오늘은 미국 국립 생명공학 정보 센터 (National Center for Biotechnology Information)에 게제된 "니겔라 사티바가 제2형 당뇨병에 미치는 영향: 체계적인 검토"에 대한 자료를 공유해 드리고자 합니다.
원본의 출처는 아래와 같습니다.

Diabetes mellitus is one of the most prevalent metabolic disorders that affect people of all genders, ages, and races. Medicinal herbs have gained wide attention from researchers and have been considered to be a beneficial adjuvant agent to oral antidiabetic ...
www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
Effects of Nigella Sativa on Type-2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Systematic Review
니겔라 사티바가 제2형 당뇨병에 미치는 영향: 체계적인 검토
1병에 100캡슐... 국내에 정식으로 수입된 터키산 블랙씨드 오일~
Amiza Hamdan, Ruszymah Haji Idrus, and Mohd Helmy Mokhtar*
Author information Article notes Copyright and License information PMC Disclaimer
Abstract (개요)
Diabetes mellitus is one of the most prevalent metabolic disorders that affect people of all genders, ages, and races. Medicinal herbs have gained wide attention from researchers and have been considered to be a beneficial adjuvant agent to oral antidiabetic drugs because of their integrated effects. Concerning the various beneficial effects of Nigella sativa, this systematic review aims to provide comprehensive information on the effects of Nigella sativa on glucose and insulin profile status in humans. A computerized database search performed through Scopus and Medline via Ebscohost with the following set of keywords: Nigella Sativa OR black seed oil OR thymoquinone OR black cumin AND diabetes mellitus OR hyperglycemia OR blood glucose OR hemoglobin A1C had returned 875 relevant articles. A total of seven articles were retrieved for further assessment and underwent data extraction to be included in this review. Nigella sativa was shown to significantly improve laboratory parameters of hyperglycemia and diabetes control after treatment with a significant fall in fasting blood glucose, blood glucose level 2 h postprandial, glycated hemoglobin, and insulin resistance, and a rise in serum insulin. In conclusion, these findings suggested that Nigella sativa could be used as an adjuvant for oral antidiabetic drugs in diabetes control.
당뇨병은 성별, 연령, 인종을 불문하고 모든 사람에게 영향을 미치는 가장 흔한 대사 장애 중 하나입니다. 약초는 연구자들로부터 많은 관심을 받았으며 통합 효과로 인해 경구 항 당뇨병 약물의 유익한 보조제로 간주되어 왔습니다. 니겔라 사티바의 다양한 유익한 효과와 관련하여, 이 체계적인 검토는 니겔라 사티바가 인간의 포도당 및 인슐린 프로필 상태에 미치는 영향에 대한 포괄적인 정보를 제공하는 것을 목표로 합니다. 다음 키워드 세트를 사용하여 Ebscohost를 통해 Scopus 및 Medline을 통해 컴퓨터 데이터베이스 검색을 수행했습니다: 니겔라 사티바 또는 블랙 씨드 오일 또는 티모퀴논 또는 블랙 커민 및 당뇨병 또는 고혈당증 또는 혈당 또는 헤모글로빈 A1C로 검색한 결과 875건의 관련 논문이 검색되었습니다. 추가 평가를 위해 총 7편의 논문을 검색하고 데이터 추출을 거쳐 이 리뷰에 포함시켰습니다. 니겔라 사티바는 공복 혈당, 식후 2시간 혈당, 당화혈색소, 인슐린 저항성이 유의하게 감소하고 혈청 인슐린이 증가하여 치료 후 고혈당증 및 당뇨병 조절에 대한 실험실 매개변수가 유의하게 개선되는 것으로 나타났습니다. 결론적으로, 이러한 연구 결과는 당뇨병 조절에 있어 니겔라 사티바가 경구용 항당뇨병제의 보조제로 사용될 수 있음을 시사합니다.
Keywords: Nigella sativa, Type-2 diabetes mellitus, thymoquinone, antidiabetic, hypoglycemic effect
키워드: 니겔라 사티바, 제2형 당뇨병, 티모 퀴논, 항 당뇨병, 저혈당 효과
1. Introduction (도입)
Diabetes mellitus (DM) is one of the most prevalent metabolic disorders that occur throughout the world, which affects people of all genders, ages, and races. Type-2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) accounts for 90% of all DM cases as a result of the interaction between genetic predisposition and environmental factors [1]. T2DM is characterized by the defect in insulin secretion, an action that causes an elevation in blood glucose levels. This elevation promotes the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS), which cause cellular damage that promote the development of diabetic complications, including diabetic retinopathy, nephropathy, and autonomic neuropathy [2,3].
당뇨병(DM)은 전 세계적으로 발생하는 가장 흔한 대사 장애 중 하나로 성별, 연령, 인종을 불문하고 모든 사람에게 영향을 미칩니다. 제2형 당뇨병(T2DM)은 유전적 소인과 환경적 요인의 상호작용으로 인해 전체 당뇨병 사례의 90%를 차지합니다[1]. T2DM은 인슐린 분비에 결함이 있어 혈당 수치가 상승하는 것이 특징입니다. 이러한 혈당 상승은 활성 산소종(ROS)의 생성을 촉진하여 당뇨병성 망막증, 신장병증 및 자율 신경 병증을 포함한 당뇨병 합병증의 발병을 촉진하는 세포 손상을 유발합니다[2,3].
Besides that, T2DM can also be associated with cardiovascular risk factors such as dyslipidemia, hypertension, and obesity. Measurements of fasting blood glucose (FBG), blood glucose level 2 h postprandial (2hPG), and glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) have been used to assess glycemic control in patients with T2DM [4]. Medicinal herbs have gained wide attention from researchers and have been considered to be a beneficial adjuvant agent to oral antidiabetic drugs because of their integrated effects [5,6]. Besides that, Nigella sativa (NS) has also been considered to be safer compared to oral antidiabetic drugs [7]. NS is an annual herbaceous flowering plant, belonging to the Rununculaceae family which can be found mostly in Middle Eastern countries. It is also known as “black seed” or “kalonji” and has been widely used in food as spices and condiments. Different forms of NS like extract, oil, and powder have been utilized in traditional medicine to treat several illnesses such as fever, cough, diarrhea, bronchitis, and gastrointestinal diseases [8,9]. NS was reported to possess various therapeutic effects such as antidiabetic, antioxidant, anticancer, hypolipidemic, and anti-inflammatory properties [10].
그 외에도 제2형 당뇨병은 이상지질혈증, 고혈압, 비만과 같은 심혈관 질환 위험 요인과도 관련이 있을 수 있습니다. 공복 혈당(FBG), 식후 2시간 혈당 수치(2hPG), 당화혈색소(HbA1c) 측정은 제2형 당뇨병 환자의 혈당 조절을 평가하는 데 사용되어 왔습니다[4]. 약초는 연구자들로부터 많은 관심을 받아왔으며, 통합적인 효과로 인해 경구용 항당뇨병 약물의 유익한 보조제로 간주되어 왔습니다 [5,6]. 그 외에도 니겔라 사티바(NS)는 경구용 항당뇨제에 비해 더 안전한 것으로 여겨져 왔습니다 [7]. NS는 주로 중동 국가에서 볼 수 있는 미나리아재비과에 속하는 일년생 초본 꽃 식물입니다. "블랙 씨드" 또는 "칼론지"로도 알려져 있으며 향신료와 조미료로 음식에 널리 사용되어 왔습니다. 추출물, 오일 및 분말과 같은 다양한 형태의 NS는 전통 의학에서 발열, 기침, 설사, 기관지염 및 위장 질환과 같은 여러 질병을 치료하는 데 활용되었습니다 [8,9]. NS는 항당뇨, 항산화, 항암, 고지혈증, 항염증 등 다양한 치료 효과가 있는 것으로 보고되었습니다 [10].
Screening for novel bioactive compounds from NS has gained researchers’ attention due to its therapeutic effects. The therapeutic effects of NS are mainly contributed to thymoquinone, which is one of the major bioactive compounds that was discovered to have a protective effect against diabetes [11]. Previous studies revealed that thymoquinone induced a marked decrease in FBG and a marked increase in insulin levels in rats [12]. The other compounds, namely thymol, thymohydroquinone, dithymoquinone, nigellone, alpha-hederin, flavonoids, and fatty acids were also found to have participated in the therapeutic properties of NS [13]. The efficacy of NS therapeutic properties is contributed by the synergistic effect between the different compounds presents in the plant extracts. Furthermore, NS was shown to have no severe side effects or toxicological effects in human and animal models [14].
NS에서 새로운 생리 활성 화합물을 스크리닝하는 것은 그 치료 효과로 인해 연구자들의 주목을 받고 있습니다. NS의 치료 효과는 주로 당뇨병에 대한 보호 효과가 있는 것으로 밝혀진 주요 생리 활성 화합물 중 하나인 티모퀴논에 기인합니다 [11]. 이전 연구에 따르면 티모퀴논은 쥐에서 FBG의 현저한 감소와 인슐린 수치의 현저한 증가를 유도하는 것으로 나타났습니다 [12]. 다른 화합물, 즉 티몰, 티모하이드로퀴논, 디티모퀴논, 니겔론, 알파 헤데린, 플라보노이드 및 지방산도 NS의 치료 특성에 관여하는 것으로 밝혀졌습니다 [13]. NS 치료 특성의 효능은 식물 추출물에 존재하는 다양한 화합물 간의 시너지 효과에 의해 기여합니다. 또한 NS는 인간 및 동물 모델에서 심각한 부작용이나 독성학적 영향이 없는 것으로 나타났습니다 [14].
Concerning the various beneficial effects of NS, this systematic review was performed to provide comprehensive information on the effect of supplementation of NS in combination with oral antidiabetic drugs on glucose and insulin profile status in humans. Besides that, it may help to establish NS as a beneficial adjuvant to oral antidiabetic drugs for diabetes patients.
NS의 다양한 유익한 효과와 관련하여 이 체계적 문헌고찰은 경구용 항당뇨약과 함께 NS를 보충하는 것이 사람의 혈당 및 인슐린 프로필 상태에 미치는 영향에 대한 포괄적인 정보를 제공하기 위해 수행되었습니다. 또한 당뇨병 환자를 위한 경구용 항당뇨병 약물의 유익한 보조제로서 NS를 확립하는 데 도움이 될 수 있습니다.
2. Materials and Methods (자료 및 방법)
2.1. Literature Review (문헌 검토)
A systematic review of the literature was conducted to identify relevant studies about the reported effect of Nigella sativa (NS) on Type-2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). To conduct a comprehensive search of biomedical science journals, two databases, namely Scopus (published between 1823 and November 2019) and Medline via Ebscohost (published between 1865 and November 2019) were used. The search strategy involved a combination of the following two sets of keywords Nigella sativa OR black seed oil OR thymoquinone OR black cumin AND diabetes mellitus OR hyperglycemia OR blood glucose OR hemoglobin A1C
니겔라 사티바(NS)가 제2형 당뇨병(T2DM)에 미치는 영향에 대해 보고된 관련 연구를 확인하기 위해 문헌에 대한 체계적인 검토가 수행되었습니다. 생의학 학술지를 포괄적으로 검색하기 위해 1823년부터 2019년 11월 사이에 출판된 Scopus와 1865년부터 2019년 11월 사이에 출판된 Ebscohost를 통한 Medline의 두 가지 데이터베이스를 사용했습니다. 검색 전략에는 다음과 같은 두 가지 키워드 세트의 조합이 포함되었습니다. 니겔라 사티바 OR 블랙 씨드 오일 OR 티모퀴논 OR 블랙 커민 AND 당뇨병 OR 고혈당증 OR 혈당 또는 헤모글로빈 A1C.
2.2. Selection of Research Articles (연구 논문 선정)
The results were limited to original articles that were published in English and included abstracts. Review articles, news, case reports, and other original articles not associated with NS and T2DM were excluded from the review. For this review, only studies that reported the association of NS and T2DM were included.
결과는 영어로 출판되고 초록이 포함된 원본 논문으로 제한되었습니다. 리뷰 기사, 뉴스, 사례 보고서 및 NS 및 제2형 당뇨병과 관련이 없는 기타 원본 논문은 검토 대상에서 제외되었습니다. 이 리뷰에서는 NS와 T2DM의 연관성을 보고한 연구만 포함되었습니다.
2.3. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria (포함 및 제외 기준)
For this review, only studies that reported the direct effect of NS on T2DM was included. The inclusion criteria were as follows: (i) Clinical human studies including but not limited to observational study, randomized controlled trial, AND double-blind randomized controlled trial or single-blind, non-randomized controlled trial design, AND (ii) studies involving human adult subjects, AND (iii) studies examining the effects of a crude plant preparation and not its bioactive components, AND (iv) research that reported sufficient information on at least one T2DM blood parameter, such as fasting blood glucose, HbA1c or blood glucose level 2 h postprandial (2hPG), AND (v) studies that examined the antidiabetic effects of any form of NS (powder, oil, capsule, or tea).
이 리뷰에서는 NS가 제2형 당뇨병에 미치는 직접적인 영향을 보고한 연구만 포함했습니다. 포함 기준은 다음과 같습니다: (i) 관찰 연구, 무작위 대조 시험, 이중 맹검 무작위 대조 시험 또는 단일 맹검 비무작위 대조 시험 설계를 포함하되 이에 국한되지 않는 임상 인간 연구, (ii) 성인 인간 피험자를 대상으로 한 연구, (iii) 생리 활성 성분이 아닌 조제 식물 제제의 효과를 조사한 연구, 그리고 (iv) 공복 혈당, 당화혈색소(HbA1c) 또는 식후 2시간 혈당 수치(2hPG) 등 적어도 하나의 제2형 당뇨병 혈액 매개변수에 대한 충분한 정보를 보고한 연구, 그리고 (v) 모든 형태의 NS(분말, 오일, 캡슐 또는 차)의 항당뇨 효과를 검토한 연구입니다.
The following exclusions were also considered: (i) studies that investigated the impacts of an individual bioactive component of NS, OR (ii) studies on NS in combination with other herbs of ingredients as a mixture, OR (iii) studies on animals, OR (iv) studies on Type-1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM) or gestational diabetes (GDM).
(i) NS의 개별 생리 활성 성분의 영향을 조사한 연구, 또는 (ii) 다른 허브 성분과 혼합하여 NS에 대한 연구, 또는 (iii) 동물을 대상으로 한 연구, 또는 (iv) 제1형 당뇨병(T1DM) 또는 임신성 당뇨병(GDM)에 대한 연구도 제외 대상으로 고려했습니다.
2.4. Data Extraction and Management (데이터 추출 및 관리)
Papers were screened in three phases before they were included in the review. In the first phase, studies that did not match the inclusion criteria based solely on the title were excluded. In the second phase, abstracts of the remaining studies were screened, and studies that did not meet the inclusion criteria were excluded. In order to standardize the data collection, all data extraction was performed independently with the use of a data extraction form. The following data were recorded from the studies: Type of NS used, treatment groups, biochemical parameters measured, a summary of T2DM related outcome measures, and a conclusion of the study.
논문은 검토 대상에 포함되기 전에 3단계에 걸쳐 선별되었습니다. 첫 번째 단계에서는 제목만으로는 포함 기준에 부합하지 않는 연구가 제외되었습니다. 두 번째 단계에서는 나머지 연구의 초록을 선별하여 포함 기준에 부합하지 않는 연구를 제외했습니다. 데이터 수집을 표준화하기 위해 모든 데이터 추출은 데이터 추출 양식을 사용하여 독립적으로 수행되었습니다. 연구에는 다음과 같은 데이터가 기록되었습니다: 사용된 NS의 유형, 치료 그룹, 측정된 생화학적 파라미터,제2형 당뇨병 관련 결과 측정 요약, 연구 결론.
판매자도 지난 5년간 계속 복용하고 있는 뷰티텐더 블랙씨드(캡슐타입)입니다.
3.1. Search Results (검색 결과)
The literature searches identified 875 potentially relevant articles. Of those, 866 articles were excluded because they were not associated with Nigella sativa (NS) or its bioactive compound and were not related to T2DM. The search was limited to original articles written in the English, with an abstract available, and studies only in humans with T2DM and combined treatment of an oral antidiabetic drug with NS. From the remaining nine articles, one duplicate article and one systematic review article was removed before the full papers were retrieved for thorough reading. A total of seven articles were retrieved for further assessment and underwent data extraction to be included in this review. A flow chart of the selection process, including reasons for exclusion, is shown in Figure 1.
문헌 검색을 통해 875개의 관련 가능성이 있는 논문을 확인했습니다. 이 중 866건의 논문은 니겔라 사티바(NS) 또는 그 생리 활성 화합물과 관련이 없고 제2형 당뇨병과 관련이 없기 때문에 제외되었습니다. 검색은 영어로 작성된 원저 논문으로 제한되었으며, 초록이 제공되고, 제2형 당뇨병이 있고 경구용 항당뇨병제와 NS의 병용 치료를 받은 사람에 대한 연구로만 제한되었습니다. 나머지 9편의 논문 중 중복 논문 1편과 체계적 문헌고찰 논문 1편을 제거한 후 전체 논문을 검색하여 꼼꼼히 읽었습니다. 추가 평가를 위해 총 7편의 논문을 검색하고 데이터 추출을 거쳐 이 리뷰에 포함시켰습니다. 제외 사유를 포함한 선정 과정의 흐름도는 그림 1에 나와 있습니다.
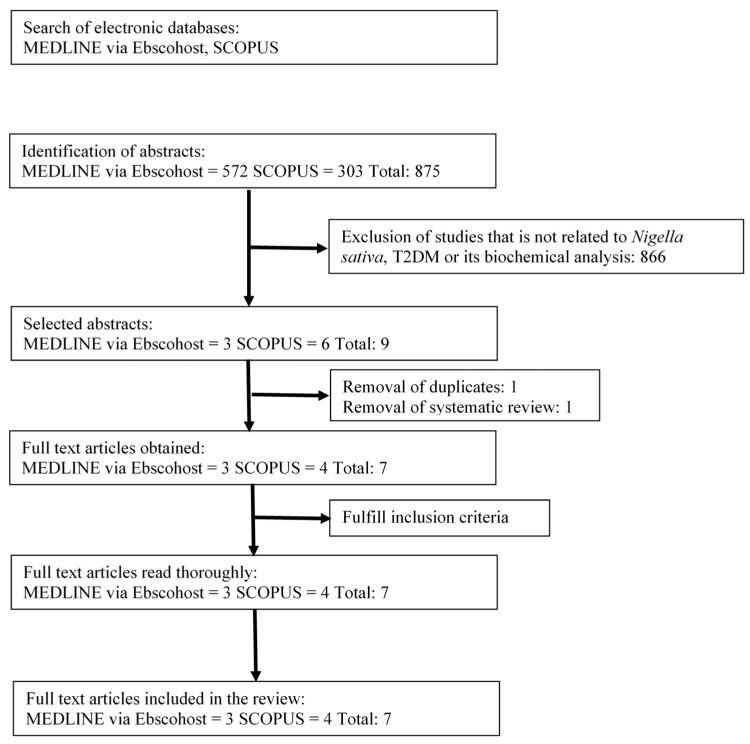
Figure 1
Flowchart of the selection process.
그림 1
선택 과정의 순서도.
3.2. Study Characteristics (연구 특성)
The summary of the characteristics of all studies is displayed in Table 1. All studies were published between the year 2009 and 2015. Four different types of NS form were used for the treatment which include oil (n = 3) [15,16,17], capsule (n = 2) [18,19], powder (n = 1) [20], and tea (n = 1) [21]. Different treatments of NS were used in the studies with the treatment of the oil form including varying doses of 0.7 g/day, 3 g/day, and 5 mL/day. For capsule form, the treatments were in the range of 1 to 3 g/day, while the treatments for powder form and tea forms were 2 g/day and 5 g/day, respectively.
모든 연구의 특징에 대한 요약은 표 1에 나와 있습니다. 모든 연구는 2009년부터 2015년 사이에 발표되었습니다. 오일(n = 3) [15,16,17], 캡슐(n = 2) [18,19], 분말(n = 1) [20], 차(n = 1) [21]를 포함한 네 가지 유형의 NS 형태가 치료에 사용되었습니다. 오일 형태의 경우 0.7g/일, 3g/일, 5mL/일의 다양한 용량을 포함하여 다양한 NS 치료법이 연구에 사용되었습니다. 캡슐 형태의 경우 1일 1~3g/일, 분말 형태와 차 형태의 경우 각각 1일 2g/일, 1일 5g의 용량을 투여했습니다.
Table 1
Effects of Nigella sativa on Type-2 diabetes mellitus.
|
REF
|
Study Design
|
Type of Nigella sativa
|
Methodology
|
T2DM Related Biochemical Outcome
|
Conclusions
|
||
|
Treatment Group
|
|
Biochemical Analysis
|
|||||
|
[17]
|
Interventional study (pre-post study).
|
Nigella sativa oil (from 0.7 g Nigella sativa seeds purchased from Rawalpindi, Pakistan) to be consumed orally for 40 d.
|
Forty-one T2DM patients consumed Nigella sativa oil for the 1st 40 d (NS treatment) followed by wheat bran for the 2nd 40 d (placebo), combined with their usual oral antidiabetic drug at constant dose.
|
|
Analysis of blood samples: Fasting blood glucose (FBG), insulin level blood urea, platelet count, total leucocytes count (TLC), serum alanine aminotransferase (ALT), and serum aspartate aminotransferase (AST).
|
FBG significantly decreased from 190.780 ± 8.042 mg/dL to 168.317 ± 7.150 mg/dL following the 1st treatment before significantly increasing back to 186.487 ± 7.491 mg/dL after the 2nd treatment.
Although not significant, insulin levels increased from 8.013 ± 0.758 lU/mL to 13.194 ± 1.404 ulU/mL after the 1st treatment before decreasing back to 8.850 ± 0.694 ulU/mL after the 2nd treatment. |
Nigella sativa oil decreased FBG and increased insulin levels when combined with oral antidiabetic drug.
|
|
[19]
|
Interventional study (pre-post study).
|
Nigella sativa seed (Bioextract (Pvt) Ltd, Sri Lanka) in capsules contain 500 mg of grounded Nigella sativa to be consumed orally in three different doses 1, 2, and 3 g/day for 12 weeks.
|
Ninety-four T2DM patients divided randomly into 3 groups. Thirty patients receiving 1 g/day dose, 32 patients receiving 2 g/day dose, and 32 patients receiving 3 g/day dose together with their oral antidiabetic drug for 4, 8, and 12 weeks.
|
|
Analysis of blood samples: FBG, blood glucose level 2 h postprandial (2hPG), glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c), insulin resistance index, β-cell function, serum C-peptide, and body mass index (BMI).
|
(a) FBG at 0, 4, 8, and 12 weeks showed no significant changes with the 1 g/day capsule with 189 ± 14.3, 186 ± 38, 171 ± 10.1, and 171 ± 7.8 mg/dL, respectively. With 2 g/day capsule, FBG at 0, 4, 8, and 12 weeks showed a significant reduction from 219 ± 12.3, 174 ± 10.1, 157 ± 10.8, to 162 ± 9.2 mg/dL accordingly. With 3 g/day capsule, FBG at 0, 4, 8, and 12 weeks showed a significant reduction from 204 ± 18.2, 176 ± 15.2, 157 ± 9.9, to 169 ± 16.4 mg/dL, respectively. (b) 2hPG levels at 0, 4, 8, and 12 weeks did not change with 1 g/day capsule with readings of 286 ± 23.3, 244 ± 22.5, 241 ± 19.2, and 218 ± 15.6 mg/dL, respectively. With 2 g/day capsule, 2hPG levels at 0, 4, 8, and 12 weeks decreased significantly with readings of 289 ± 24.2, 213 ± 27.8, 231 ± 26.58, and 256 ± 28.1 mg/dL, respectively. Although not significant, 2hPG levels increased with 3 g/day capsule with readings at 0, 4, 8, and 12 weeks of 277 ± 54.3, 301 ± 54.3, 229 ± 9.9, and 234 ± 80.3 mg/dL, respectively. (c) HbA1c at 12 weeks did not significantly decrease from baseline with 1 g/day capsule, with readings from 8.36 ± 0.31 to 8.01 ± 0.27 %. With 2 g/day capsule, HbA1c decreased significantly from 9.09 ± 0.24 to 7.57 ± 0.30 %. With 3 g/day capsule, HbA1c decreased significantly from 9.35 ± 0.41 to 7.31 ± 0.37 %. (d) Insulin resistance index did not significantly change from 2.75 ± 0.34 to 2.82 ± 0.26 with 1 g/day capsule. With 2 g/day capsule, insulin resistance index significantly decreased at 12 weeks from 3.20 ± 0.36 to 2.37 ± 0.20. Although not significant, with 3 g/day capsule, insulin resistance index increased at 12 weeks from 4.11 ± 0.55 to 2.98 ± 0.49. (e) β-cell function decreased with 1 g/day capsule from 61.75 ± 7.79 to 59.12 ± 8.19, while it increased with 2 g/day and 3 g/day capsule, going from 45.03 ± 6.28 to 63.63 ± 9.59 and from 41.89 ± 9.83 to 88.90 ± 36.05, respectively. All changes in β-cell function were not statistically significant.
|
Nigella sativa at dose 2 g/day significantly improves diabetic control when combined with oral antidiabetic drug.
|
|
[21]
|
Interventional study (pre-post study).
|
Nigella sativa tea. Extract by hot water. The tea was 5 g/day for 6 months.
|
Sixty-six T2DM patients divided into 2 groups. Forty-one T2DM patients (diabetic group) and 25 healthy peoples (normal group). T2DM patients combined their oral antidiabetic drug with Nigella sativa tea.
|
|
Analysis of blood samples: FBG; 2hPG; HbA1c, kidney function test (serum creatinine), kidney function test (blood urea), liver function test (AST), liver function test (ALT), serum total bilirubin, direct bilirubin, and indirect bilirubin.
|
(a) FBG for the normal group: FBG significantly decreased from 80.22 ± 10.8 to 78.14 ± 10.3 after 1 month, highly significant decrease to 76.79 ± 8.66 after 2 months, very highly significant decrease to 75.30 ± 8.97 after 3 months and after 6 months to 73.34 ± 8.71. FBG for the diabetic group: Very highly significant decrease in FBG for all months from 148.7 ± 26.59 to 137.93 ± 28.36 after 1 month, to 131.64 ± 26.33 after 2 months, to 126.46 ± 23.14 after 3 months, and to 127.67 ± 22.01 after 6 months. Nigella sativa tea significantly decreased FBG for the diabetic group after 3 months, and also 6 months for normal group. (b) 2hPG for the normal group: Very highly significant decrease in 2hPG for all months from 101.13 ± 15.25 to 96.01 ± 14.12 after 1 month, to 93.16 ± 12.93 after 2 months, to 92.20 ± 13.58 after 3 months, and 89.49 ± 12.38 after 6 months. 2hPG for the diabetic group: Very highly significant decrease in 2hPG for all months from 251.42 ± 76.88 to 216.39±61.09 after 1 months, to 192.86 ± 46.11 after 2 months, to 174.27 ± 36.60 after 3 months, and to 164.12 ± 28.72 after 6 months. Nigella sativa tea very highly significant decrease in 2hPG for normal and diabetic groups. (c) HbA1c for the normal group: No significant decrease in HbA1c from 4.43±0.36 to 4.26 ± 0.51 after 3 months, highly significant decrease to 4.14 ± 0.47 after 6 months. HbA1c for the diabetic group: Very highly significant decrease in HbA1c from 7.18 ± 0.83 to 6.59 ± 0.62 after 3 months and to 6.02 ± 0.58 after 6 months. Nigella sativa tea very highly significant decrease in HbA1c after 3 and 6 months treatment.
|
Nigella sativa tea extract 5 g/day showed improvement in blood glucose levels and when combined with oral antidiabetic drug.
|
|
[16]
|
Randomized, double-blind, and controlled trial.
|
Nigella sativa oil purchased from local market in Tehran city. Cold press procedure is used to produce the Nigella sativa oil. 5 mL Nigella sativa per day for 3 months.
|
Seventy T2DM patients divided into 2 groups of 35 each. Group 1 (Nigella sativa group - Nigella sativa oil), group 2 (placebo group-mineral oil). All subjects taken oral antidiabetic drug combined with Nigella sativa oil.
|
|
Analysis of blood samples: FBG, 2hPG, HbA1C, creatinine, cholesterol, triglyceride, high-density lipoproteins (HDL); low-density lipoproteins (LDL), body mass index (BMI), serum glutamic oxaloacetic transaminase (SGOT), serum glutamic pyruvic transaminase (SGPT), and alkaline phosphatase (ALP).
|
(a) FBG for group 1: Significant decrease in FBG from 180.2 ± 31.8 to 161.9 ± 45.3. FBG for group 2: Increased FBG from 179.8 ± 32.3 to 186.3 ± 42.1. Nigella sativa oil significantly decreased FBG after treatment combined with oral antidiabetic drug. (b) 2hPG for group 1: Significant decrease in 2hPG from 183.0 ± 38.7 to 167.9 ± 37.5. 2hPG for group 2: Increase in 2hPG from 189.7 ± 42.8 to 192.2 ± 41.7. Nigella sativa oil significantly decreased 2hPG for Group 1. (c) HbA1c for group 1: Significant decrease in HbA1c from 8.82 ± 0.73 to 8.52 ± 0.68. HbA1c for group 2: Decrease in HbA1c from 8.79 ± 0.55 to 8.70 ± 0.67. Nigella sativa oil significantly decreased HbA1c for Group 1.
|
Nigella sativa oil at dose 5 mL significantly decreased FBG levels, 2hPG, and HbA1c when combined with oral antidiabetic drug.
|
|
[18]
|
Randomized, single-blind, and controlled trial.
|
Nigella sativa seeds as powder in capsules of 500 mg (Sri Lanka). Dose used in this study was 2 g/day.
|
One-hundred-and-fourteen T2DM patients divided into 2 groups. Fifty-seven patients in control group (Charcoal capsule) and 57 patients in Nigella sativa group. Results were taken every 3 months until 1 year. All patients continued their own oral antidiabetic drug.
|
|
Analysis of blood samples: FBG, HbA1c, insulin resistance (IR), β-cell activity, C-peptide, total antioxidant capacity (TAC), superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase (CAT), and glutathione and thiobarbituric acid reactive substances (TBARS).
|
(a) FBG for the Nigella sativa group: Significant decrease in FBG from 195 ± 6.57 to 163 ± 6.31 after 3 months, to 164 ± 5.97 after 6 months, to 176 ± 6.59 after 9 months, and to 172 ± 5.83 after 12 months. FBG for the control group: Increase in FBG from 180 ± 5.75 to 184 ± 5.81 after 3 months, to 185 ± 5.59 after 6 months, to 183 ± 5.41 after 9 months, and to 180 ± 5.59 after 12 months. Nigella sativa capsule significant decrease FBG after 3, 6, 9, and 12 months for the Nigella sativa group. (b) HbA1c for the Nigella sativa group: Significant decrease in HbA1c from 8.6 ± 0.13 to 7.9 ± 0.18 after 3 months, to 7.8 ± 0.22 after 6 months, to 7.9 ± 0.19 after 9 months, and to 8.2 ± 0.14 after 12 months. HbA1c for the control group: Increase in HbA1c from 8.2 ± 0.12 to 8.3 ± 0.12 after 3 months, to 8.3 ± 0.13 after 6 months, to 8.5 ± 0.15 after 9 months, and to 8.5 ± 0.14 after 12 months. Nigella sativa capsule significantly decreased HbA1c after 3, 6, 9, and 12 months for the Nigella sativa group. (c) Insulin resistance (IR) for the Nigella sativa group: Significant decrease in insulin resistance from 3.0±0.24 to 2.5±0.16 after 3 months, to 2.4 ± 0.17 after 6 months, to 2.5 ± 0.19 after 9 months, and to 2.5 ± 0.18 after 12 months. IR for the control group: Increase in insulin resistance from 2.5 ± 0.17 to 2.6 ± 0.16 after 3 months, to 2.7 ± 0.19 after 6 months, to 2.7 ± 0.16 after 9 months, and to 2.5 after 12 months. Nigella sativa capsule significantly decreased insulin resistance after 3, 6, 9, and 12 months for the Nigella sativa group.
|
Nigella sativa capsule 2 g/day significantly decreased FBG, HbA1c, insulin resistance (IR) when combined with oral antidiabetic drug.
|
|
[20]
|
Randomized, single-blind, and controlled trial.
|
Nigella sativa powdered 2 g/day for 1 year.
|
Sixty T2DM patients divided into a control group that received charcoal and test group that received Nigella sativa powdered. Combined with oral antidiabetic drug.
|
|
Analysis of blood samples: HbA1c, BMI, pulse rate, and mean arterial pressure (MAP).
|
(a) HbA1c for the test group: Significant decrease in HbA1c from 8.84 ± 0.96 to 8.40 ± 1.07 after 12 months. Decrease in HbA1c from 8.78 ± 0.95 to 8.14 ± 1.69 after 6 months. HbA1c for the control group: Increase in HbA1c from 8.14 ± 0.79 to 8.28 ± 0.80 after 6 months. Increase in HbA1c from 8.18 ± 0.77 to 8.26 ± 0.90 after 12 months.
|
Nigella sativa powdered 2 g/day for 1 year significantly decreased HbA1c when combined with oral antidiabetic drug.
|
|
[15]
|
Randomized, double-blind, and controlled trial.
|
Nigella sativa oil in soft gel capsule 3 g/day for 12 weeks.
|
Seventy-two T2DM patients. Thirty-six participants in the intervention group received Nigella sativa oil, and 36 participants in control group received sunflower soft gel capsules. Combined with oral antidiabetic drug.
|
|
Analysis of blood samples: FBG, HbA1c, insulin, Homeostatic Model Assessment of Insulin Resistance (HOMA-IR), triglyceride, total cholesterol, HDL-cholesterol, and LDL-cholesterol.
|
(a) FBG for the intervention group: Significant decrease in FBG from 183.4 ± 42.1 to 166.3 ± 38.5. FBG for the control group: Increase in FBG from 201.8 ± 63.9 to 204.9 ± 63.2. Nigella sativa soft gel capsule significantly decreased FBG. (b) HbA1c for the
intervention group: Significant decrease in HbA1c from 8.3 ± 0.9 to 7.8 ± 0.8. HbA1c for the control group: Increase in HbA1c from 8.3 ± 1.0 to 8.6 ± 1.0 Nigella sativa soft gel capsule significantly decreased HbA1c. |
Nigella sativa oil in soft gel capsule 3 g/day significantly decreased FBG and HbA1c when combined with oral antidiabetic drug.
|
표 1
Nigella sativa 가 제2형 당뇨병에 미치는 영향.
|
참조
|
연구 설계
|
나이젤라 사티바 의 종류
|
방법론
|
T2DM 관련 생화학적 결과
|
결론
|
|
|
치료군
|
생화학적 분석
|
|||||
|
[ 17 ]
|
중재 연구(사후 연구).
|
나이젤라 사티바 오일( 파키스탄 라왈핀디에서 구입한 나이젤라 사티 바 씨앗 0.7g )을 40일간 경구 섭취합니다.
|
41명의 T2DM 환자는 1차 40일(NS 치료) 동안 나이젤라 사티바 오일을 섭취한 후 2차 40일(위약) 동안 밀기울을 섭취하고, 일반적인 경구용 항당뇨병제를 일정한 용량으로 병용했습니다.
|
혈액 샘플 분석: 공복 혈당(FBG), 인슐린 수치 혈액 요소, 혈소판 수, 총 백혈구 수(TLC), 혈청 알라닌 아미노트랜스퍼라제(ALT) 및 혈청 아스파르테이트 아미노트랜스퍼라제(AST).
|
FBG는 1차 치료 후 190.780 ± 8.042 mg/dL에서 168.317 ± 7.150 mg/dL로 크게 감소했다가 2차 치료 후 다시 186.487 ± 7.491 mg/dL로 크게 증가했습니다.
유의미하지는 않지만, 인슐린 수치는 1차 치료 후 8.013 ± 0.758 lU/mL에서 13.194 ± 1.404 ulU/mL로 증가한 후 2차 치료 후 8.850 ± 0.694 ulU/mL로 다시 감소했습니다. |
나이젤라 사티바 오일은 경구 항당뇨병제와 병용했을 때 FBG를 감소시키고 인슐린 수치를 증가시켰습니다.
|
|
[ 19 ]
|
중재 연구(사후 연구).
|
캡슐에 들어 있는 Nigella sativa 씨앗(Bioextract (Pvt) Ltd, 스리랑카)에는 분쇄된 Nigella sativa 500mg이 포함되어 있으며 12주 동안 하루 1, 2, 3g의 세 가지 용량으로 경구 섭취할 수 있습니다.
|
94명의 T2DM 환자를 무작위로 3개 그룹으로 나누었습니다. 30명의 환자는 1g/일 용량을, 32명의 환자는 2g/일 용량을, 32명의 환자는 4주, 8주 및 12주 동안 경구용 항당뇨병제와 함께 3g/일 용량을 투여받았습니다.
|
혈액 샘플 분석: FBG, 식후 2시간 혈당 수치(2hPG), 당화혈색소(HbA1c), 인슐린 저항성 지수, 베타 세포 기능, 혈청 C-펩타이드 및 체질량 지수(BMI).
|
(a) 0주, 4주, 8주 및 12주차의 FBG는 1g/일 캡슐에서 각각 189 ± 14.3, 186 ± 38, 171 ± 10.1 및 171 ± 7.8 mg/dL로 유의미한 변화를 나타내지 않았습니다. 2g/일 캡슐을 사용하면 0주, 4주, 8주, 12주차의 FBG가 219 ± 12.3, 174 ± 10.1, 157 ± 10.8에서 162 ± 9.2 mg/dL로 크게 감소한 것으로 나타났습니다. 3g/일 캡슐을 사용하면 0주, 4주, 8주 및 12주차의 FBG가 각각 204 ± 18.2, 176 ± 15.2, 157 ± 9.9, 169 ± 16.4 mg/dL로 유의하게 감소한 것으로 나타났습니다. (b) 0주, 4주, 8주 및 12주차의 2hPG 수준은 각각 286 ± 23.3, 244 ± 22.5, 241 ± 19.2 및 218 ± 15.6 mg/dL의 판독값으로 1g/일 캡슐에서 변화하지 않았습니다. 2g/일 캡슐을 사용하면 0주, 4주, 8주 및 12주차의 2hPG 수치가 각각 289 ± 24.2, 213 ± 27.8, 231 ± 26.58 및 256 ± 28.1 mg/dL로 크게 감소했습니다. 중요하지는 않지만, 2hPG 수치는 3g/일 캡슐로 증가했으며, 0주차, 4주차, 8주차, 12주차 수치는 각각 277±54.3, 301±54.3, 229±9.9, 234±80.3mg/dL이었습니다. (c) 12주차의 HbA1c는 1일 1g 캡슐 사용 시 기준선보다 크게 감소하지 않았으며 판독값은 8.36 ± 0.31 ~ 8.01 ± 0.27%였습니다. 2g/일 캡슐 사용 시 HbA1c는 9.09 ± 0.24에서 7.57 ± 0.30%로 크게 감소했습니다. 3g/일 캡슐 사용 시 HbA1c는 9.35 ± 0.41에서 7.31 ± 0.37%로 크게 감소했습니다. (d) 인슐린 저항성 지수는 1g/일 캡슐 사용 시 2.75 ± 0.34에서 2.82 ± 0.26으로 크게 변하지 않았습니다. 1일 2g 캡슐 투여 시 인슐린 저항성 지수는 12주차 3.20±0.36에서 2.37±0.20으로 유의하게 감소했습니다. 유의미하지는 않지만 3g/일 캡슐을 사용하면 인슐린 저항성 지수가 12주차에 4.11 ± 0.55에서 2.98 ± 0.49로 증가했습니다. (e) β 세포 기능은 1g/일 캡슐에서 61.75 ± 7.79에서 59.12 ± 8.19로 감소한 반면, 2g/일 및 3g/일 캡슐에서는 45.03 ± 6.28에서 63.63 ± 9.59로, 41.89에서 증가했습니다. 각각 ± 9.83 ~ 88.90 ± 36.05. β-세포 기능의 모든 변화는 통계적으로 유의하지 않았습니다.
|
Nigella sativa를 하루 2g씩 경구 항당뇨병제와 병용하면 당뇨병 조절이 크게 향상됩니다.
|
|
[ 21 ]
|
중재 연구(사후 연구).
|
나이젤라 사티 바 차. 뜨거운 물로 추출합니다. 차는 6개월 동안 하루 5g씩 섭취했습니다.
|
66명의 T2DM 환자를 2개의 그룹으로 나누었습니다. 41명의 T2DM 환자(당뇨병 그룹)와 25명의 건강한 사람(정상 그룹). T2DM 환자는 경구용 항당뇨병제와 Nigella sativa 차를 병용했습니다.
|
혈액 샘플 분석: FBG; 2hPG; HbA1c, 신장 기능 검사(혈청 크레아티닌), 신장 기능 검사(혈액 요소), 간 기능 검사(AST), 간 기능 검사(ALT), 혈청 총 빌리루빈, 직접 빌리루빈, 간접 빌리루빈.
|
(a) 정상군의 FBG: FBG는 80.22±10.8에서 1개월 후 78.14±10.3으로 유의하게 감소하였고, 2개월 후에는 76.79±8.66으로 매우 유의하게 감소하였고, 3개월 후와 6개월 후에는 75.30±8.97로 매우 유의하게 감소하였다. 73.34 ± 8.71. 당뇨병군의 FBG: 1개월 후 148.7±26.59에서 137.93±28.36으로, 2개월 후 131.64±26.33, 3개월 후 126.46±23.14, 6개월 후 127.67±22.01로 모든 달 동안 FBG가 매우 유의미하게 감소했습니다. 개월. 나이젤라 사티바차는 당뇨병 그룹의 경우 3개월 후, 정상 그룹의 경우 6개월 후에 FBG를 유의하게 감소시켰습니다. (b) 정상 그룹의 2hPG: 1개월 후 101.13 ± 15.25에서 96.01 ± 14.12로, 2개월 후 93.16 ± 12.93으로, 3개월 후 92.20 ± 13.58로, 89.49 ± 12.38로 모든 달에 걸쳐 2hPG의 매우 매우 유의미한 감소 6개월 후. 당뇨병 환자군의 2hPG: 1개월 후 251.42 ± 76.88에서 216.39±61.09로, 2개월 후 192.86 ± 46.11로, 3개월 후 174.27 ± 36.60으로, 6개월 후 164.12 ± 28.72로 모든 달에 걸쳐 2hPG가 매우 매우 유의미하게 감소했습니다. 개월. 나이젤라 사티바차는 정상 및 당뇨병 그룹의 경우 2hPG가 매우 크게 감소했습니다. (c) 정상군의 HbA1c: 3개월 후 HbA1c는 4.43±0.36에서 4.26±0.51로 유의한 감소가 없었고, 6개월 후 4.14±0.47로 매우 유의하게 감소하였다. 당뇨병 그룹의 HbA1c: HbA1c가 3개월 후 7.18 ± 0.83에서 6.59 ± 0.62로, 6개월 후 6.02 ± 0.58로 매우 매우 유의하게 감소했습니다. Nigella sativa 차는 3개월 및 6개월 치료 후 HbA1c가 매우 크게 감소했습니다.
|
나이젤라 사티 바 차 추출물 5g/일은 경구용 항당뇨병제와 병용했을 때 혈당 수치가 개선된 것으로 나타났습니다.
|
|
[ 16 ]
|
무작위, 이중 맹검 및 대조 시험.
|
나이젤라 사티 바 오일은 테헤란 시내 시장에서 구입했습니다. Nigella sativa 오일을 생산하려면 냉간 압착 공정이 사용됩니다 . 3개월 동안 매일 Nigella sativa 5mL를 투여합니다 .
|
70명의 T2DM 환자를 각각 35명씩 두 그룹으로 나눴습니다. 그룹 1( 나이젤라 사티바 그룹 - 나이젤라 사티 바 오일), 그룹 2( 위약 그룹 - 미네랄 오일). 모든 피험자는 Nigella sativa 오일과 결합된 경구 항당뇨병 약물을 복용했습니다.
|
혈액 샘플 분석: FBG, 2hPG, HbA1C, 크레아티닌, 콜레스테롤, 중성지방, 고밀도 지질단백질(HDL); 저밀도 지질단백질(LDL), 체질량 지수(BMI), 혈청 글루타민산 옥살로아세트산 트랜스아미나제(SGOT), 혈청 글루타민산 피루브산 트랜스아미나제(SGPT) 및 알칼리성 포스파타제(ALP).
|
(a) 그룹 1의 FBG: FBG가 180.2 ± 31.8에서 161.9 ± 45.3으로 크게 감소했습니다. 그룹 2의 FBG: FBG가 179.8 ± 32.3에서 186.3 ± 42.1로 증가했습니다. 나이젤라 사티바 오일은 경구용 항당뇨병제와 병용 치료 후 FBG를 크게 감소시켰습니다. (b) 그룹 1의 2hPG: 2hPG가 183.0 ± 38.7에서 167.9 ± 37.5로 크게 감소했습니다. 그룹 2의 경우 2hPG: 2hPG가 189.7 ± 42.8에서 192.2 ± 41.7로 증가합니다. 나이젤라 사티 바 오일은 그룹 1의 경우 2hPG를 크게 감소시켰습니다. (c) 그룹 1의 HbA1c: HbA1c가 8.82 ± 0.73에서 8.52 ± 0.68로 크게 감소했습니다. 그룹 2의 HbA1c: HbA1c가 8.79 ± 0.55에서 8.70 ± 0.67로 감소합니다. 나이젤라 사티 바 오일은 그룹 1의 HbA1c를 크게 감소시켰습니다.
|
나이젤라 사티바 오일 5mL 용량은 경구 항당뇨병제와 병용했을 때 FBG 수준, 2hPG 및 HbA1c를 크게 감소시켰습니다.
|
|
[ 18 ]
|
무작위, 단일 맹검 및 대조 시험.
|
Nigella sativa 씨앗은 500mg 캡슐에 분말로 들어 있습니다(스리랑카). 본 연구에 사용된 용량은 2g/일이었습니다.
|
141명의 T2DM 환자를 2개의 그룹으로 나누었습니다. 대조군(숯 캡슐) 환자는 57명, Nigella sativa 환자는 57명이었습니다 . 결과는 1년까지 3개월마다 수집되었습니다. 모든 환자는 자신의 경구용 항당뇨병 약물을 계속 복용했습니다.
|
혈액 샘플 분석: FBG, HbA1c, 인슐린 저항성(IR), β세포 활성, C-펩타이드, 총 항산화 능력(TAC), 슈퍼옥사이드 디스뮤타제(SOD), 카탈라제(CAT), 글루타티온 및 티오바르비투르산 반응 물질( TBARS).
|
(a) Nigella sativa 그룹의 FBG: 3개월 후 195 ± 6.57에서 163 ± 6.31로, 6개월 후 164 ± 5.97, 9개월 후 176 ± 6.59, 12개월 후 172 ± 5.83으로 FBG가 크게 감소했습니다. . 대조군의 FBG: FBG가 180±5.75에서 3개월 후 184±5.81로, 6개월 후 185±5.59, 9개월 후 183±5.41, 12개월 후 180±5.59로 증가했습니다. Nigella sativa 캡슐은 Nigella sativa 그룹 의 경우 3, 6, 9, 12개월 후에 FBG를 유의하게 감소시켰습니다 . (b) Nigella sativa 의 HbA1c그룹: HbA1c가 3개월 후 8.6±0.13에서 7.9±0.18로, 6개월 후 7.8±0.22, 9개월 후 7.9±0.19, 12개월 후 8.2±0.14로 크게 감소했습니다. 대조군의 HbA1c: HbA1c는 3개월 후 8.2±0.12에서 8.3±0.12로, 6개월 후 8.3±0.13, 9개월 후 8.5±0.15, 12개월 후 8.5±0.14로 증가했습니다. Nigella sativa 캡슐은 Nigella sativa 그룹 의 경우 3, 6, 9, 12개월 후에 HbA1c를 유의하게 감소시켰습니다 . (c) Nigella sativa 에 대한 인슐린 저항성(IR)그룹: 3개월 후 3.0±0.24에서 2.5±0.16으로, 6개월 후 2.4±0.17, 9개월 후 2.5±0.19, 12개월 후 2.5±0.18로 인슐린 저항성이 크게 감소했습니다. 대조군의 IR: 3개월 후 2.5±0.17에서 2.6±0.16으로, 6개월 후 2.7±0.19, 9개월 후 2.7±0.16, 12개월 후 2.5로 인슐린 저항성이 증가했습니다. Nigella sativa 캡슐은 Nigella sativa 그룹 의 경우 3, 6, 9, 12개월 후에 인슐린 저항성을 유의하게 감소시켰습니다 .
|
Nigella sativa 캡슐 2g/일은 경구용 항당뇨병제와 병용 시 FBG, HbA1c, 인슐린 저항성(IR)을 크게 감소시켰습니다.
|
|
[ 20 ]
|
무작위, 단일 맹검 및 대조 시험.
|
Nigella sativa 가루로 1년 동안 하루 2g씩 섭취하세요.
|
60명의 T2DM 환자를 숯을 투여받은 대조군과 Nigella sativa 분말을 투여한 시험군으로 나누었습니다. 경구용 항당뇨병제와 병용.
|
혈액 샘플 분석: HbA1c, BMI, 맥박수 및 평균 동맥압(MAP).
|
(a) 시험군의 HbA1c: 12개월 후 HbA1c가 8.84±0.96에서 8.40±1.07로 유의하게 감소함. 6개월 후 HbA1c가 8.78 ± 0.95에서 8.14 ± 1.69로 감소했습니다. 대조군의 HbA1c: 6개월 후 HbA1c가 8.14 ± 0.79에서 8.28 ± 0.80으로 증가했습니다. 12개월 후 HbA1c가 8.18 ± 0.77에서 8.26 ± 0.90으로 증가했습니다.
|
Nigella sativa 분말 2g/일을 1년 동안 경구용 항당뇨병제와 병용했을 때 HbA1c가 크게 감소했습니다.
|
|
[ 15 ]
|
무작위, 이중 맹검 및 대조 시험.
|
나이젤라 사티바 오일을 연질 젤 캡슐로 12주 동안 하루 3g씩 섭취합니다.
|
72명의 T2DM 환자. 중재 그룹의 36명의 참가자는 나이젤라 사티바 오일을 받았고, 대조군의 36명의 참가자는 해바라기 연질 젤 캡슐을 받았습니다. 경구용 항당뇨병제와 병용.
|
혈액 샘플 분석: FBG, HbA1c, 인슐린, 인슐린 저항성의 항상성 모델 평가(HOMA-IR), 중성지방, 총 콜레스테롤, HDL-콜레스테롤 및 LDL-콜레스테롤.
|
(a) 개입 그룹의 FBG: FBG가 183.4±42.1에서 166.3±38.5로 크게 감소했습니다. 대조군의 FBG: FBG가 201.8±63.9에서 204.9±63.2로 증가했습니다. Nigella sativa 연질 젤 캡슐은 FBG를 크게 감소시켰습니다. (b)
중재 그룹의 HbA1c: HbA1c가 8.3 ± 0.9에서 7.8 ± 0.8로 크게 감소했습니다. 대조군의 HbA1c: HbA1c가 8.3 ± 1.0에서 8.6 ± 1.0으로 증가했습니다. Nigella sativa 연질 젤 캡슐은 HbA1c를 크게 감소시켰습니다. |
연질 젤 캡슐 3g/일의 나이젤라 사티바 오일은 경구용 항당뇨병제와 병용했을 때 FBG 및 HbA1c를 크게 감소시켰습니다.
|
In this study, we reviewed the analysis of blood samples such as fasting blood glucose (FBG), blood glucose level 2 h postprandial (2hPG), glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c), as well as insulin level and insulin resistance.
이 연구에서는 공복 혈당(FBG), 식후 2시간 혈당 수치(2hPG), 당화혈색소(HbA1c), 인슐린 수치 및 인슐린 저항성과 같은 혈액 샘플 분석을 검토했습니다.
1알에 1000mg, 냉압착으로 착유한 터키산 블랙오일~
3.3. Fasting Blood Glucose (FBG) (공복 혈당(FBG))
From the seven studies reviewed, six studies measured the changes of the fasting blood glucose (FBG) parameter. According to Ahmad et al. (2009), FBG levels significantly decreased after treatment with NS oil for 40 days [17]. Bamosa et al. (2010) showed a significant reduction in FBG after 12 weeks of treatment with 2 g/day NS [19]. El-Shamy et al. (2011) reported a highly significant reduction of FBG in patients receiving 5 gm/day of NS tea for 6 months [21]. Hosseini et al. (2013) recorded a significant FBG decrease in the group receiving 2.5 mL NS oil [16]. Kaatabi et al. (2015) also recorded a highly significant decrease in FBG after 12 months of treatment with NS capsule 2 g/day, and Heshmati et al. (2015) showed a significant decrease in FBG levels after treatment with NS oil in soft gel capsule 3 g/day for 12 weeks [15,18].
검토된 7건의 연구 중 6건의 연구에서 공복 혈당(FBG) 매개변수의 변화를 측정했습니다. (2009)에 따르면, 40일 동안 NS 오일로 치료한 후 FBG 수치가 유의하게 감소했다고 합니다[17]. Bamosa 등(2010)은 2g/일 NS로 12주간 치료한 후 FBG가 유의하게 감소한 것으로 나타났습니다[19]. El-Shamy 등(2011)은 6개월 동안 5g/일 NS 차를 투여한 환자에서 FBG가 매우 유의미하게 감소했다고 보고했습니다[21]. 호세이니 등(2013)은 2.5mL NS 오일을 투여한 그룹에서 유의미한 FBG 감소를 기록했습니다[16]. Kaatabi 등(2015)도 NS 캡슐 2g/일 치료 12개월 후 FBG가 매우 유의미하게 감소했으며, Heshmati 등(2015)은 12주 동안 연질 젤 캡슐 3g/일 NS 오일로 치료한 후 FBG 수치가 유의미하게 감소했다고 보고했습니다[15,18].
3.4. Blood Glucose Level 2 h Postprandial (2hPG) (식후 2시간 혈당 수치(2hPG))
Of the seven studies reviewed, three articles studied the blood glucose level 2 h postprandial (2hPG) parameter. Bamosa et al. (2010) reported a significant decrease in 2hPG after 4 and 8 weeks of treatment with 2 g/day NS [19]. El-Shamy et al. (2011) also recorded a decrease in 2hPG levels after consumption of 5 gm/day NS tea for 6 months [21]. Meanwhile, Hosseini et al. (2013) revealed a significant decrease in 2hPG levels in the group receiving 2.5 mL NS oil compared with the placebo group [16].
검토된 7건의 연구 중 3건의 논문은 식후 2시간 혈당 수치(2hPG) 매개변수를 연구했습니다. Bamosa 등(2010)은 2g/일 NS로 4주 및 8주 치료 후 2hPG가 유의하게 감소했다고 보고했습니다[19]. El-Shamy 등(2011)도 6개월 동안 5g/일 NS 차를 섭취한 후 2hPG 수치가 감소했다고 기록했습니다[21]. 한편, 호세이니 등(2013)은 위약 그룹에 비해 2.5mL NS 오일을 투여한 그룹에서 2hPG 수치가 유의하게 감소했다고 밝혔습니다[16].
3.5. Glycated Hemoglobin (HbA1c) (당화 헤모글로빈(HbA1c))
Of the seven papers reviewed, six articles investigated HbA1c. Bamosa et al. (2010) reported a significant decrease in HbA1c levels following 12 weeks treatment with 2 g/day and 3 g/day of NS [19]. El Shamy et al. (2011) showed a significant decrease of HbA1c levels after consumption of 5 gm/day NS tea for 6 months [21]. Hosseini MS et al. (2013) also reported NS oil at dose 5 mL/day significantly decreased HbA1c levels, which is in line with Kaatabi et al. (2015) who reported treatment with NS capsule 2 g/day significantly decreased HbA1c levels after 12 months treatment [16,18]. Heshmati et al. (2015) and Bamosa et al. (2015) also showed similar findings with the treatment of NS significantly reducing the HbA1c levels [15,20].
검토된 7편의 논문 중 6편의 논문이 당화혈색소(HbA1c)를 조사했습니다. Bamosa 등(2010)은 2g/일 및 3g/일 NS로 12주간 치료한 후 당화혈색소 수치가 유의하게 감소했다고 보고했습니다[19]. 엘 샤미 등(2011)은 6개월 동안 5g/일 NS 차를 섭취한 후 HbA1c 수치가 유의하게 감소했다고 보고했습니다[21]. Hosseini MS 등(2013)도 NS 오일 5mL/일 용량이 HbA1c 수치를 유의하게 감소시켰다고 보고했는데, 이는 12개월 치료 후 NS 캡슐 2g/일 치료가 HbA1c 수치를 유의하게 감소시켰다고 보고한 Kaatabi 등(2015)의 연구와 일치합니다[16,18]. Heshmati 등(2015)과 Bamosa 등(2015)도 NS 치료가 HbA1c 수치를 유의하게 감소시킨다는 유사한 결과를 보여주었습니다[15,20].
3.6. Insulin Level and Insulin Resistance (인슐린 수치와 인슐린 저항성)
Of the seven papers reviewed, four articles studied insulin level and insulin resistance. Ahmad et al. (2009) showed that the insulin levels significantly increased after treatment with NS oil for 40 d [17]. NS at dose 2 g/day significantly decreased insulin resistance index and increased β-cell function after 12 weeks of treatment [19]. According to Kaatabi et al. (2015), 2 g/day NS capsule significantly decreased insulin resistance after 3, 6, 9, and 12 months treatment [18]. Meanwhile, Hesmati et al. (2015) revealed that insulin levels and insulin resistance decreased in the intervention group, but they were not significant after adjusting for confounder factors [15].
검토 된 7 개의 논문 중 4 개의 논문은 인슐린 수치와 인슐린 저항성을 연구했습니다. Ahmad 등 (2009)은 40 일 동안 NS 오일로 치료 한 후 인슐린 수치가 유의하게 증가했음을 보여주었습니다 [17]. 2 g / 일 용량의 NS는 12 주 치료 후 인슐린 저항성 지수를 유의하게 감소시키고 β 세포 기능을 증가시켰습니다 [19]. Kaatabi 등(2015)에 따르면, 2g/일 NS 캡슐은 3, 6, 9, 12개월 치료 후 인슐린 저항성을 유의하게 감소시켰다고 합니다[18]. 한편, 헤스마티 등(2015)은 중재군에서 인슐린 수치와 인슐린 저항성이 감소했지만 교란 요인을 조정한 후에는 유의하지 않다고 밝혔습니다[15].
블랙씨드 오일 구매는 '뷰티텐더 블랙씨드(캡슐타입)'로~
4. Discussion (논의)
Plants have long been used as medicinal herbs in Arabian countries, Asia, and Africa [22]. To date, there has been growing attention on the use of medicinal herbs as an alternative to the standard care in treating diseases, mainly diabetes. Extensive investigations have been conducted to evaluate the potential of medicinal herbs in treating diseases. Only 15% of the total of 300,000 medicinal herbs have been explored for their pharmacological properties [23]. Among the various naturally medicinal herbs, Nigella sativa (NS) has a promising future in the prevention and treatment of diabetic diseases due to its capacity to treat multiple diseases, as well as being cost-efficient and having fewer side effects compared to synthetic medicines [24].
식물은 아라비아 국가, 아시아 및 아프리카에서 오랫동안 약초로 사용되어 왔습니다 [22]. 현재까지 주로 당뇨병과 같은 질병을 치료하는 데 있어 표준 치료의 대안으로 약초를 사용하는 것에 대한 관심이 높아지고 있습니다. 질병 치료에서 약초의 잠재력을 평가하기 위해 광범위한 조사가 수행되었습니다. 총 30만 종의 약초 중 15%만이 약리학적 특성에 대해 연구되었습니다[23]. 다양한 천연 약초 중 니겔라 사티바(NS)는 여러 질병을 치료할 수 있을 뿐만 아니라 합성 의약품에 비해 비용 효율적이고 부작용이 적어 당뇨병 질환의 예방 및 치료에 유망한 미래가 기대됩니다 [24].
In this systematic review, we have assessed the effects of NS supplementation on fasting blood glucose (FBG), blood glucose level 2 h postprandial (2hPG), glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c), insulin level, and insulin resistance. NS was given as an adjuvant therapy in patients with Type-2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) in addition to their oral antidiabetic drug.
이 체계적 문헌고찰에서는 공복 혈당(FBG), 식후 2시간 혈당 수치(2hPG), 당화혈색소(HbA1c), 인슐린 수치, 인슐린 저항성에 대한 NS 보충제의 효과를 평가했습니다. NS는 제2형 당뇨병(T2DM) 환자에게 경구용 항당뇨병제에 추가하여 보조 요법으로 투여되었습니다.
The literature search revealed six studies that showed treatment with different forms of NS caused marked reduction in the level of FBG and HbA1c compared to the control group [15,16,17,18,19,21]. Meanwhile, three studies reported NS treatments significantly reduced 2hPG compared to the corresponding baseline [16,19,21]. These findings reflect the potential use of NS as a complementary treatment for T2DM. This assumption is further confirmed by studies conducted using animal models, in which treatment of NS for 1 month significantly reduced FBG in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats [25]. Reduction in HbA1c levels could also be seen in streptozotocin-nicotinamide induced diabetic rats treated with thymoquinone [26]. Najmi et al. (2008) reported that treatment of 2.5 mL NS oil twice daily for 6 weeks had shown an improvement on FBG, suggesting that NS oil might be a beneficial adjuvant to the oral antidiabetic drug [27]. Besides that, treatment of 1.5 and 3 mL/day NS oil for 20 d resulted in a reduction of HbA1c and FBG levels in patients with metabolic syndrome risks [28]. HbA1c is an indicator of long-term glycemic control due to its ability to reflect the cumulative glycemic history of the preceding 2 to 3 months. It also correlates with the risk of long-term diabetes complications. Thus, a reduction in HbA1c could reduce the risk of diabetes complications [29].
문헌 검색 결과, 다양한 형태의 NS 치료가 대조군에 비해 당화혈색소 및 당화혈색소 수치를 현저하게 감소시키는 것으로 나타난 6건의 연구가 있었습니다[15,16,17,18,19,21]. 한편, 3건의 연구에서 NS 치료가 해당 기준선에 비해 2hPG를 유의하게 감소시켰다고 보고했습니다[16,19,21]. 이러한 결과는 제2형 당뇨병에 대한 보완적 치료로서 NS의 잠재적 사용을 반영합니다. 이 가정은 동물 모델을 사용하여 수행된 연구에서 더욱 확인되었는데, 1개월 동안 NS를 치료하면 스트렙토조토신으로 유도된 당뇨병 쥐의 FBG가 유의하게 감소했습니다[25]. 스트렙토조토신-니코틴아미드로 유도된 당뇨병 쥐에 티모퀴논을 처리한 경우에도 당화혈색소 수치가 감소하는 것을 볼 수 있었습니다[26]. Najmi 등(2008)은 2.5mL의 NS 오일을 6주 동안 매일 2회 투여한 결과 FBG가 개선되었다고 보고했는데, 이는 NS 오일이 경구용 항당뇨제에 유익한 보조제가 될 수 있음을 시사합니다[27]. 그 외에도 대사증후군 위험이 있는 환자에게 1.5mL 및 3mL/일 NS 오일을 20일간 투여한 결과, HbA1c 및 FBG 수치가 감소했습니다[28]. HbA1c는 이전 2~3개월의 누적 혈당 이력을 반영할 수 있기 때문에 장기적인 혈당 조절의 지표로 사용됩니다. 또한 장기적인 당뇨병 합병증 위험과도 관련이 있습니다. 따라서 당화혈색소 수치를 낮추면 당뇨병 합병증의 위험을 줄일 수 있습니다[29].
It has been reported that chronic elevation of blood glucose promotes oxidative stress through overproduction of reactive oxygen species (ROS). Excessive levels of ROS cause an increase in insulin resistance and β-cell dysfunction, thus contributing to the advancement of diabetic complications [30,31,32]. Pancreatic β-cells are easily destructed by oxidative stress due to the low level of free-radical quenching enzymes, which will decrease insulin secretion [33].
만성적인 혈당 상승은 활성 산소 종(ROS)의 과잉 생성을 통해 산화 스트레스를 촉진하는 것으로 보고되었습니다. 과도한 수준의 ROS는 인슐린 저항성과 베타 세포 기능 장애를 증가시켜 당뇨병 합병증의 진행에 기여합니다[30,31,32]. 췌장 베타 세포는 낮은 수준의 활성 산소 소거 효소로 인해 산화 스트레스에 의해 쉽게 파괴되어 인슐린 분비를 감소시킵니다 [33].
Most of the studies reviewed demonstrated NS supplementation combined with oral antidiabetic drugs enhanced glycemic control manifested by improvement in pancreatic β-cell function and insulin resistance compared to the corresponding baseline. Based on findings by Bamosa et al. (2010), the insulin resistance was significantly reduced by 2 g daily supplementation of NS [19]. The same treatment of NS also produced a significant increase in β-cell function. These findings were in line with the study by Nehar and Kumari (2013), which showed the NS seed extract can ameliorate insulin resistance, thus reducing blood glucose levels [34]. Besides that, Fararh et al. (2004) also highlighted the treatment of NS oil for 4 weeks in streptozotocin plus nicotinamide-induced diabetic hamsters caused a significant increase in serum insulin levels [35]. These hypoglycemic effects of NS have been reported to be regulated through the activation of insulin and AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) pathways [36].
검토된 대부분의 연구에서 NS 보충제를 경구용 항당뇨제와 함께 복용하면 해당 기준선에 비해 췌장 베타세포 기능과 인슐린 저항성이 개선되어 혈당 조절이 향상되는 것으로 나타났습니다. Bamosa 등(2010)의 연구 결과에 따르면, NS를 매일 2g씩 보충하면 인슐린 저항성이 현저히 감소했습니다[19]. 동일한 NS 치료는 또한 베타 세포 기능을 크게 증가시켰습니다. 이러한 결과는 NS 종자 추출물이 인슐린 저항성을 개선하여 혈당 수치를 낮출 수 있음을 보여준 Nehar와 Kumari (2013)의 연구와 일치했습니다 [34]. 그 외에도 Fararh 등(2004)은 스트렙토조토신과 니코틴아미드로 유도한 당뇨병 햄스터에 4주간 NS 오일을 처리한 결과 혈청 인슐린 수치가 유의하게 증가했다고 강조했습니다[35]. NS의 이러한 저혈당 효과는 인슐린 및 AMP 활성화 단백질 키나아제(AMPK) 경로의 활성화를 통해 조절되는 것으로 보고되었습니다[36].
Hypoglycemic effects of NS have been attributed to its antioxidant properties [37]. Antioxidants are one of the potential strategies for diabetic treatment. Thymoquinone is a major antioxidant component of NS which possesses antioxidant potential that can scavenge free radicals [38]. It could reduce oxidative stress and promote the proliferation of pancreatic β-cell integrity, thus leading to the improvement in insulin secretion [39]. Besides that, hypoglycemic effects of thymoquinone contribute by its downregulating effect on the gluconeogenic enzymes expression and its ability in reducing intestinal absorption for glucose [40]. It may also inhibit gluconeogenesis via activating adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase (AMPK) in muscles and the liver [41].
NS의 저혈당 효과는 항산화 특성에 기인합니다 [37]. 항산화제는 당뇨병 치료를 위한 잠재적 전략 중 하나입니다. 티모퀴논은 활성 산소를 제거할 수 있는 항산화 잠재력을 가진 NS의 주요 항산화 성분입니다[38]. 산화 스트레스를 줄이고 췌장 베타 세포의 증식을 촉진하여 인슐린 분비를 개선할 수 있습니다 [39]. 그 외에도 티모퀴논의 저혈당 효과는 포도당 생성 효소 발현에 대한 하향 조절 효과와 포도당의 장내 흡수를 감소시키는 능력에 의해 기여합니다 [40]. 또한 근육과 간에서 아데노신 모노포스페이트 활성화 단백질 키나아제(AMPK)를 활성화하여 포도당 생성을 억제할 수도 있습니다[41].
This systematic review also revealed different that forms of Nigella sativa such as oil, water extract, and powder produce similar hypoglycemic effects, in which these treatments resulted in significantly reduced HbA1c levels. This finding suggests that other constituents in Nigella sativa seed also possess the same beneficial properties as thymoquinone which is a major component of NS oil fraction [42].
이 체계적인 검토에 따르면 오일, 물 추출물 및 분말과 같은 니겔라 사티바의 다른 형태도 유사한 저혈당 효과를 나타내며, 이러한 치료법은 HbA1c 수치를 현저히 감소시키는 것으로 나타났습니다. 이 발견은 니겔라 사티바 씨앗의 다른 성분도 NS 오일 분획의 주요 성분인 티모퀴논과 동일한 유익한 특성을 가지고 있음을 시사합니다[42].
Some limitations are notable in this systematic review and must be considered. This current study included a small number of relevant studies. Besides that, all included studies utilized different preparations, doses, and duration of supplementation. Thus, our findings on the efficacies of supplementation of NS in combination with oral antidiabetic drugs should be interpreted with caution.
이 체계적 문헌고찰에는 몇 가지 한계점이 있으므로 이를 고려해야 합니다. 본 연구에서는 소수의 관련 연구만 포함되었습니다. 그 외에도, 포함된 모든 연구는 서로 다른 제제, 용량 및 보충 기간을 사용했습니다. 따라서 경구용 항당뇨병제와 함께 NS를 보충하는 효과에 대한 본 연구 결과는 신중하게 해석해야 합니다.
5. Conclusions (결론)
All studies included in this review reported positive effect of NS on T2DM. NS was showed to improve laboratory parameters of hyperglycemia and diabetes control with a significant fall in fasting blood glucose, and a significant rise in serum insulin. These findings suggest that NS could be used as an adjuvant for oral antidiabetic drugs in diabetes control. However, further studies are needed since it is difficult to determine effective type and dosage of NS in diabetes management due to chemical compositions of different sources of NS, dosage, and duration of intervention.
이 리뷰에 포함된 모든 연구에서 NS가 제2형 당뇨병에 미치는 긍정적인 효과가 보고되었습니다. NS는 공복 혈당을 유의하게 떨어뜨리고 혈청 인슐린을 유의하게 증가시켜 고혈당증과 당뇨병 조절에 대한 실험실 매개변수를 개선하는 것으로 나타났습니다. 이러한 결과는 NS가 당뇨병 조절에 있어 경구용 항당뇨병제의 보조제로 사용될 수 있음을 시사합니다. 그러나 NS의 화학 성분, 용량, 투여 기간 등이 다양하기 때문에 당뇨병 관리에 효과적인 NS의 종류와 용량을 결정하기는 어렵기 때문에 추가 연구가 필요합니다.
Author Contributions (저자 기고)
Conceptualization, R.H.I. and M.H.M.; methodology, A.H., R.H.I. and M.H.M.; resources, A.H.; writing—original draft preparation, A.H. and M.H.M.; supervision, R.H.I.
개념화, R.H.I. 및 M.H.M.; 방법론, A.H., R.H.I. 및 M.H.M.; 리소스, A.H.; 글쓰기-원고 준비, A.H. 및 M.H.M.; 감수, R.H.I..
Funding (연구비 지원)
This research received no external funding.
이 연구는 외부 자금 지원을 받지 않았습니다.
Conflicts of Interest (이해상충)
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
저자는 이해 상충이 없음을 선언합니다.
REFERENCES (참조) - 생략
'게시판' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 고혈압의 약물 치료 관리를 위한 잠재적 인 허브, 니겔라 사티바 (블랙씨드) : 검토 (0) | 2024.06.07 |
|---|---|
| 니겔라 사티바(블랙씨드)와 그 활성 성분(티모퀴논)의 항당뇨 활동 : 인체 및 실험동물 연구 검토 (0) | 2024.06.07 |
| 기관지 천식에서 니겔라 사티바의 의학적 이점: 문헌 검토 (0) | 2024.06.07 |
| 류마티스 관절염 치료에서 니겔라 사티바(블랙커민씨드)의 생리 활성 화합물의 역할 - 최신 보고서 (0) | 2024.06.06 |
| 니겔라 사티바(블랙 커민)의 항암 활동 (0) | 2024.06.06 |