보고했습니다.[65] N. sativa 오일의 저지방 및 저혈당 효과. 비알코올성 지방간 환자를 대상으로 실시한 무작위, 이중 맹검, 위약 대조 임상 시험에서 라시드메이반(Rashidmayvan) 등이 N. sativa 오일(8주 동안 1000 mg/일)을 투여하여 확인했습니다.[66] 나즈미(Najmi) 등은 N. sativa 오일을 투여(2. 6주 동안 하루 2회 5mL)를 대사증후군 환자에게 투여한 결과, FBG와 LDL 수치가 유의하게 감소하고 HDL 수치가 증가했습니다.[67] Hadi 등은 임상시험 연구에서 43명의 T2D 환자를 대상으로 1일 1000mg/일 N. sativa 오일 보충제의 효과를 조사했습니다. 12주 동안 N. sativa 오일을 보충한 결과 공복 혈당, HbA1c, LDL-C, TG의 혈청 수치가 유의미하게 감소한 것으로 나타났습니다.[68] 표 2는 건강한 피험자와 환자 피험자를 대상으로 N. sativa 보충제의 효과를 평가한 임상시험을 요약한 것입니다.
MECHANISMS OF HYPOGLYCEMIC EFFECT OF NIGELLA SATIVA (니겔라 사티바의 저혈당 효과 메커니즘)
N. sativa promotes glucose homeostasis and improves the lipid profile in diabetic animals and humans with T2M through several routes. Mainly, N. sativa improve peripheral insulin sensitivity and circulating insulin.[52,53,69] It also enhances the activation of the AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) pathway in skeletal muscle and liver and to increased GLUT-4 in skeletal muscle.[70] Acetyl-CoA carboxylase (ACC) is a key component of the insulin-independent, metabolic sensing, and AMPK pathway. In fact, it has been reported that N. sativa stimulates ACC and the AMPK pathways in both hepatocyte cell lines and skeletal muscles in vitro.[70] Andaloussi et al. reported that in vivo N. sativa treatment can elevate the phosphorylation of ACC in skeletal muscle tissues and liver. The phosphorylation of ACC decreases its activity and shows a reduction of lipogenesis in the liver, whereas it increases fatty acid oxidation in skeletal muscle. These effects on lipid metabolism can justify the functionality of N. sativa to decrease plasma and tissue TG. Finally, it is known that the activation of the AMPK pathway can lead to growing synthesis of GLUT-4[71] [Figure 3]. Many researches suggested that the anti-hyperglycemia and anti-hyperlipidemia features of N. sativa are due to antioxidant components.[44,52,67,72,73] TQ and dithymoquinone are the main antioxidant components of N. sativa. Several studies have reported that N. sativa can enhance antioxidant enzymes and decrease lipid peroxidation.[73] When oxidative stress is reduced, this may help to regeneration of pancreatic beta-cells, increase number of islets, keep the integrity of pancreatic beta-cells, reduction in insulin resistance, increase insulin secretion and inhibition of advanced glycation end product.[59] N. sativa oil has been shown to decrease hepatic glucose production from gluconeogenic precursors (alanine, glycerol, and lactate) in STZ-induced diabetic hamster.[74] Furthermore, an in vitro study indicated direct inhibition of electrogenic intestinal absorption of glucose by N. sativa extract.[32]
N. sativa는 여러 경로를 통해 포도당 항상성을 촉진하고 T2M을 가진 당뇨병 동물과 인간의 지질 프로필을 개선합니다. 주로 말초 인슐린 감수성과 순환 인슐린을 개선합니다.[52,53,69] 또한 골격근과 간에서 AMP 활성화 단백질 키나아제(AMPK) 경로의 활성화와 골격근의 GLUT-4 증가를 향상시킵니다.[70] 아세틸-CoA 카르복실라제(ACC)는 인슐린 독립, 대사 감지 및 AMPK 경로의 핵심 구성 요소입니다. 실제로, N. sativa는 시험관 내에서 간세포 세포주와 골격근 모두에서 ACC와 AMPK 경로를 자극하는 것으로 보고되었습니다.[70] 안달루시 등은 생체 내 N. sativa 처리가 골격근 조직과 간에서 ACC의 인산화를 증가시킬 수 있다고 보고했습니다. ACC의 인산화는 활성을 감소시키고 간에서 지방 생성을 감소시키는 반면 골격근에서 지방산 산화를 증가시킵니다. 지질 대사에 대한 이러한 효과는 혈장 및 조직 TG를 감소시키는 N. sativa의 기능을 정당화 할 수 있습니다. 마지막으로, AMPK 경로의 활성화는 GLUT-4의 합성을 증가시킬 수 있는 것으로 알려져 있습니다[71] [그림 3]. 많은 연구에서 N. sativa의 항고혈당 및 항 고지혈증 특징은 항산화 성분 때문이라고 제안했습니다.[44,52,67,72,73] TQ와 디티 모퀴논은 N. sativa의 주요 항산화 성분입니다. 여러 연구에 따르면 N. sativa는 항산화 효소를 강화하고 지질 과산화를 감소시킬 수 있다고 보고했습니다.[73] 산화 스트레스가 감소하면 췌장 베타 세포의 재생, (췌장)섬 수 증가, 췌장 베타 세포의 완전성 유지, 인슐린 저항성 감소, 인슐린 분비 증가 및 진행성 당화 최종 산물의 억제에 도움이 될 수 있습니다. [59] N. sativa 오일은 STZ 유도 당뇨병 햄스터에서 포도당 생성 전구체 (알라닌, 글리세롤 및 젖산염)로부터 간 포도당 생성을 감소시키는 것으로 나타났습니다.[74] 또한 시험관 내 연구에 따르면 N. sativa 추출물에 의한 포도당의 전기적 장 흡수의 직접적인 억제가 나타났습니다.[32]

Figure 3
Potential mechanisms of the effect of N. sativa on diabetes. ACC = Acetyl-CoA carboxylase; AMPK = AMP-activated protein kinase
그림 3
당뇨병에 대한 N. sativa의 영향의 잠재적 메커니즘. ACC = 아세틸-CoA 카르복실라아제; AMPK = AMP 활성화 단백질 키나아제
EFFECTS OF NIGELLA SATIVA IN RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS (류마티스 관절염에 대한 니겔라 사티바의 효과)
The anti-RA properties of N. sativa and its active ingredient TQ in an animal model were evaluated in experimentally induced arthritis. Findings of a study indicated that treatment with TQ orally (5 mg/kg once daily for 21 days) decreased levels of inflammatory cytokines (IL-1β, IL-6, tumor necrosis factor-α [TNF-α], interferon-gamma [IFN-γ], and prostaglandin E2 [PGE2]) and oxidative stress indices such as articular elastase, myeloperoxidase, lipoxygenase, nitric oxide (NO) significantly and increased levels of anti-inflammatory cytokine IL-10 and the activity of superoxide dismutase (SOD), glutathione peroxidase (GPX), and catalase (CAT).[75] The results of a study to elucidate the molecular mechanism of the protective effects of TQ showed that the administration of 5 mg/kg TQ orally for 7 days significantly reduced LPS-induced IL-1β, TNF-α, cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2), metalloproteinase 13 (MMP-13), and PGE2.[76] Some of the studies reported on the effect of N. sativa on anti-RA are summarized in Table 1.
실험적으로 유도된 관절염 동물 모델에서 N. sativa와 그 활성 성분인 TQ의 항 RA 특성을 평가했습니다. 연구 결과에 따르면 TQ를 경구 투여(21일 동안 매일 1회 5mg/kg)한 결과 염증성 사이토카인(IL-1β, IL-6, 종양괴사인자-α[TNF-α], 인터페론-감마[IFN-γ], 프로스타글란딘 E2[PGE2])과 관절 엘라스타제 같은 산화 스트레스 지표가 감소한 것으로 나타났습니다, 미엘로페록시다제, 리폭시게나제, 산화질소(NO)를 유의하게 증가시키고 항염증 사이토카인 IL-10과 슈퍼옥사이드 디스뮤타제(SOD), 글루타치온 퍼옥시다제(GPX), 카탈라아제(CAT)의 활성 수준을 증가시켰습니다. [75] TQ의 보호 효과에 대한 분자적 메커니즘을 규명하기 위한 연구 결과에 따르면 5mg/kg TQ를 7일간 경구 투여하면 LPS로 유도된 IL-1β, TNF-α, 사이클로옥시게나제-2(COX-2), 메탈로프로테아제13(MMP-13) 및 PGE2가 유의하게 감소했습니다.[76] N. sativa의 항RA 효과에 대해 보고된 연구 중 일부는 표 1에 요약되어 있습니다.
Clinical studies (임상 연구)
Clinical trial studies in patients with RA have shown similar results. Hadi et al. and Kheirouri et al. indicated that two capsules of 500 mg/day N. sativa oil for 8 weeks in patients with RA is significantly reduced in MDA, NO, high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hs-CRP) level, cytotoxic T-cells (CD8+), Disease Activity Score-28 (DAS-28), and a decreased number of swollen joints in comparison with baseline and placebo groups. Furthermore, N. sativa oil is significantly increased in serum level of IL-10, CD4+ T-cell percentage, T regulatory cell percentage (CD4+ CD25+ T-cell), and CD4+/CD8+ ratio. These findings suggest that N. sativa by shifting T-helper lymphocyte cells type 1 (Th1) to T-helper lymphocyte cells type 2 (Th2) can improve RA.[77] In another study, the administration of twice capsules 500 mg/day N. sativa oil for 4 weeks significantly reduced DAS-28, joint inflammation, and morning stiffness, which could be attributed to the effect of N. sativa on the immunomodulatory system.[78] Table 2 summarizes studies investigating the effects of N. sativa and its main active ingredient TQ on the anti-RA and anti-inflammatory in clinical studies.
RA 환자를 대상으로 한 임상 시험 연구에서도 비슷한 결과가 나타났습니다. 하디(Hadi) 박사와 케이루리(Kheirouri) 박사는 류마티스관절염 환자에게 하루 500mg의 N. sativa 오일 2캡슐을 8주간 복용하게 한 결과, 기준선 및 위약 그룹에 비해 MDA, NO, 고감도 C 반응성 단백질(hs-CRP) 수치, 세포독성 T 세포(CD8+), 질병 활성 점수-28(DAS-28), 부은 관절의 수가 유의하게 감소한 것으로 나타났다고 발표했습니다. 또한, N. sativa 오일은 혈청 IL-10 수준, CD4+ T 세포 비율, T 조절 세포 비율(CD4+ CD25+ T 세포) 및 CD4+/CD8+ 비율이 유의하게 증가했습니다. 이러한 연구 결과는 N. sativa가 T-헬퍼 림프구 세포 1형(Th1)을 T-헬퍼 림프구 세포 2형(Th2)으로 전환하여 RA를 개선할 수 있음을 시사합니다.[77] 또 다른 연구에서는 하루 두 캡슐 500 mg/day의 N. sativa 오일을 4주 동안 두 번 투여한 결과, 면역 조절 시스템에 대한 N. sativa의 효과에 기인할 수 있는 DAS-28, 관절 염증 및 아침 강직이 유의하게 감소했습니다.[78] 표 2는 임상 연구에서 항 RA 및 항염증에 대한 N. sativa 및 주요 활성 성분 TQ의 효과를 조사한 연구들을 요약한 것입니다.
A MECHANISM OF IMMUNO-MODULATORY PROPERTIES OF NIGELLA SATIVA (니겔라 사티바의 면역 조절 특성 메커니즘)
Several mechanisms for the anti-RA effects of N. sativa have been proposed. N. sativa with antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and immunomodulatory properties can be effective.[77] Figure 4 shows the probable mechanisms of the effect of N. sativa on RA.
N. sativa의 항 RA 효과에 대한 몇 가지 메커니즘이 제안되었습니다. 항산화, 항염증 및 면역 조절 특성을 가진 N. sativa가 효과적 일 수 있습니다.[77] 그림 4는 N. sativa가 RA에 미치는 영향의 가능한 메커니즘을 보여줍니다.
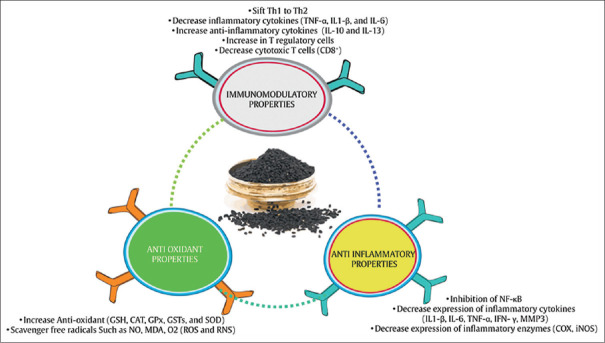
Figure 4
Probable mechanisms of the effect of N. sativa on rheumatoid arthritis. NF-κB = Inhibition of the nuclear factor-kappa B; TNF-α = Tumor necrosis factor-alpha; IL-1β = Interleukin-1β; IL-6 = Interleukin-6; IFN-γ = Interferon-gamma; MMP-3 = Matrix metalloproteinase 3; COX = Cyclooxygenase; iNOS = Inducible nitric oxide synthase; GSH = Glutathione; CAT = Catalase; GPX = Glutathione peroxidase; GSTs = Glutathione S-transferases; SOD = Superoxide dismutase; NO = Nitric oxide; MDA = Malondialdehyde; ROS = Reactive oxygen species; RNS = Reactive nitrogen species; Th1 = Type 1 helper T-cells; Th2 = Type 2 helper T-cells; IL-10 = Interleukin-10; IL-13 = Interleukin-13
그림 4
류마티스 관절염에 대한 N. sativa의 영향에 대한 가능한 메커니즘. NF-κB = 핵 인자-카파 B 억제; TNF-α = 종양괴사인자-알파; IL-1β = 인터루킨-1β; IL-6 = 인터루킨-6; IFN-γ = 인터페론-감마; MMP-3 = 매트릭스 메탈로프로테아제 3; COX = 사이클로옥시게나제; iNOS = 유도성 산화 질소 합성 효소; GSH = 글루타치온; CAT = 카탈라제; GPX = 글루타치온 퍼옥시다아제; GST = 글루타치온 S-전이효소; SOD = 슈퍼옥사이드 디스뮤타제; NO = 산화질소; MDA = 말론디알데히드; ROS = 활성 산소 종; RNS = 활성 질소 종; Th1 = 제1형 헬퍼 T세포; Th2 = 제2형 헬퍼 T세포; IL-10 = 인터루킨-10; IL-13 = 인터루킨-13
Antioxidant properties (항산화 특성)
According to the results of studies, reactive oxygen species (ROS), such as O2, OH, and reactive nitrogen species (RNS) such as NO, play an important role in the enhancement of inflammation and progression of RA.[75,79,80,81] Therefore, strengthening the antioxidant defense system is very important in reducing chronic diseases.[82] Numerous studies have shown the potentiation of the antioxidant system of N. sativa.[34] N. sativa exerts its antioxidant properties by direct and indirect antioxidant mechanisms and inhibits the expression of oxidative-producing enzymes (inducible NO synthase [iNOS]). Direct antioxidant activities of N. sativa may restore other antioxidants including glutathione (GSH), Vitamin E and Vitamin A, metal chelators, and scavenger free radicals (ROS and RNS). N. sativa also exerts its indirect antioxidant role by activating transcription factors involved in the expression of antioxidant enzymes including SOD, glutathione S-transferases (GSTs), GPX, and CAT.[83]
연구 결과에 따르면, O2, OH와 같은 활성 산소 종 (ROS) 및 NO와 같은 활성 질소 종 (RNS)은 RA의 염증 및 진행을 강화하는 데 중요한 역할을합니다.[75,79,80,81] 따라서 항산화 방어 시스템을 강화하는 것은 만성 질환을 줄이는 데 매우 중요합니다. [82] 수많은 연구에서 N. sativa의 항산화 시스템의 강화가 밝혀졌습니다.[34] N. sativa는 직접 및 간접 항산화 메커니즘을 통해 항산화 특성을 발휘하고 산화 생성 효소(유도성 NO 합성 효소[iNOS])의 발현을 억제합니다. N. sativa의 직접적인 항산화 활동은 글루타치온(GSH), 비타민 E 및 비타민 A, 금속 킬레이트, 스캐빈저 자유 라디칼(ROS 및 RNS)을 포함한 다른 항산화 물질을 회복시킬 수 있습니다. 또한, N. 사티바는 SOD, 글루타치온 S-전이효소(GST), GPX, CAT를 포함한 항산화 효소의 발현에 관여하는 전사인자를 활성화하여 간접적인 항산화 역할을 수행합니다[83].
Anti-inflammatory properties (항염증 특성)
Inhibition of the nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB) pathway is a known mechanism marking anti-inflammatory effects of N. sativa.[84] NF-κB is a transcription factor that causes an exacerbation of inflammatory status. This transcription factor is present in the cytosol and has two subunits called P50 and P65. It also binds to the inhibitor of κB (IκBα) inhibitory protein. Factors such as ROS, TNFα, interleukin-1 beta (IL-1B), and bacterial lipopolysaccharides (LPSs) induce NF-κB activity.[85] These factors via activation of IκB kinase (IKK) results in the phosphorylation and destruction of IκBα which results in the activation of NF-κB and its transfer to the nucleus. NF-κB is located in a nucleus on a specific gene sequence that will eventually lead to increased expression of various types of inflammatory cytokines (IL-1β, IL-6, TNF-α, IFN-γ, and MMP3), COX-2, and iNOS.[86] These inflammatory cytokines are not only upregulated by NF-κB but also activate NF-κB leading to continuity of inflammatory status.[87] Therefore, N. sativa may probably rupture these interactions by NF-κB suppression and plays an important duty in its anti-inflammatory activity.[88] Inhibition of the NF-κB pathway by N. sativa can be done in several ways: (1) preventing NF-κB transfer from the cytosol to the nucleus, (2) blocking the NF-KB subunit P50 bonded to the promoter of genes expressing inflammatory factors, especially TNF-α, (3) inhibition of NF-κB p65 subunit nuclear expression, and (4) prevention of phosphorylation and degradation of I-KBα (binding of I-KBα to NF-κB causes inactivation of this transcription factor).[87]
핵 인자-카파 B (NF-κB) 경로의 억제는 N. sativa의 항 염증 효과를 나타내는 알려진 메커니즘입니다.[84] NF-κB는 염증 상태를 악화시키는 전사 인자입니다. 이 전사 인자는 세포질에 존재하며 P50과 P65라는 두 개의 하위 유닛을 가지고 있습니다. 또한 κB (IκBα) 억제 단백질의 억제제와 결합합니다. ROS, TNFα, 인터루킨-1 베타(IL-1B), 박테리아 지질다당류(LPS)와 같은 인자는 NF-κB 활성을 유도합니다.[85] 이러한 인자는 IκB 키나아제(IKK)의 활성화를 통해 IκBα의 인산화 및 파괴를 초래하여 NF-κB가 활성화되고 핵으로 이동합니다. NF-κB는 특정 유전자 서열의 핵에 위치하여 결국 다양한 유형의 염증성 사이토카인(IL-1β, IL-6, TNF-α, IFN-γ 및 MMP3), COX-2 및 iNOS의 발현을 증가시킵니다. [86] 이러한 염증성 사이토카인은 NF-κB에 의해 상향 조절될 뿐만 아니라 NF-κB를 활성화시켜 염증 상태를 지속시킵니다.[87] 따라서 N. sativa는 NF-κB 억제를 통해 이러한 상호 작용을 파열하고 항염증 작용에 중요한 역할을 할 수 있습니다. [88] N. sativa에 의한 NF-κB 경로의 억제는 여러 가지 방법으로 수행될 수 있습니다. (1) 세포질에서 핵으로의 NF-κB 이동 방지, (2) 염증 인자, 특히 TNF-α를 발현하는 유전자의 프로모터에 결합된 NF-KB 서브 유닛 P50 차단, (3) NF-κB p65 서브 유닛 핵 발현 억제, (4) I-KBα의 인산화 및 분해 방지(I-KBα와 NF-κB의 결합은 이 전사 인자의 비활성화를 유발) [87]
Immunomodulatory properties (면역 조절 특성)
Studies suggest that N. sativa can regulate immune responses.[82] In RA, decreased expression of IL-10 produced by Th2 can be accountable for the dominance of T-helper 1 over T-helper 2 cells at sites of inflamed synovium and in the peripheral blood and reduce in Th2 may exacerbate the inflammatory process in RA. N. sativa probably shifts the immune response from Th1 that produces pro-inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6 to Th2 that results in anti-inflammatory cytokines such as IL-10 and IL-3. Studies have shown that an increase in IL-10 and IL-3 leads to an increase in T regulatory cell percentage (CD4+CD25+T-cell).[89,90,91] T regulatory cells reduce the abnormal proliferation of immune cells, such as cytotoxic T-cells (CD8+) and Th1 cells, which is responsible for the secretion of many inflammatory cytokines.[91,92,93] Therefore, N.sativa by regulation of T-lymphocytes leading to improve clinical symptoms of RA.[91]
연구에 따르면 N. sativa는 면역 반응을 조절할 수 있습니다.[82] RA에서 Th2에 의해 생성되는 IL-10의 발현 감소는 염증이 있는 활막 부위와 말초 혈액에서 T 헬퍼 2 세포보다 T 헬퍼 1의 우위를 차지할 수 있으며 Th2의 감소는 RA의 염증 과정을 악화시킬 수 있습니다. N. sativa는 면역 반응을 TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6와 같은 전 염증성 사이토카인을 생성하는 Th1에서 IL-10, IL-3와 같은 항염증성 사이토카인을 생성하는 Th2로 전환할 수 있습니다. 연구에 따르면 IL-10과 IL-3의 증가는 T 조절 세포 비율(CD4+CD25+T 세포)의 증가로 이어집니다.[89,90,91] T 조절 세포는 많은 염증성 사이토카인의 분비를 담당하는 세포 독성 T 세포(CD8+)와 Th1 세포와 같은 면역 세포의 비정상적인 증식을 감소시킵니다.[91,92,93] 따라서 N.sativa는 T 림프구를 조절하여 RA의 임상 증상을 개선합니다.
Conclusion (결론)
This review article demonstrated that N. sativa could reduce oxidative stress and inflammation with various mechanisms have been proposed to contribute to the beneficial properties of N. sativa, including a reduction of lipid peroxidation via its antioxidant properties; agonist of PPAR-γ in adipose tissue; activation of AMPK, increased antioxidants inhibition of NF-κB pathway; increased in IL-10 expression, CD4+ T-cell percentage, T regulatory cell percentage in peripheral blood, and CD4+/CD8+ ratio. Therefore, N. sativa may be beneficial in chronic diseases (CVD, T2D, and RA) and can be used as an adjunct therapy. Furthermore, clinical studies have shown a positive effect of N. sativa on BP, FBG, and lipid profile, but to prove this claim, it is necessary to conduct experimental and well-designed clinical trial studies with a larger sample size on the effects of N. sativa on these chronic diseases.
이 리뷰 논문에서는 항산화 특성을 통한 지질 과산화 감소, 지방 조직에서 PPAR-γ의 작용제, AMPK의 활성화, 항산화 물질의 증가로 인한 NF-κB 경로 억제, IL-10 발현 증가, CD4+ T 세포 비율, 말초 혈액의 T 조절 세포 비율, CD4+/CD8+ 비율 등 다양한 메커니즘을 통해 산화 스트레스와 염증을 줄일 수 있다는 사실을 입증했습니다. 따라서 N. sativa는 만성 질환(CVD, T2D, RA)에 유익할 수 있으며 보조 요법으로 사용할 수 있습니다. 또한, 임상 연구에 따르면 N. sativa는 혈압, FBG 및 지질 프로필에 긍정적인 영향을 미쳤지만 이 주장을 증명하려면 이러한 만성 질환에 대한 N. sativa의 효과에 대해 더 큰 샘플 크기로 실험적이고 잘 설계된 임상 시험 연구를 수행 할 필요가 있습니다.
Financial support and sponsorship (재정 지원 및 후원)
Nil.
없음.
Conflicts of interest (이해 상충)
There are no conflicts of interest.
이해 상충이 없습니다.
REFERENCES (참조) - 생략
'게시판' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 당뇨병 및 합병증에 대한 니겔라 사티바(블랙씨드)의 잠재적 건강상의 이점 : 실험실 연구에서 임상 시험에 이르는 검토 (0) | 2024.06.09 |
|---|---|
| 니겔라 사티바(블랙씨드)가 특정 위장 질환에 미치는 영향 (0) | 2024.06.07 |
| 니겔라 사티바(블랙씨드) : 만성 질환 관리의 귀중한 관점 (0) | 2024.06.07 |
| 고혈압의 약물 치료 관리를 위한 잠재적 인 허브, 니겔라 사티바 (블랙씨드) : 검토 (0) | 2024.06.07 |
| 니겔라 사티바(블랙씨드)와 그 활성 성분(티모퀴논)의 항당뇨 활동 : 인체 및 실험동물 연구 검토 (0) | 2024.06.07 |